|
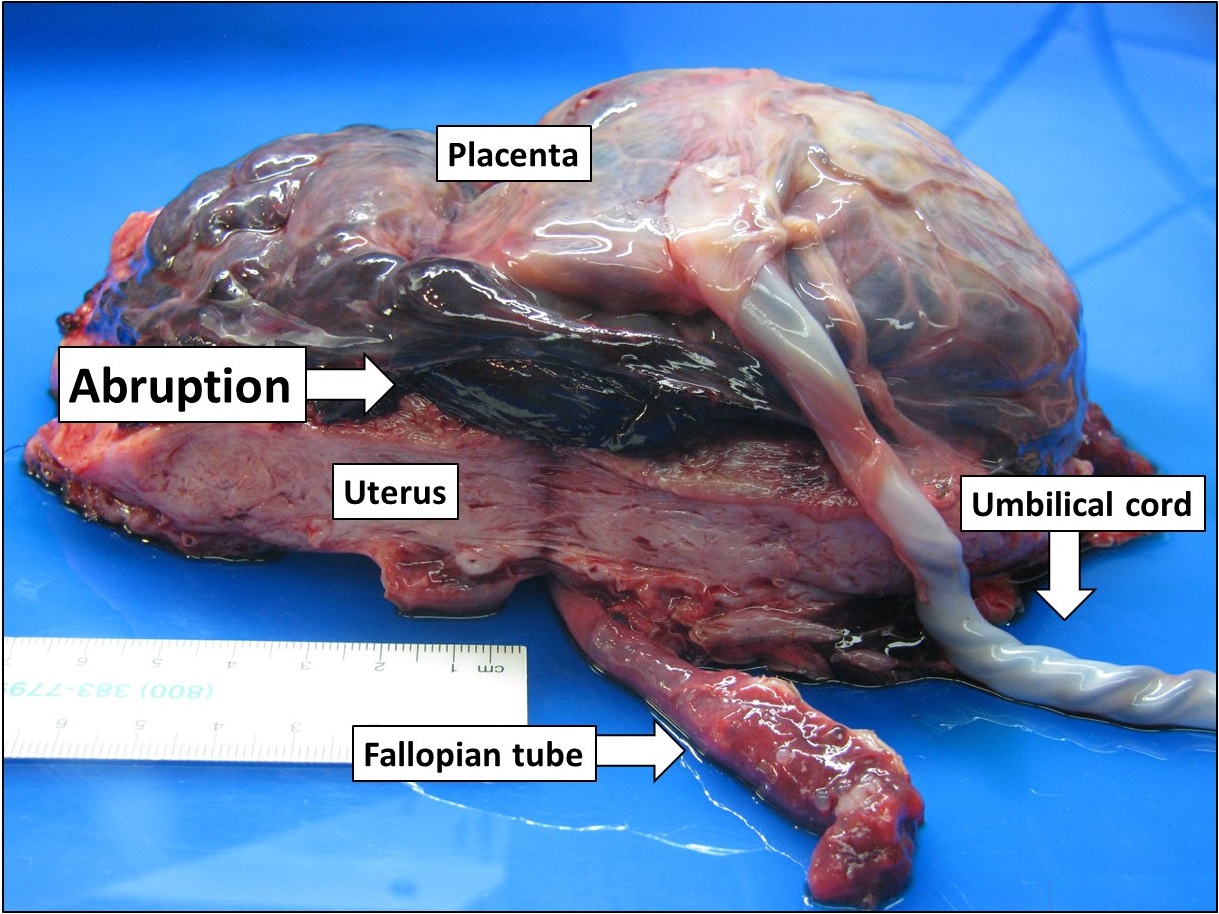
Abruption
Placental abruption is when the placenta separates early from the uterus, in other words separates before childbirth. It occurs most commonly around 25 weeks of pregnancy. Symptoms may include vaginal bleeding, lower abdominal pain, and dangerously low blood pressure. Complications for the mother can include disseminated intravascular coagulopathy and kidney failure. Complications for the baby can include fetal distress, low birthweight, preterm delivery, and stillbirth. The cause of placental abruption is not entirely clear. Risk factors include smoking, pre-eclampsia, prior abruption (most important and predictive risk factor), trauma during pregnancy, cocaine use, and previous cesarean section. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and supported by ultrasound. It is classified as a complication of pregnancy. For small abruption, bed rest may be recommended, while for more significant abruptions or those that occur near term, delivery may be recommended. If everything is stable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complication Of Pregnancy
Complications of pregnancy are health problems that are related to pregnancy. Complications that occur primarily during childbirth are termed obstetric labor complications, and problems that occur primarily after childbirth are termed puerperal disorders. Severe complications of pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium are present in 1.6% of mothers in the US, and in 1.5% of mothers in Canada. In the immediate postpartum period (puerperium), 87% to 94% of women report at least one health problem. Long-term health problems (persisting after six months postpartum) are reported by 31% of women. In 2016, complications of pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium resulted globally in 230,600 deaths, down from 377,000 deaths in 1990. The most common causes of maternal mortality are maternal bleeding, postpartum infections including maternal sepsis, hypertensive diseases of pregnancy, obstructed labor, and pregnancy with abortive outcome, which includes miscarriage, ectopic pregnan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preterm Delivery
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between 28 and 32 weeks, early preterm birth occurs between 32 and 36 weeks, late preterm birth is between 34 and 36 weeks' gestation. These babies are also known as premature babies or colloquially preemies (American English) or premmies (Australian English). Symptoms of preterm labor include uterine contractions which occur more often than every ten minutes and/or the leaking of fluid from the vagina before 37 weeks. Premature infants are at greater risk for cerebral palsy, delays in development, hearing problems and problems with their vision. The earlier a baby is born, the greater these risks will be. The cause of spontaneous preterm birth is often not known. Risk factors include diabetes, high blood pressure, multiple gestation (being pregn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstetrics
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgical field. Main areas Prenatal care Prenatal care is important in screening for various complications of pregnancy. This includes routine office visits with physical exams and routine lab tests along with telehealth care for women with low-risk pregnancies: Image:Ultrasound_image_of_a_fetus.jpg, 3D ultrasound of fetus (about 14 weeks gestational age) Image:Sucking his thumb and waving.jpg, Fetus at 17 weeks Image:3dultrasound 20 weeks.jpg, Fetus at 20 weeks First trimester Routine tests in the first trimester of pregnancy generally include: * Complete blood count * Blood type ** Rh-negative antenatal patients should receive RhoGAM at 28 weeks to prevent Rh disease. * Indirect Coombs test (AGT) to assess risk of hemolyti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Bleeding
Vaginal bleeding is any expulsion of blood from the vagina. This bleeding may originate from the uterus, vaginal wall, or cervix. Generally, it is either part of a normal menstrual cycle or is caused by hormonal or other problems of the reproductive system, such as abnormal uterine bleeding. Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy can be normal, especially in early pregnancy. However, bleeding may also indicate a pregnancy complication that needs to be medically addressed. During pregnancy bleeding is usually, but not always, related to the pregnancy itself. Regular monthly vaginal bleeding during the reproductive years, menstruation, is a normal physiologic process. During the reproductive years, bleeding that is excessively heavy (menorrhagia or heavy menstrual bleeding), occurs between monthly menstrual periods ( intermenstrual bleeding), occurs more frequently than every 21 days ( abnormal uterine bleeding), occurs too infrequently (oligomenorrhea), or occurs after vaginal inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placenta Previa
Placenta praevia is when the placenta attaches inside the uterus but in a position near or over the cervical opening. Symptoms include vaginal bleeding in the second half of pregnancy. The bleeding is bright red and tends not to be associated with pain. Complications may include placenta accreta, dangerously low blood pressure, or bleeding after delivery. Complications for the baby may include fetal growth restriction. Risk factors include pregnancy at an older age and smoking as well as prior cesarean section, labor induction, or termination of pregnancy. Diagnosis is by ultrasound. It is classified as a complication of pregnancy. For those who are less than 36 weeks pregnant with only a small amount of bleeding recommendations may include bed rest and avoiding sexual intercourse. For those after 36 weeks of pregnancy or with a significant amount of bleeding, cesarean section is generally recommended. In those less than 36 weeks pregnant, corticosteroids may be given to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Bleeding
Vaginal bleeding is any expulsion of blood from the vagina. This bleeding may originate from the uterus, vaginal wall, or cervix. Generally, it is either part of a normal menstrual cycle or is caused by hormonal or other problems of the reproductive system, such as abnormal uterine bleeding. Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy can be normal, especially in early pregnancy. However, bleeding may also indicate a pregnancy complication that needs to be medically addressed. During pregnancy bleeding is usually, but not always, related to the pregnancy itself. Regular monthly vaginal bleeding during the reproductive years, menstruation, is a normal physiologic process. During the reproductive years, bleeding that is excessively heavy (menorrhagia or heavy menstrual bleeding), occurs between monthly menstrual periods ( intermenstrual bleeding), occurs more frequently than every 21 days ( abnormal uterine bleeding), occurs too infrequently (oligomenorrhea), or occurs after vaginal inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cesarean Section
Caesarean section, also known as C-section or caesarean delivery, is the surgical procedure by which one or more babies are delivered through an incision in the mother's abdomen, often performed because vaginal delivery would put the baby or mother at risk. Reasons for the operation include obstructed labor, twin pregnancy, high blood pressure in the mother, breech birth, and problems with the placenta or umbilical cord. A caesarean delivery may be performed based upon the shape of the mother's pelvis or history of a previous C-section. A trial of vaginal birth after C-section may be possible. The World Health Organization recommends that caesarean section be performed only when medically necessary. Most C-sections are performed without a medical reason, upon request by someone, usually the mother. A C-section typically takes 45 minutes to an hour. It may be done with a spinal block, where the woman is awake, or under general anesthesia. A urinary catheter is used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stillbirth
Stillbirth is typically defined as fetal death at or after 20 or 28 weeks of pregnancy, depending on the source. It results in a baby born without signs of life. A stillbirth can result in the feeling of guilt or grief in the mother. The term is in contrast to miscarriage, which is an early pregnancy loss, and Sudden Infant Death Syndrome, where the baby dies a short time after being born alive. Often the cause is unknown. Causes may include pregnancy complications such as pre-eclampsia and birth complications, problems with the placenta or umbilical cord, birth defects, infections such as malaria and syphilis, and poor health in the mother. Risk factors include a mother's age over 35, smoking, drug use, use of assisted reproductive technology, and first pregnancy. Stillbirth may be suspected when no fetal movement is felt. Confirmation is by ultrasound. Worldwide prevention of most stillbirths is possible with improved health systems. Around half of stillbirths oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Trauma
Major trauma is any injury that has the potential to cause prolonged disability or death. There are many causes of major trauma, blunt and penetrating, including falls, motor vehicle collisions, stabbing wounds, and gunshot wounds. Depending on the severity of injury, quickness of management, and transportation to an appropriate medical facility (called a trauma center) may be necessary to prevent loss of life or limb. The initial assessment is critical, and involves a physical evaluation and also may include the use of imaging tools to determine the types of injuries accurately and to formulate a course of treatment. In 2002, unintentional and intentional injuries were the fifth and seventh leading causes of deaths worldwide, accounting for 6.23% and 2.84% of all deaths. For research purposes the definition often is based on an injury severity score (ISS) of greater than 15. Classification Injuries generally are classified by either severity, the location of damage, or a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bloody Show
Bloody show is the passage of a small amount of blood or blood-tinged mucus through the vagina near the end of pregnancy. It is caused by the detachment of the cervical mucus plug that seals the cervix during pregnancy, and is one of the signs that labor may be imminent. Although the bloody show is a common and harmless cause of bleeding in late pregnancy, there are many other possible causes for vaginal bleeding, some of which may indicate serious medical problems such as miscarriage or placental abruption, and vaginal bleeding should not be ignored as a possible sign of serious complications. See also * Antepartum hemorrhage Antepartum bleeding, also known as antepartum haemorrhage (APH) or prepartum hemorrhage, is genital bleeding during pregnancy after the 28th week of pregnancy up to delivery. It can be associated with reduced fetal birth weight. Use of aspirin b ... * Obstetrical hemorrhage References Obstetrics Health issues in pregnancy Midwifery {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-eclampsia
Pre-eclampsia is a disorder of pregnancy characterized by the onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe cases of the disease there may be red blood cell breakdown, a low blood platelet count, impaired liver function, kidney dysfunction, swelling, shortness of breath due to fluid in the lungs, or visual disturbances. Pre-eclampsia increases the risk of undesirable outcomes for both the mother and the fetus. If left untreated, it may result in seizures at which point it is known as eclampsia. Risk factors for pre-eclampsia include obesity, prior hypertension, older age, and diabetes mellitus. It is also more frequent in a woman's first pregnancy and if she is carrying twins. The underlying mechanism involves abnormal formation of blood vessels in the placenta amongst other factors. Most cases are diagnosed before delivery. Commonly, pre-eclampsia continues i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetal Distress
Fetal distress, also known as non-reassuring fetal status, is a condition during pregnancy or labor in which the fetus shows signs of inadequate oxygenation. Due to its imprecision, the term "fetal distress" has fallen out of use in American obstetrics. The term "non-reassuring fetal status" has largely replaced it. It is characterized by changes in fetal movement, growth, heart rate, and presence of meconium stained fluid. Risk factors for fetal distress/non-reassuring fetal status include anemia, restriction of fetal growth, maternal hypertension or cardiovascular disease, low amniotic fluid or meconium in the amniotic fluid, or a post-term pregnancy. The condition is detected most often with electronic fetal heart rate (FHR) monitoring through cardiotocography (CTG), which allows clinicians to measure changes in the fetal cardiac response to declining oxygen. Specifically, heart rate decelerations detected on CTG can represent danger to the fetus and to delivery. Treatment pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |