|
Ablate
Ablation ( – removal) is the removal or destruction of something from an object by vaporization, chipping, erosive processes, or by other means. Examples of ablative materials are described below, including spacecraft material for ascent and atmospheric reentry, ice and snow in glaciology, biological tissues in medicine and passive fire protection materials. Artificial intelligence In artificial intelligence (AI), especially machine learning, ablation is the removal of a component of an AI system. The term is by analogy with biology: removal of components of an organism. Biology Biological ablation is the removal of a biological structure or functionality. Genetic ablation is another term for gene silencing, in which gene expression is abolished through the alteration or deletion of genetic sequence information. In cell ablation, individual cells in a population or culture are destroyed or removed. Both can be used as experimental tools, as in loss-of-function experiment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermabrasion
Dermabrasion is a type of surgical skin planing, generally with the goal of removing acne, scarring and other skin or tissue irregularities, typically performed in a professional medical setting by a dermatologist or plastic surgeon trained specifically in this procedure. Dermabrasion has been practiced for many years (before the advent of lasers) and involves the controlled deeper abrasion (wearing away) of the upper to mid layers of the skin with any variety of strong abrasive devices including a wire brush, diamond wheel or fraise, sterilized sandpaper, salt crystals or other mechanical means. Dermabrasion procedures are surgical, invasive procedures that typically require a local anaesthetic. Often, they are performed in surgical suites or in professional medical centers. Since the procedure can typically remove the top to deeper layers of the epidermis and extend into the reticular dermis, there is always minor skin bleeding. The procedure carries risks of scarring, skin d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
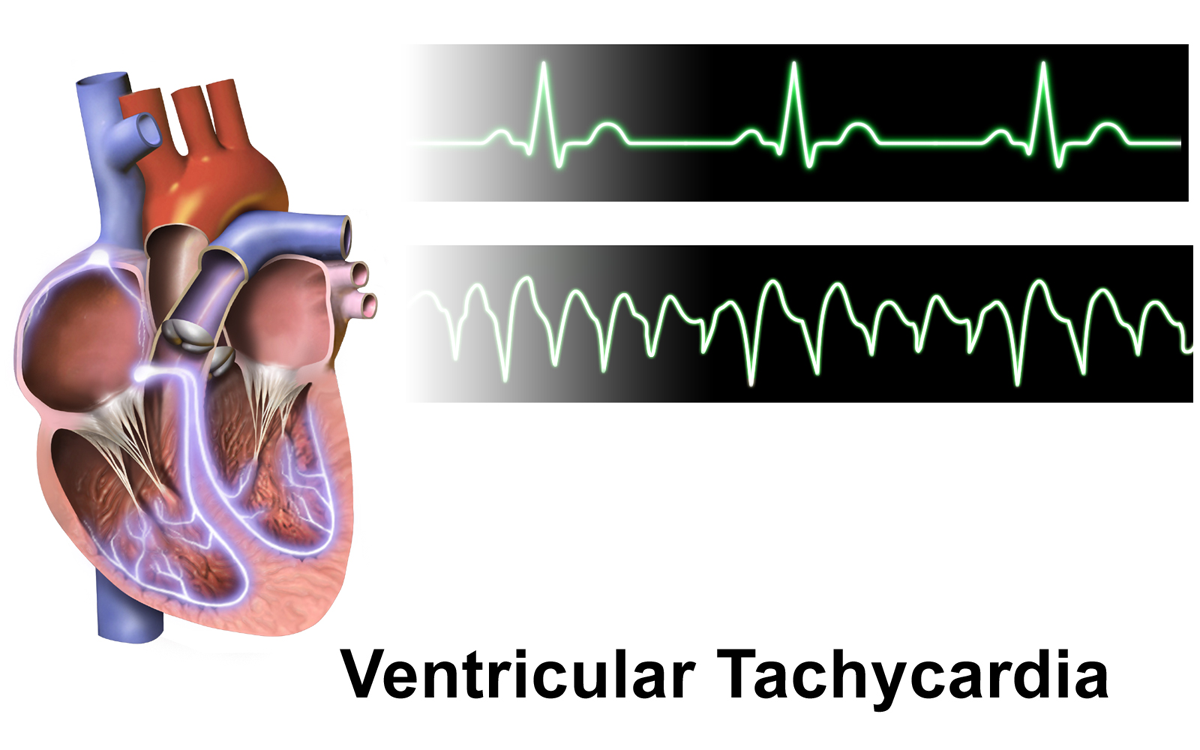
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT) is a cardiovascular disorder in which fast heart rate occurs in the ventricles of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple episodes over a short period of time are referred to as an electrical storm. Short periods may occur without symptoms, or present with lightheadedness, palpitations, shortness of breath, chest pain, and decreased level of consciousness. Ventricular tachycardia may lead to coma and persistent vegetative state due to lack of blood and oxygen to the brain. Ventricular tachycardia may result in ventricular fibrillation (VF) and turn into cardiac arrest. This conversion of the VT into VF is called the degeneration of the VT. It is found initially in about 7% of people in cardiac arrest. Ventricular tachycardia can occur due to coronary heart disease, aortic stenosis, cardiomyopathy, electrolyte imbalance, or a heart attack. Diagnosis is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolff–Parkinson–White Syndrome
Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome (WPWS) is a disorder due to a specific type of problem with the electrical system of the heart involving an accessory pathway able to conduct electrical current between the atria and the ventricles, thus bypassing the atrioventricular node. About 60% of people with the electrical problem develop symptoms, which may include an abnormally fast heartbeat, palpitations, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, or syncope. Rarely, cardiac arrest may occur. The most common type of arrhythmia (abnormal heart rate) associated with WPWS is paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. The cause of WPW is typically unknown and is likely due to a combination of chance and genetic factors. A small number of cases are due to a mutation of the PRKAG2 gene which may be inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion. The underlying mechanism involves an accessory electrical conduction pathway between the atria and the ventricles. It is associated with other cond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is an umbrella term for fast heart rhythms arising from the upper part of the heart. This is in contrast to the other group of fast heart rhythms – ventricular tachycardia, which start within the lower chambers of the heart. There are four main types of SVT: atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT), and Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome. The symptoms of SVT include palpitations, feeling of faintness, sweating, shortness of breath, and/or chest pain. These abnormal rhythms start from either the atria or atrioventricular node. They are generally due to one of two mechanisms: re-entry or increased automaticity. Diagnosis is typically by electrocardiogram (ECG), Holter monitor, or event monitor. Blood tests may be done to rule out specific underlying causes such as hyperthyroidism, pheochromocytomas, or electrolyte abnormalities. A normal resting heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute. A r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
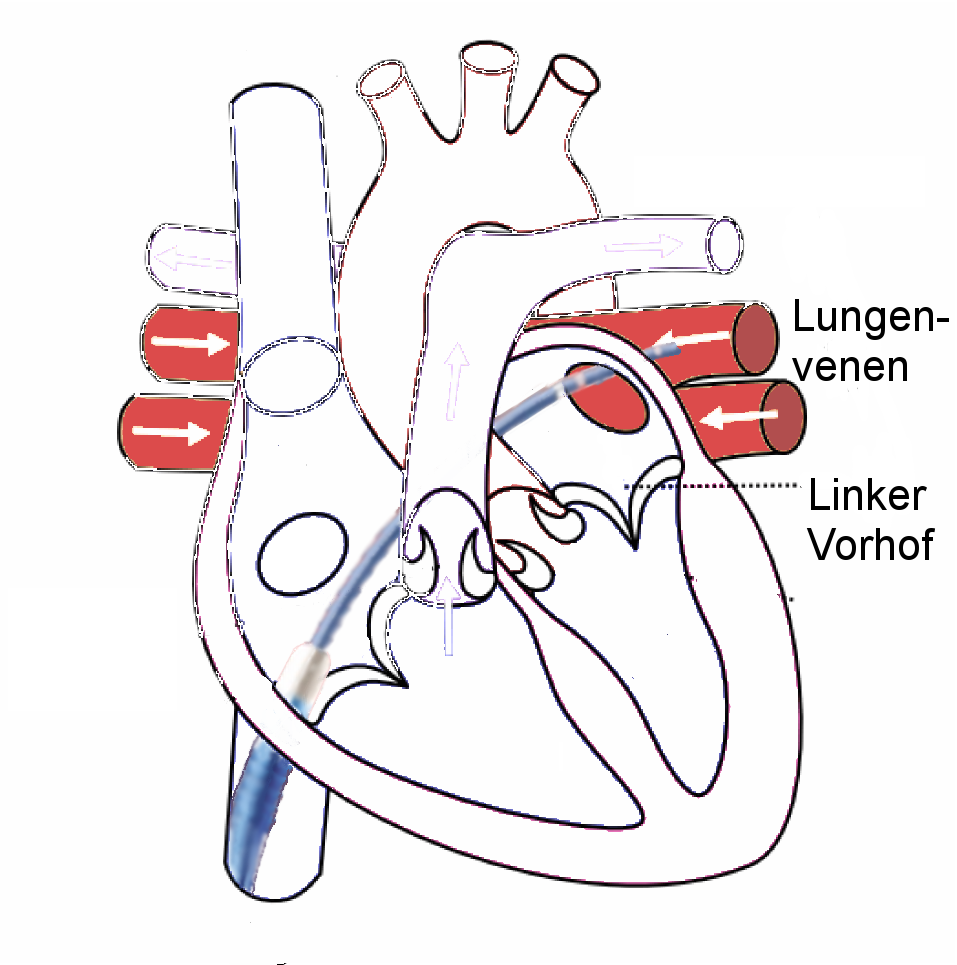
Radiofrequency Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA), also called fulguration, is a medical procedure in which part of the electrical conduction system of the heart, tumor, sensory nerves or a dysfunctional tissue is ablated using the heat generated from medium frequency alternating current (in the range of 350–500 kHz). RFA is generally conducted in the outpatient setting, using either a local anesthetic or twilight anesthesia. When it is delivered via catheter, it is called radiofrequency catheter ablation. Two advantages of radio frequency current (over previously used low frequency AC or pulses of DC) are that it does not directly stimulate nerves or heart muscle, and therefore can often be used without the need for general anesthesia, and that it is specific for treating the desired tissue without significant collateral damage. Due to this, RFA is an alternative for eligible patients who have comorbidities or do not want to undergo surgery. Documented benefits have led to RFA becomin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snoring
Snoring is an abnormal breath sound caused by partially obstructed, turbulent airflow and vibration of tissues in the upper respiratory tract (e.g., uvula, soft palate, base of tongue) which occurs during sleep. It usually happens during inhalations (breathing in). Primary snoring is snoring without any associated sleep disorders and usually without any serious health effects. It is usually defined as apnea–hypopnea index score or respiratory disturbance index score less than 5 events per hour (as diagnosed with polysomnography or home sleep apnea test) and lack of daytime sleepiness. Snoring may also be a symptom of upper airway resistance syndrome or obstructive sleep apnea (apneic snoring). In obstructive sleep apnea, snoring occurs in combination with breath holding, gasping, or choking. Classification In the International Classification of Sleep Disorders third edition (ICSD-3), snoring is listed under "Isolated symptoms and normal variants" in the section " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otolaryngology
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, nose, throat, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management of cancers and benign tumors and reconstruction of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face, scalp, and neck. Etymology The term is a combination of Neo-Latin combining forms ('' oto-'' + ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rejuvenation (aging)
Rejuvenation is a medical discipline focused on the practical reversal of the aging process. Rejuvenation is distinct from life extension. Life extension strategies often study the causes of aging and try to oppose those causes to slow aging. Rejuvenation is the ''reversal'' of aging and thus requires a different strategy, namely repair of the damage that is associated with aging or replacement of damaged tissue with new tissue. Rejuvenation can be a means of life extension, but most life extension strategies do not involve rejuvenation. Historical and cultural background Various myths tell the stories about the quest for rejuvenation. It was believed that magic or intervention of a supernatural power can bring back youth and many mythical adventurers set out on a journey to do that, for themselves, their relatives or some authority that sent them anonymously. An ancient Chinese emperor sent out ships of young men and women to find a pearl that would rejuvenate him. This le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrinkles
A wrinkle, also known as a rhytid, is a fold, ridge or crease in an otherwise smooth surface, such as on skin or fabric. Skin wrinkles typically appear as a result of ageing processes such as glycation, habitual sleeping positions, loss of body mass, sun damage, or temporarily, as the result of prolonged immersion in water. Age wrinkling in the skin is promoted by habitual facial expressions, aging, sun damage, smoking, poor hydration, and various other factors. In humans, it can also be prevented to some degree by avoiding excessive solar exposure and through diet (in particular through consumption of carotenoids, tocopherols and flavonoids, vitamins (A, C, D and E), essential omega-3-fatty acids, certain proteins and lactobacilli). Skin Causes for aging wrinkles Development of facial wrinkles is a kind of fibrosis of the skin. Misrepair-accumulation aging theory suggests that wrinkles develop from incorrect repairs of injured elastic fibers and collagen fibers. Repeat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aging
Ageing (or aging in American English) is the process of becoming Old age, older until death. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi; whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortal. In a broader sense, ageing can refer to single cells within an organism which have Cellular senescence, ceased dividing, or to the Population ageing, population of a species. In humans, ageing represents the accumulation of changes in a human being over time and can encompass physical, psychological, and social changes. Reaction time, for example, may slow with age, while memories and general knowledge typically increase. Of the roughly 150,000 people who die each day across the globe, about two-thirds die from age-related causes. Current Theory of aging, ageing theories are assigned to the damage concept, whereby the accumulation of damage (such as DNA oxidation) may cause biological systems to fail, or to the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulguration
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA), also called fulguration, is a medical procedure in which part of the electrical conduction system of the heart, tumor, sensory nerves or a dysfunctional Tissue (biology), tissue is Ablation#Medicine, ablated using the heat generated from medium frequency alternating current (in the range of 350–500 kHz). RFA is generally conducted in the outpatient setting, using either a local anesthetic or twilight anesthesia. When it is delivered via catheter, it is called radiofrequency catheter ablation. Two advantages of radio frequency current (over previously used low frequency AC or pulses of DC) are that it does not directly stimulate nerves or heart muscle, and therefore can often be used without the need for general anesthetics, general anesthesia, and that it is specific for treating the desired tissue without significant collateral damage. Due to this, RFA is an alternative for eligible patients who have comorbidity, comorbidities or do not wan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |