|
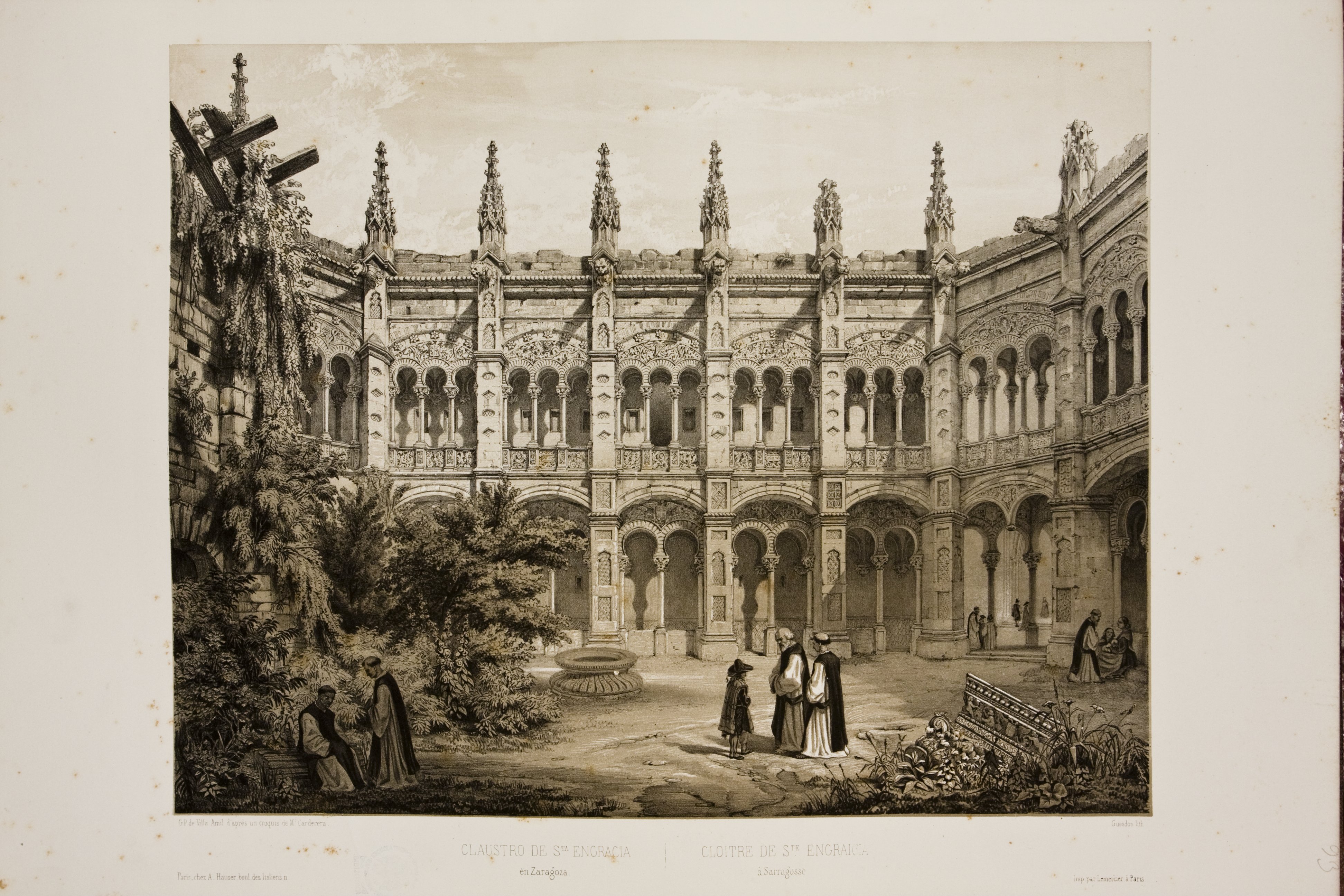
Abbey Of Santa Engracia
The Abbey of Santa Engracia () was a monastery in Zaragoza, Aragon, Spain, established to house the relics of Saint Engratia and the many martyrs of Saragossa. The date of 392 was traditionally claimed as a foundation date, which was linked with the travels of Saint Paulinus. The church was believed to have been sited on the spot of the martyrdom of Engratia. Today only the crypt and part of the façade remain and are preserved in the Church of Santa Engracia de Zaragoza. The monastery was ruined during the sieges (1808 and 1809) by Napoleon Bonaparte, that the Aragonese capital suffered in the Peninsular War. However, the upper cloister survived, but was demolished in 1836. The monastery was noted for its rich Isabelline and Renaissance architecture. History After the Peace of Constantine an abbey was built over the tomb in the cemetery of the Martyrs. There are some who attribute its foundation to Saint Paulinus during his pilgrimage to Zaragoza in 392. The monks may ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Monasterio De Santa Engracia (Lejeune)
Monasterio is a municipality located in the province of Guadalajara, Castile-La Mancha, Spain. According to the 2004 census A census (from Latin ''censere'', 'to assess') is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording, and calculating population information about the members of a given Statistical population, population, usually displayed in the form of stati ... ( INE), the municipality has a population of 24 inhabitants. References Municipalities in the Province of Guadalajara {{CastileLaMancha-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Braulio Of Zaragoza
Braulio (), 585 – 651 AD, was bishop of Zaragoza and a learned cleric living in the Kingdom of the Visigoths. Both as pastor and writer, he is one of the most celebrated of saints of the Visigothic Kingdom of Hispania that lasted from the 5th to the 8th century (see History of Spain). Life Braulio was born of a noble Hispano-Roman family. His father, Gregory, was Bishop of Osma. His sister and two brothers were all to hold key posts in the Catholic Church. In 610 Braulio took the habit of a monk, and was later to study at Isidore's school in Seville. Archbishop Isidore faced a rising threat of Gothic barbarism. His strategic thrust was teaching. Braulio was ordained by Isidore in 624, and joined the clergy serving Seville. The next year, Braulio returned to Zaragoza where his brother John was then bishop, and served as his archdeacon. Upon his brother's death in 631, Braulio succeeded him as bishop. Known for his personal austerity, almsgiving and preaching, he was an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hieronymites
The Hieronymites or Jeronimites, also formally known as the Order of Saint Jerome (; abbreviated OSH), is a Catholic enclosed religious orders, cloistered religious order and a common name for several congregations of hermit monks living according to the Rule of Saint Augustine, though the role principle of their lives is that of the 5th-century hermit and biblical scholar Jerome. The principal group with this name was founded in the Iberian Peninsula around the 14th century. Their religious habit is a white tunic with a brown, hooded scapular and a brown Mantle (vesture), mantle. For liturgy, liturgical services, they wear a brown cowl. Iberian Hieronymites Origins Established near Toledo, Spain, the order developed from a spontaneous interest of a number of hermit, eremitical communities in both Spain and Portugal imitating the life of Jerome and Paula of Rome. This way of life soon became widespread in Spain. Two of these hermits, Pedro Fernández y Pecha and Fernando Yá ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ferdinand II Of Aragon
Ferdinand II, also known as Ferdinand I, Ferdinand III, and Ferdinand V (10 March 1452 – 23 January 1516), called Ferdinand the Catholic, was King of Aragon from 1479 until his death in 1516. As the husband and co-ruler of Queen Isabella I of Castile, he was also King of Castile from 1475 to 1504 (as Ferdinand V). He reigned jointly with Isabella over a Dynastic union, dynastically unified Spain; together they are known as the Catholic Monarchs. Ferdinand is considered the ''de facto'' first king of Spain, and was described as such during his reign, even though, legally, Crown of Castile, Castile and Crown of Aragon, Aragon remained two separate kingdoms until they were formally united by the Nueva Planta decrees issued between 1707 and 1716. The Crown of Aragon that Ferdinand inherited in 1479 included the kingdoms of Kingdom of Aragon, Aragon, Kingdom of Valencia, Valencia, Kingdom of Majorca, Majorca, Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia, and Kingdom of Sicily, Sicily, as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
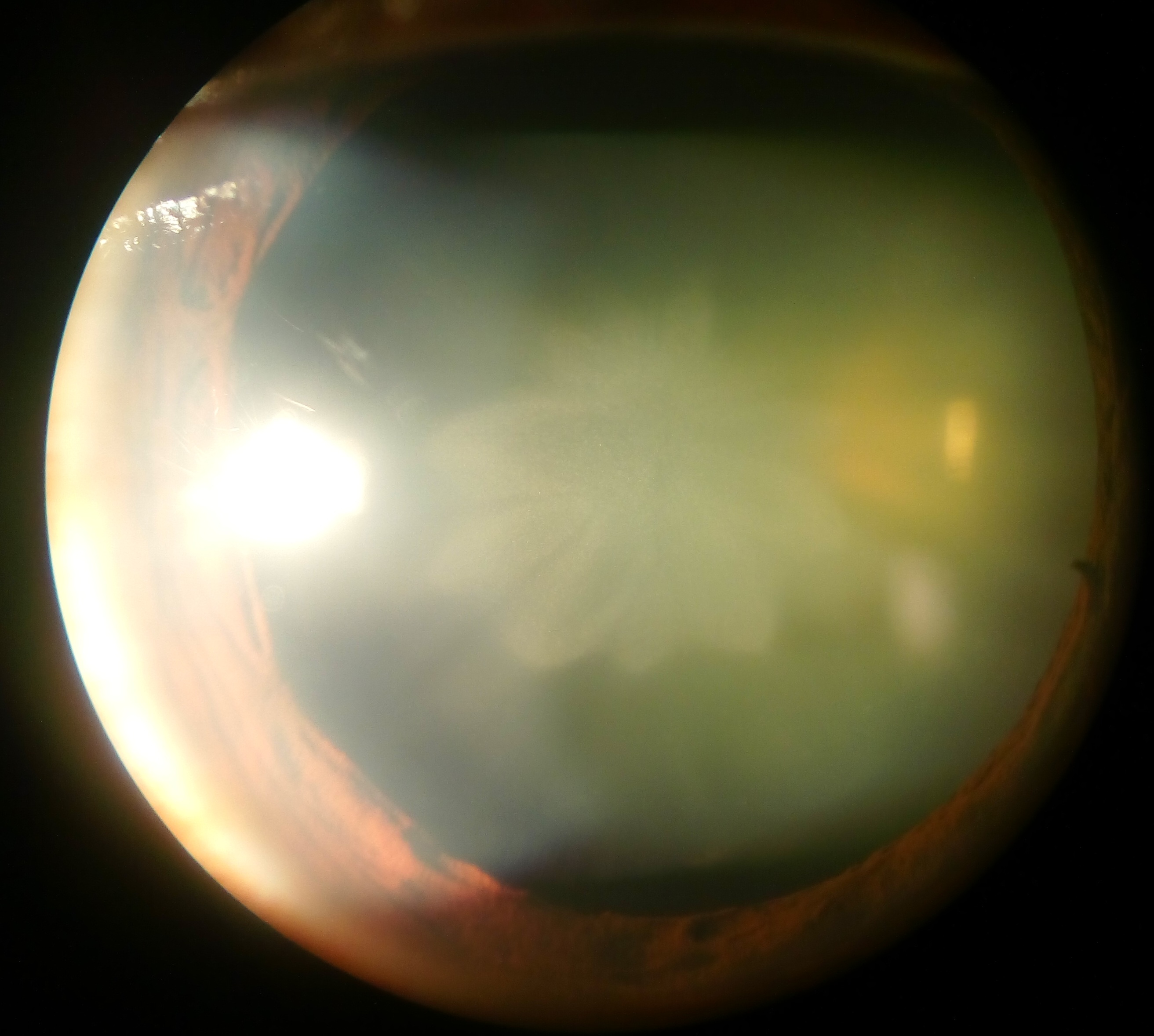
Cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens (anatomy), lens of the eye that leads to a visual impairment, decrease in vision of the eye. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colours, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and Nyctalopia, difficulty seeing at night. This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognizing faces. Poor vision caused by cataracts may also result in an increased risk of Falling (accident), falling and Depression (mood), depression. Cataracts cause 51% of all cases of blindness and 33% of visual impairment worldwide. Cataracts are most commonly due to senescence, aging but may also occur due to Trauma (medicine), trauma or radiation exposure, be congenital cataract, present from birth, or occur following eye surgery for other problems. Risk factors include diabetes mellitus, diabetes, longstanding use of corticosteroid medication, smoking tobacco, prolonged exposu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
John II Of Aragon
John II (Spanish language, Spanish: ''Juan II'', Catalan language, Catalan: ''Joan II'', Aragonese language, Aragonese: ''Chuan II'' and ; 29 June 1398 – 20 January 1479), called the Great (''el Gran'') or the Faithless (''el Sense Fe''), was King of Aragon from 1458 until his death in 1479. As the husband of Queen Blanche I of Navarre, he was King of Navarre from 1425 to 1479. John was also King of Sicily from 1458 to 1468. Biography John was born at Medina del Campo (in the Crown of Castile), the son of King Ferdinand I of Aragon and Eleanor of Alburquerque. In his youth he was one of the ''infantes'' (princes) of Aragon who took part in the dissensions of Castile during the minority and reign of John II of Castile. Until middle life he was also lieutenant-general in Aragon for his brother and predecessor Alfonso V of Aragon, Alfonso V, whose reign was mainly spent in Italy. In his old age he was preoccupied by incessant conflicts with his Aragonese and Catalan subjects, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mozarabs
The Mozarabs (from ), or more precisely Andalusi Christians, were the Christians of al-Andalus, or the territories of Iberia under Muslim rule from 711 to 1492. Following the Umayyad conquest of the Visigothic Kingdom in Hispania, the Christian population of much of Iberia came under Muslim control. Initially, the vast majority of Mozarabs kept Christianity and their dialects descended from Latin. Gradually, the population converted to Islam—an estimated 50% by the year 951 ''Cited in'' —and was influenced, in varying degrees, by Arab customs and knowledge, and sometimes acquired greater social status in doing so. The local Romance vernaculars, with an important contribution of Arabic and spoken by Christians and Muslims alike, are referred to as Andalusi Romance (also called ''Mozarabic language''). Mozarabs were mostly Catholics of the Visigothic or Mozarabic Rite. Due to Sharia and fiqh being confessional and only applying to Muslims, the Christians paid the jizya tax, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Niche (architecture)
In architecture, a niche (Canadian English, CanE, or ) is a recess or cavity constructed in the thickness of a wall for the reception of decorative objects such as statues, busts, urns, and vases. In Classical architecture examples are an exedra or an apse that has been reduced in size, retaining the half-dome heading usual for an apse. In the first century B.C, there was no exact mention of niches, but rather a zotheca or small room. These rooms closely resemble alcoves similar to a niche but slightly larger. Different sizes and sculpture methods suggest the term niche was understood. Greeks and Romans especially, used niches for important family tombs. Etymology The word derives from the Latin (), via the French . The Italian ''Contrade of Siena#Nicchio (Seashell), nicchio'' () may also be involved in the origin of the word, as the traditional decoration for the top of a niche is a scallop shell, hence also the alternative term of semi-dome, "conch" for a semi-dome, usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lupercus Of Berytus
Lupercus of Berytus (Greek ) was a Greek grammarian active during the 3rd century CE, likely flourishing shortly before the brief reign of Emperor Claudius Gothicus (268–270 CE). He was associated with the scholarly milieu of Berytus (modern-day Beirut Beirut ( ; ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, just under half of Lebanon's population, which makes it the List of largest cities in the Levant region by populatio ...), a prominent center of Roman and Hellenistic learning. Lupercus authored several works, including ''On the Word'' (), ''The Foundation of Arsinoe in Egypt'', and other treatises. His writings contributed to the grammatical and rhetorical literature of his time and were occasionally cited by later scholars. Although much of his work has not survived, references to his contributions are found in historical sources. References 3rd-century Greek writers 3rd-century Romans 3rd-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Engratia
Engratia (, ) is venerated as a virgin martyr and saint. Tradition states that she was martyred with eighteen companions in 303 AD. History Although her martyrdom is traditionally placed around 303 during the Diocletianic Persecution, more recently it is considered probable that she died during the persecution of Valerian (254-260). Legend Engratia was a native of Braga who had been promised in marriage to a nobleman of Roussillon. He sent as her escort to Gaul her uncle Lupercius (sometimes identified with the Luperculus who was a bishop of Eauze) and a suite of sixteen noblemen and a servant named Julie or Julia. Upon reaching Zaragoza, they learned of the persecution of Christians there by the governor Dacian, who reigned in the time of the emperors Diocletian and Maximian. She attempted to dissuade him from his persecution, but was whipped and imprisoned when it was discovered that she was a Christian. She died of her wounds. Her companions were decapitated. Martyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Zaragoza - Santa Engracia - Claustro Mayor
Zaragoza (), traditionally known in English as Saragossa ( ), is the capital city of the province of Zaragoza and of the autonomous community of Aragon, Spain. It lies by the Ebro river and its tributaries, the Huerva and the Gállego, roughly in the centre of both Aragon and the Ebro basin. On 1 January 2021, the population of the municipality of Zaragoza was 675,301, (as of 2023, the fourth or fifth most populous in Spain) on a land area of . It is the 26th most populous municipality in the European Union. The population of the metropolitan area was estimated in 2006 at 783,763 inhabitants. The municipality is home to more than 50 percent of the Aragonese population. The city lies at an elevation of about above sea level. Zaragoza hosted Expo 2008 in the summer of 2008, a world's fair on water and sustainable development. It was also a candidate for the European Capital of Culture in 2012. The city is famous for its folklore, local cuisine, and landmarks such as the Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pope Gregory VII
Pope Gregory VII (; 1015 – 25 May 1085), born Hildebrand of Sovana (), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 22 April 1073 to his death in 1085. He is venerated as a saint in the Catholic Church. One of the great reforming popes, he initiated the Gregorian Reform, and is perhaps best known for the part he played in the Investiture Controversy, his dispute with Emperor Henry IV to establish the primacy of papal authority and the new canon law governing the election of the pope by the College of Cardinals. He was also at the forefront of developments in the relationship between the emperor and the papacy during the years before he became pope. He was the first pope to introduce a policy of obligatory celibacy for the clergy, which had until then commonly married, and also attacked the practice of simony. During the power struggles between the papacy and the Holy Roman Empire, Empire, Gregory excommunicated Henry IV three times, and Henry appointed An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |