|
Absolute Gain (international Relations)
According to the international relations theory of Liberalism, absolute gain is what international actors look at in determining their interests, weighing out the total effects of a decision on the state or organization and acting accordingly. The international actor's interests not only include power but also encompass the economic and cultural effects of an action as well. The theory is also interrelated with a non-zero-sum game which proposes that through use of comparative advantage, all states who engage in peaceful relations and trade can expand wealth. This differs from Realist International Relations theories that employ relative gain, which seeks to describe the actions of states only in respect to power balances and without regard to other factors, such as economics. Relative gain is related to zero-sum game Zero-sum game is a Mathematical model, mathematical representation in game theory and economic theory of a situation that involves two competition, competing e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberalism (international Relations)
Liberalism is a school of thought within international relations theory which revolves around three interrelated principles: * Rejection of power politics as the only possible outcome of international relations; it questions security/warfare principles of realism * Mutual benefits and international cooperation * The role of international organizations and nongovernmental actors in shaping state preferences and policy choices This school of thought emphasizes three factors that encourage more cooperation and less conflict among states: * International institutions, such as the United Nations, which provide a forum to resolve disputes in non-violent ways * International trade because, when countries' economies are interconnected through trade, they are less likely to go to war with each other * Spread of democracy, as well-established democracies are assumed to not go to war with one another, so if there are more democracies, interstate war will be less frequent Liberals belie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
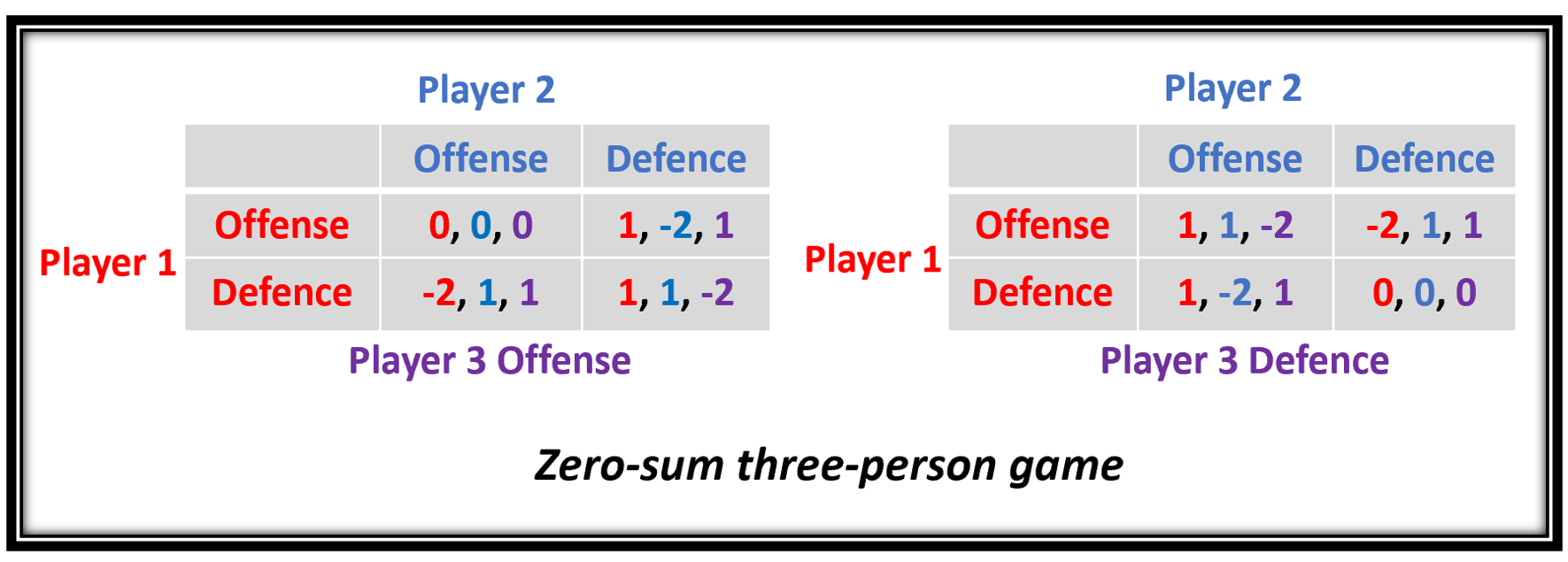
Non-zero-sum Game
Zero-sum game is a mathematical representation in game theory and economic theory of a situation that involves two competing entities, where the result is an advantage for one side and an equivalent loss for the other. In other words, player one's gain is equivalent to player two's loss, with the result that the net improvement in benefit of the game is zero. If the total gains of the participants are added up, and the total losses are subtracted, they will sum to zero. Thus, cutting a cake, where taking a more significant piece reduces the amount of cake available for others as much as it increases the amount available for that taker, is a zero-sum game if all participants value each unit of cake equally. Other examples of zero-sum games in daily life include games like poker, chess, sport and bridge where one person gains and another person loses, which results in a zero-net benefit for every player. In the markets and financial instruments, futures contracts and options are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparative Advantage
Comparative advantage in an economic model is the advantage over others in producing a particular Goods (economics), good. A good can be produced at a lower relative opportunity cost or autarky price, i.e. at a lower relative marginal cost prior to trade. Comparative advantage describes the economic reality of the gains from trade for individuals, firms, or nations, which arise from differences in their factor endowments or technological progress. David Ricardo developed the classical theory of comparative advantage in 1817 to explain why countries engage in international trade even when one country's workers are more efficient at producing ''every'' single good than workers in other countries. He demonstrated that if two countries capable of producing two commodities engage in the free market (albeit with the assumption that the capital and labour do not move internationally), then each country will increase its overall consumption by exporting the good for which it has a comparat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Gain (international Relations)
Relative gain, in international relations, is the actions of states only in respect to power balances and without regard to other factors, such as economics. In international relations, cooperation may be necessary to balance power, but concerns about relative gains will limit that cooperation due to the low quality of information about other states' behavior and interests. Such relative-gains concerns, however, may sometimes be mitigated by individual social preferences. Relative gain is related to zero-sum game Zero-sum game is a Mathematical model, mathematical representation in game theory and economic theory of a situation that involves two competition, competing entities, where the result is an advantage for one side and an equivalent loss for the o ..., which states that wealth cannot be expanded and the only way a state can become richer is to take wealth from another state. It differs from absolute gain, which is the total effect of a decision on the state or organiza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero-sum Game
Zero-sum game is a Mathematical model, mathematical representation in game theory and economic theory of a situation that involves two competition, competing entities, where the result is an advantage for one side and an equivalent loss for the other. In other words, player one's gain is equivalent to player two's loss, with the result that the net improvement in benefit of the game is zero. If the total gains of the participants are added up, and the total losses are subtracted, they will sum to zero. Thus, Fair cake-cutting, cutting a cake, where taking a more significant piece reduces the amount of cake available for others as much as it increases the amount available for that taker, is a zero-sum game if marginal utility, all participants value each unit of cake equally. Other examples of zero-sum games in daily life include games like poker, chess, sport and Contract bridge, bridge where one person gains and another person loses, which results in a zero-net benefit for every ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Relations Theory
International relations theory is the study of international relations (IR) from a theoretical perspective. It seeks to explain behaviors and outcomes in international politics. The three most prominent School of thought, schools of thought are Realism (international relations), realism, Liberalism (international relations), liberalism and Constructivism (international relations), constructivism. Whereas realism and liberalism make broad and specific predictions about international relations, constructivism and rational choice are methodological approaches that focus on certain types of social explanation for phenomena. International relations, as a discipline, is believed to have emerged after World War I with the establishment of a Chair of International Relations, the Woodrow Wilson Chair held by Alfred Eckhard Zimmern at the University of Wales, Aberystwyth. The modern study of international relations, as a theory, has sometimes been traced to realist works such as E. H. Carr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |