|
Adenosylcobalamin
Adenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl), also known as coenzyme B12, cobamamide, and dibencozide, is one of the biologically active forms of vitamin B12. Adenosylcobalamin participates as a cofactor in radical-mediated 1,2-carbon skeleton rearrangements. These processes require the formation of the deoxyadenosyl radical through homolytic dissociation of the carbon-cobalt bond. This bond is exceptionally weak, with a bond dissociation energy of 31 kcal/mol, which is further lowered in the chemical environment of an enzyme active site. An enzyme that uses adenosylcobalamin as a coenzyme is methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (MCM). Further experimentation has also determined adenosylcobalamin's role in regulating expression of some bacterial genes. By binding to CarH, AdoCbl can modulate carotenoid genes, which confer warm colors onto various plants. Carotenoid transcription is activated by sunlight, due to the response from AdoCbl. There are other photoreceptors across different bacterial communities, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cobalamin Biosynthesis
Cobalamin biosynthesis is the process by which bacteria and archea make Vitamin B12, cobalamin, vitamin B12. Many steps are involved in converting aminolevulinic acid via uroporphyrinogen III and adenosylcobyric acid to the final forms in which it is used by enzymes in both the producing organisms and other species, including humans who acquire it through their diet. The feature which distinguishes the two main Biosynthesis, biosynthetic routes is whether the cobalt that is at the catalytic site in the coenzyme is incorporated early (in anaerobic organisms) or late (in aerobic organisms) and whether oxygen is required. In both cases, the macrocycle that will form a coordination complex with the cobalt ion is a corrin ring, specifically one with seven Carboxylic acid, carboxylate groups called cobyrinic acid. Subsequently, amide groups are formed on all but one of the carboxylates, giving cobyric acid, and the cobalt is ligand, ligated by an adenosine, adenosyl group. In the final ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cyanocobalamin
Cyanocobalamin is a form of Vitamin B12, vitamin used to treat and prevent vitamin B12 deficiency, vitamin deficiency except in the presence of cyanide toxicity. The deficiency may occur in pernicious anemia, following gastrectomy, surgical removal of the stomach, with fish tapeworm, or due to bowel cancer. It is used by mouth, by injection into a muscle, or as a nasal spray. Cyanocobalamin is generally well tolerated. Minor side effects may include diarrhea, nausea, upset stomach, and itchiness. Serious side effects may include anaphylaxis, and low blood potassium resulting in heart failure. Use is not recommended in those who are allergic to cobalt or have Leber's disease. No overdosage or toxicity has been reported. It is less preferred than hydroxocobalamin for treating vitamin deficiency because it has a slightly lower bioavailability. Some studies have shown it to possess an antihypotensive effect. Vitamin is an essential nutrient meaning that it cannot be made by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. One of eight B vitamins, it serves as a vital cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor in DNA synthesis and both fatty acid metabolism, fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It plays an essential role in the nervous system by supporting myelinogenesis, myelin synthesis and is critical for the maturation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. While animals require B12, plants do not, relying instead on alternative enzymatic pathways. Vitamin B12 is the most chemically complex of all vitamins, and is synthesized exclusively by certain archaea and bacteria. Natural food sources include meat, shellfish, liver, fish, poultry, Egg as food, eggs, and dairy products. It is also added to many breakfast cereals through food fortification and is available in dietary supplement and pharmaceutical forms. Supplements are commonly taken orally but may be administered via intramuscular injection to treat defic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Methylcobalamin
Methylcobalamin (mecobalamin, MeCbl, or MeB) is a cobalamin, a form of vitamin B12, vitamin B. It differs from cyanocobalamin in that the cyanide, cyano group at the cobalt is replaced with a methyl group. Methylcobalamin features an octahedral cobalt(III) centre and can be obtained as bright red crystals. From the perspective of coordination chemistry, methylcobalamin is notable as a rare example of a compound that contains metal–alkyl bonds. Nickel–methyl intermediates have been proposed for the final step of methanogenesis. __TOC__ Production Methylcobalamin can be produced in the laboratory by reducing cyanocobalamin with sodium borohydride in alkaline solution, followed by the addition of methyl iodide. Functions This vitamer, along with adenosylcobalamin, is one of two active coenzymes used by vitamin B-dependent enzymes and is the specific vitamin B form used by 5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase (MTR), also known as methionine synthase. Met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Organocobalt Compounds
Organocobalt chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to cobalt chemical bond. Organocobalt compounds are involved in several organic reactions and the important biomolecule vitamin B12, vitamin B12 has a cobalt-carbon bond. Many organocobalt compounds exhibit useful catalytic properties, the preeminent example being dicobalt octacarbonyl. Alkyl complexes Most fundamental are the cobalt complexes with only alkyl ligands. Examples include Co(4-norbornyl)4 and its cation. Alkylcobalt is represented by vitamin B12, vitamin B12 and related enzymes. In methylcobalamin the ligand is a methyl group, which is electrophilic. in vitamin B12, the alkyl ligand is an adenosyl group. Related to vitamin B12 are cobalt porphyrins, dimethylglyoxime, dimethylglyoximates, and related complexes of Schiff base ligands. These synthetic compounds also form alkyl derivatives that undergo diverse reactions reminiscent of the biological processes. The weak cobalt(III) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cofactors
Cofactor may also refer to: * Cofactor (biochemistry), a substance that needs to be present in addition to an enzyme for a certain reaction to be catalysed * A domain parameter in elliptic curve cryptography, defined as the ratio between the order of a group and that of the subgroup * Cofactor (linear algebra), the signed minor of a matrix * Minor (linear algebra) In linear algebra, a minor of a matrix (mathematics), matrix is the determinant of some smaller square matrix generated from by removing one or more of its rows and columns. Minors obtained by removing just one row and one column from square ma ..., an alternative name for the determinant of a smaller matrix than that which it describes * Shannon cofactor, a term in Boole's (or Shannon's) expansion of a Boolean function See also * Factor (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
B Vitamins
B vitamins are a class of water-soluble vitamins that play important roles in Cell (biology), cell metabolism and synthesis of red blood cells. They are a chemically diverse class of compounds. Dietary supplements containing all eight are referred to as a vitamin B complex. Individual B vitamins are referred to by B-number or by chemical name, such as B1 for thiamine, B2 for riboflavin, and B3 for niacin, while some are more commonly recognized by name than by number, such as pantothenic acid (B5), biotin (B7), and folate (B9). B vitamins are present in protein (nutrient), protein-rich foods, such as Fish as food, fish, poultry, meat, dairy products, and Eggs as food, eggs; they are also found in Leaf vegetable, leafy green vegetables, beans, and peas. food fortification, Fortified foods, such as breakfast cereals, baked products, and infant formulas, may contain B vitamins. Each B vitamin is either a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor (generally a cofactor (biochemistry), coenzym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nitric Oxide
Nitric oxide (nitrogen oxide, nitrogen monooxide, or nitrogen monoxide) is a colorless gas with the formula . It is one of the principal oxides of nitrogen. Nitric oxide is a free radical: it has an unpaired electron, which is sometimes denoted by a dot in its chemical formula (•N=O or •NO). Nitric oxide is also a heteronuclear diatomic molecule, a class of molecules whose study spawned early modern theories of chemical bonding. An important intermediate in industrial chemistry, nitric oxide forms in combustion systems and can be generated by lightning in thunderstorms. In mammals, including humans, nitric oxide is a signaling molecule in many physiological and pathological processes. It was proclaimed the " Molecule of the Year" in 1992. The 1998 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded for discovering nitric oxide's role as a cardiovascular signalling molecule. Its impact extends beyond biology, with applications in medicine, such as the development of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hydroxocobalamin
Hydroxocobalamin, also known as vitamin B12a and hydroxycobalamin, is a vitamin found in food and used as a dietary supplement. As a supplement it is used to treat vitamin B12 deficiency including pernicious anemia. Other uses include treatment for cyanide poisoning, Leber's optic atrophy, and toxic amblyopia. It is given by injection into a muscle or vein, by pill or sublingually. Side effects are generally few. They may include diarrhea, feeling sick, hot flushes, itchiness, low blood potassium, allergic reactions, and high blood pressure. Normal doses are considered safe in pregnancy. No overdosage or toxicity has been reported with this drug. Hydroxocobalamin is the natural form of vitamin B12 and a member of the cobalamin family of compounds. It is found in both raw and cooked beef, together with other cobalamins. Hydroxocobalamin, or another form of vitamin B12, are required for the body to make DNA. Hydroxocobalamin was first isolated in 1949. It is on the World H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
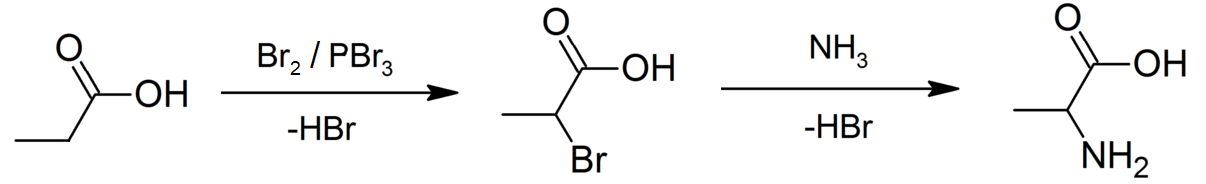
Propionate Pathway
Propionic acid (, from the Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula . It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion as well as the salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates. About half of the world production of propionic acid is consumed as a preservative for both animal feed and food for human consumption. It is also useful as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, especially polymers. History Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar. Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid by different means, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas established all the acids to be the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Carotenoid
Carotenoids () are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, corn, tomatoes, canaries, flamingos, salmon, lobster, shrimp, and daffodils. Over 1,100 identified carotenoids can be further categorized into two classes xanthophylls (which contain oxygen) and carotenes (which are purely hydrocarbons and contain no oxygen). All are derivatives of tetraterpenes, meaning that they are produced from 8 isoprene units and contain 40 carbon atoms. In general, carotenoids absorb wavelengths ranging from 400 to 550 nanometers (violet to green light). This causes the compounds to be deeply colored yellow, orange, or red. Carotenoids are the dominant pigment in autumn leaf coloration of about 15-30% of tree species, but many plant colors, especially reds and purples, are due to polyphenols. Carotenoids serve two key roles in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |