|
Actinoform Cloud
An actinoform or actiniform describes a collection of marine low clouds that takes a distinct shape. They are named after the Greek word for "ray" due to their radial structure. Actinoform clouds can spread out over across and thus cannot be easily seen with the naked eye. In addition, actinoform clouds can form "trains" that are up to six times the length of the original cloud field, yet they maintain their own distinct identity. Description In a satellite image, they look like distinct leaf-like or spokes-on-a-wheel patterns that stand out from the rest of the low-lying cloud field. However, why they have this shape or how they are formed is not known, but recent evidence suggests that the interaction of both radiation and precipitation may help to organize them on the mesoscale. The individual convective cells that collectively make up an actinoform cloud are quite shallow, with heights generally less than , and would be classified as stratocumulus clouds by an observer on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Australia is Australia's largest state, with a land area of , and is also the List of country subdivisions by area, second-largest subdivision of any country on Earth. Western Australia has a diverse range of climates, including tropical conditions in the Kimberley (Western Australia), Kimberley, deserts in the interior (including the Great Sandy Desert, Little Sandy Desert, Gibson Desert, and Great Victoria Desert) and a Mediterranean climate on the south-west and southern coastal areas. the state has 2.965 million inhabitants—10.9 percent of the national total. Over 90 percent of the state's population live in the South-West Land Division, south-west corner and around 80 percent live in the state capital Perth, leaving the remainder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
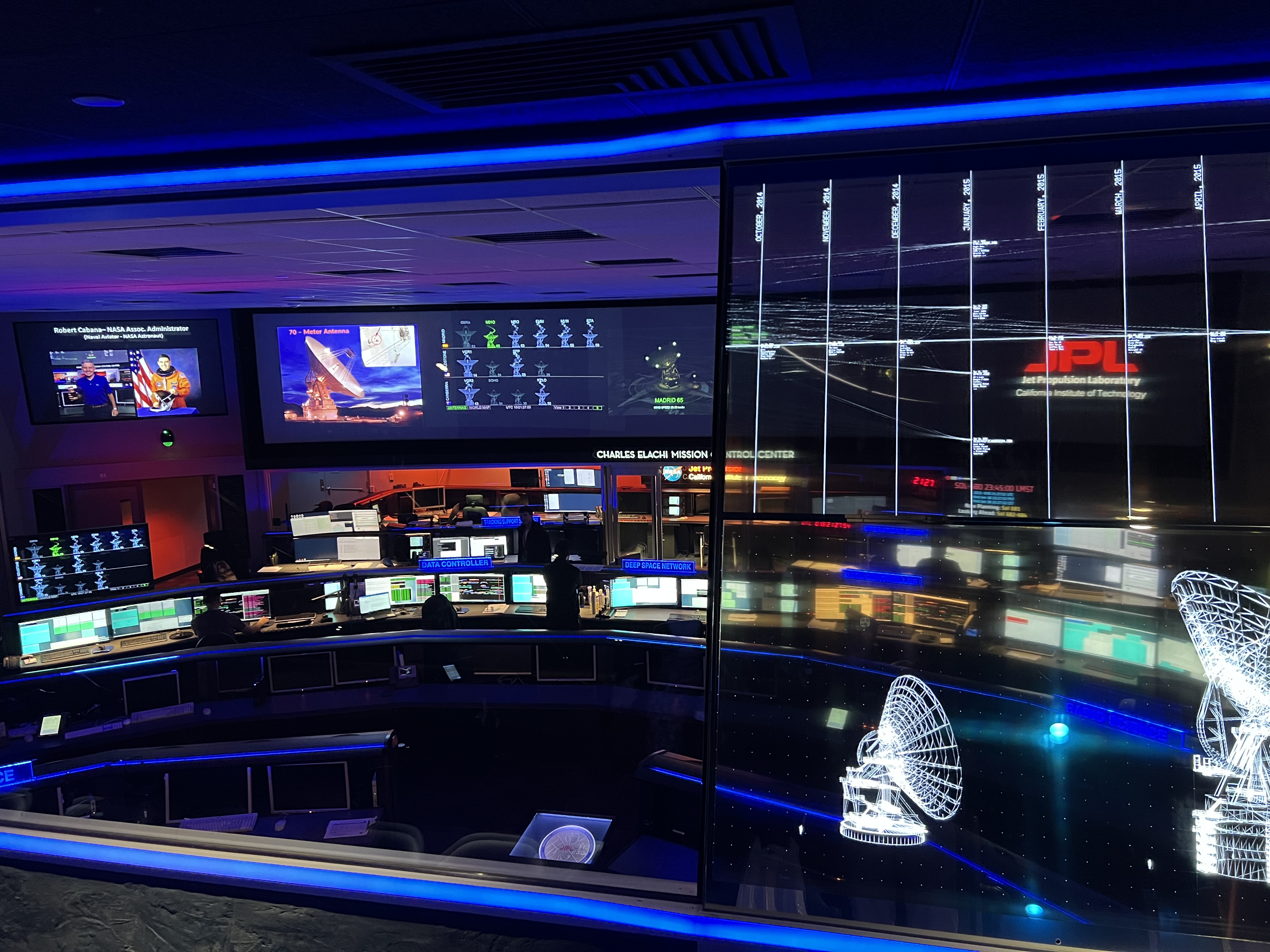
NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) in La Cañada Flintridge, California, Crescenta Valley, United States. Founded in 1936 by California Institute of Technology (Caltech) researchers, the laboratory is now owned and sponsored by NASA and administered and managed by Caltech. The primary function of the laboratory is the construction and operation of planetary robotic spacecraft, though it also conducts Earth-orbit and astronomy missions. It is also responsible for operating the NASA Deep Space Network (DSN). Among the major active projects at the laboratory, some are the Mars 2020 mission, which includes the '' Perseverance'' rover; the Mars Science Laboratory mission, including the ''Curiosity'' rover; the '' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter''; the '' Juno'' spacecraft orbiting Jupiter; the '' SMAP'' satellite for Earth surface soil moisture monitoring; the NuSTAR X-ray telescope; and the '' Psyche'' asteroid orbit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Earth Observatory
NASA Earth Observatory is an online publishing outlet for NASA which was created in 1999. It is the principal source of satellite imagery and other scientific information about the climate and the environment which are being provided by NASA for consumption by the general public. It is funded with public money, as authorized by the United States Congress, and is part of the EOS Project Science Office located at Goddard Space Flight Center. , NASA Earth Observatory has won the Webby People's Voice Award in Education three times. There were a series of publicized images issued by the website in 2008, including imagery of clouds streaming over the Caspian Sea, dust storms curling off the coast of Morocco, the crumbling of the Wilkins Ice Shelf, Hurricane Bertha, and others. See also * Earth observation * Earth observation satellite * Space exploration Space exploration is the process of utilizing astronomy and space technology to investigate outer space. While the expl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Australia in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), the Pacific Ocean is the largest division of the World Ocean and the hydrosphere and covers approximately 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of the planet's total surface area, larger than its entire land area ().Pacific Ocean . ''Encyclopædia Britannica, Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the Land and water hemispheres, water hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere, as well as the Pole of inaccessi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwealth usage), snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. Precipitation occurs when a portion of the atmosphere becomes saturated with water vapor (reaching 100% relative humidity), so that the water condenses and "precipitates" or falls. Thus, fog and mist are not precipitation; their water vapor does not condense sufficiently to precipitate, so fog and mist do not fall. (Such a non-precipitating combination is a colloid.) Two processes, possibly acting together, can lead to air becoming saturated with water vapor: cooling the air or adding water vapor to the air. Precipitation forms as smaller droplets coalesce via collision with other rain drops or ice crystals within a cloud. Short, intense periods of rain in scattered locations are called shower (p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drizzle
Drizzle is a light precipitation which consists of liquid water drops that are smaller than those of rain – generally smaller than in diameter. Drizzle is normally produced by low stratiform clouds and stratocumulus clouds. Precipitation rates from drizzle are on the order of a millimetre (0.04 in) per day or less at the ground. Owing to the small size of drizzle drops, under many circumstances drizzle largely evaporates before reaching the surface, and so may be undetected by observers on the ground. The METAR code for drizzle is DZ and for freezing drizzle is FZDZ. Effects While most drizzle has only a minor immediate impact upon humans, freezing drizzle can lead to treacherous conditions. Freezing drizzle occurs when supercooled drizzle drops land on a surface whose temperature is below freezing. These drops immediately freeze upon impact, leading to the buildup of sheet ice (sometimes called black ice) on the surface of roads. Occurrence Drizzle tends to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California, Los Angeles
The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California, United States. Its academic roots were established in 1881 as a normal school then known as the southern branch of the California State Normal School which later evolved into San Jose State University, San José State University. The branch was transferred to the University of California to become the Southern Branch of the University of California in 1919, making it the second-oldest of the ten-campus University of California system after the University of California, Berkeley. UCLA offers 337 undergraduate and graduate degree programs in a range of disciplines, enrolling about 31,600 undergraduate and 14,300 graduate and professional students annually. It received 174,914 undergraduate applications for Fall 2022, including transfers, the most of any Higher education in the United States, university in the United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere and the interactions between them. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude, longitude, terrain, altitude, land use and nearby water bodies and their currents. Climates can be classified according to the average and typical variables, most commonly temperature and precipitation. The most widely used classification scheme is the Köppen climate classification. The Thornthwaite system, in use since 1948, incorporates evapotranspiration along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloud cover, cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere, the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers to day-to-day temperature, precipitation, and other atmospheric conditions, whereas climate is the term for the averaging of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, "weather" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth. Weather is driven by atmospheric pressure, air pressure, temperature, and moisture differences between one place and another. These differences can occur due to the effect of Sun angle on climate, Sun's angle at any particular spot, which varies with latitude. The strong temperature contrast between polar and tropical air gives rise to the largest scale atmospheric circulations: the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumference, halfway between the North Pole, North and South Pole, South poles. The term can also be used for any other celestial body that is roughly spherical. In three-dimensional space, spatial (3D) geometry, as applied in astronomy, the equator of a rotating spheroid (such as a planet) is the parallel (circle of latitude) at which latitude is defined to be 0°. It is an imaginary line on the spheroid, equidistant from its geographical pole, poles, dividing it into northern and southern hemispheres. In other words, it is the intersection of the spheroid with the plane (geometry), plane perpendicular to its axis of rotation and midway between its geographical poles. On and near the equator (on Earth), noontime sunlight appears almost directly o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
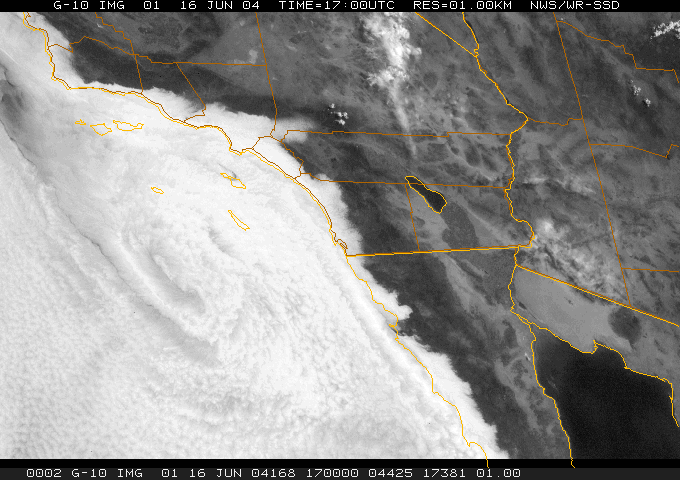
June Gloom
June Gloom is a mainly Southern California term for a weather pattern that results in cloud cover, cloudy, overcast skies with cool temperatures during the late spring and early summer. While the marine layer is most common in the month of June, it can occur in surrounding months, giving rise to other colloquialisms, such as Graypril, May Gray, No-Sky July, and Summer Bummer and Junuary in the Puget Sound region. Low-altitude stratus clouds form over the cool water of the California Current, and spread overnight into the coastal regions of California. The overcast skies often are accompanied by fog and drizzle, though usually not rain. June Gloom usually clears up between mid-morning and early afternoon, depending on the strength of the marine layer and the distance of the location from the Pacific Ocean, and gives way to sunny skies. May and June together are usually the cloudiest months in coastal California. June Gloom is stronger in years associated with a La Niña, and wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |