|
Acid Perfusion Test
Acid perfusion test, also called the Bernstein test, is a test done to reproduce the pain when the lower esophagus is irrigated with an acid solution in people with GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease). There will be a negative result in normal people, but a false positive reading may be seen in up to 15% of people. Bernstein test is simple and cheap but mostly obsolete nowadays. Esophageal pH monitoring Esophageal pH monitoring is the current gold standard for diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It provides direct physiologic measurement of acid in the esophagus and is the most objective method to document reflux disease, asses ... is the gold standard for GERD. However, the initial management is with proton pump inhibitors. If the patient does not respond to it, and continues to have symptoms of GERD, i.e. heartburn, hoarseness, chronic cough, then 24 hr pH monitoring should be considered. References Medical tests {{digestive-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage." In medical diagnosis, pain is regarded as a symptom of an underlying condition. Pain motivates the individual to withdraw from damaging situations, to protect a damaged body part while it heals, and to avoid similar experiences in the future. Most pain resolves once the noxious stimulus is removed and the body has healed, but it may persist despite removal of the stimulus and apparent healing of the body. Sometimes pain arises in the absence of any detectable stimulus, damage or disease. Pain is the most common reason for physician consultation in most developed countries. It is a major symptom in many medical conditions, and can interfere with a person's quality of life and general functioning. Simp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is a fibromuscular tube, about long in adults, that travels behind the trachea and heart, passes through the diaphragm, and empties into the uppermost region of the stomach. During swallowing, the epiglottis tilts backwards to prevent food from going down the larynx and lungs. The word ''oesophagus'' is from Ancient Greek οἰσοφάγος (oisophágos), from οἴσω (oísō), future form of φέρω (phérō, “I carry”) + ἔφαγον (éphagon, “I ate”). The wall of the esophagus from the lumen outwards consists of mucosa, submucosa (connective tissue), layers of muscle fibers between layers of fibrous tissue, and an outer layer of connective tissue. The mucosa is a stratified squamous epith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GERD
Gerd or GERD may refer to: * Gerd (given name), a list of people with the given name or nickname * Gerd (moon), a moon of Saturn * Gerd Island, South Orkney Islands, Antarctica * Gastroesophageal reflux disease, a chronic symptom of mucosal damage caused by stomach acid coming up from the stomach into the esophagus * Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam, Benishangul-Gumuz Region, Ethiopia Fictional and mythological figures * Gerðr, sometimes modernly anglicized as ''Gerd'' or Gerth, the wife of the Norse god Freyr * Gerd Frentzen, in the Japanese anime ''Blassreiter'' See also * Gird (other) The Moscow-based Group for the Study of Reactive Motion (also 'Group for the Investigation of Reactive Engines and Reactive Flight' and 'Jet Propulsion Study Group') (russian: Группа изучения реактивного движения, ... * Gurd (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
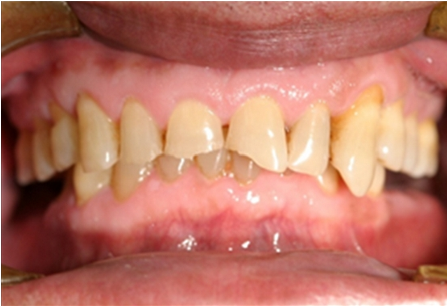
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the upper gastrointestinal chronic diseases where stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or complications. Symptoms include dental corrosion, dysphagia, heartburn, odynophagia, regurgitation, non-cardiac chest pain, extraesophageal symptoms such as chronic cough, hoarseness, reflux-induced laryngitis, or asthma. On the long term, and when not treated, complications such as esophagitis, esophageal stricture, and Barrett's esophagus may arise. Risk factors include obesity, pregnancy, smoking, hiatal hernia, and taking certain medications. Medications that may cause or worsen the disease include benzodiazepines, calcium channel blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, NSAIDs, and certain asthma medicines. Acid reflux is due to poor closure of the lower esophageal sphincter, which is at the junction between the stomach a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
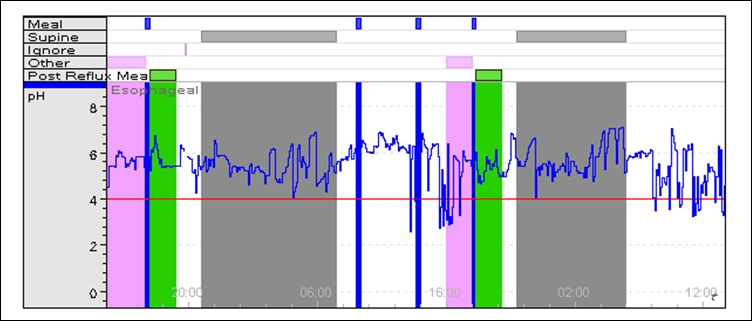
Esophageal PH Monitoring
Esophageal pH monitoring is the current gold standard for diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It provides direct physiologic measurement of acid in the esophagus and is the most objective method to document reflux disease, assess the severity of the disease and monitor the response of the disease to medical or surgical treatment. It can also be used in diagnosing laryngopharyngeal reflux. Background The importance of refluxed gastric contents in the pathogenesis of GERD was emphasized by Winkelstein who introduced the term "peptic esophagitis" and by Bernstein and Baker who reported the symptom of heartburn following instillation of hydrochloric acid in the distal esophagus in what was then became known as the acid perfusion test. Formal measurement of acid in the esophagus was first described in 1960 by Tuttle. He used a glass pH probe to map the gastroesophageal pH gradient, and demonstrated a sharp gradient in normal subjects and a gradual, slopi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |