|
Zenaga People
The Sanhaja (, or زناگة ''Znāga''; , pl. Iẓnagen, and also Aẓnaj, pl. Iẓnajen) were once one of the largest Berber tribal confederations, along with the Zanata and Masmuda confederations. Many tribes in Algeria, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Senegal, Tunisia and Western Sahara bore and still carry this ethnonym, especially in its Berber form. Other names for the population include ''Zenaga'', ''Znaga'', ''Sanhája'', ''Sanhâdja'' and ''Senhaja''. Triad Ibn Khaldun and others defined the Sanhaja as a grouping made up of three separate confederations, not as a single confederation. The distinction is usually made with a diacritical point placed above or below that is present in the Arabic text and often lost in English. # Danhāǧa/Sanhaja anhaja of the first typeis a confederation of: Kutāma- Zawāwa of the Kabyle mountains, including some areas like Algiers and Constantine that no longer speak Taqbaylit dialects (they occupied all the northern part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
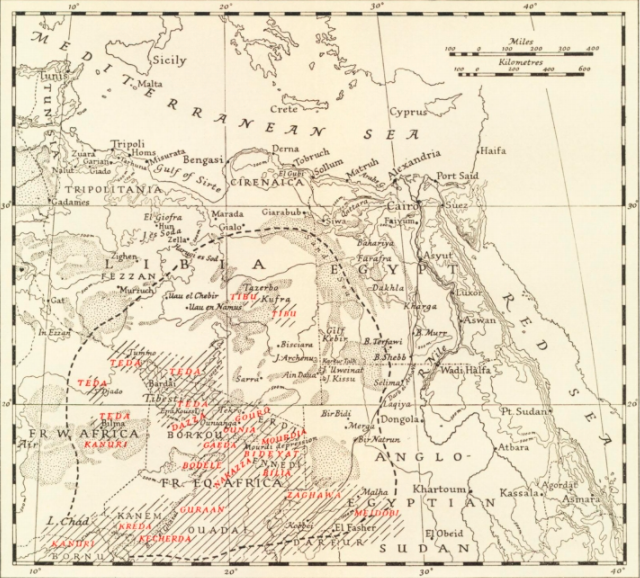
Map Of Berber Languages
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowing humans t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammadid Dynasty
The Hammadid dynasty (), also known as the Hammadid Emirate or the Kingdom of Bejaia, was a medieval Islamic kingdom in the central Maghreb, encompassing what is now Algeria. It was established at the beginning of the 11th century when Hammad ibn Buluggin declared himself emir, thus splitting the Zirid domains into two separate dynasties. Under the reign of Emir Al Nasir, the emirate briefly became the most important state in the Maghreb, and reached its greatest territorial extent, stretching from Tlemcen in the west to Tunis in the east, and from the Mediterranean Sea in the north to the desert oasis of Ouargla and Oued Righ in the south. While they briefly controlled the principality of Fez in the west and cities like Sfax, Kairouan, Laribus, and Tripoli to the east. At first, Hammad built a fortified city that would serve as the capital for his newly declared kingdom. Later, upon the arrival of the Arabic Banu Hilal tribes, the capital would be replaced by another ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barghawata
The Barghawatas (or Barghwata, Berghouata) were a Berbers, Berber tribal confederation and religious movement that ruled a region of the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast in present-day Morocco between the 8th and 11th centuries. They belonged to the Masmuda confederacy. After allying with the Sufri Berber Revolt, rebellion against the Umayyad Caliphate, they established an independent state (AD744-1058) in the area of Tamasna, Tamesna on the Atlantic coast between Safi, Morocco, Safi and Salé under the leadership of Tarif al-Matghari. Etymology Some historians believe that the term ''Barghawata'' is a phonetic deformation of the term ''Barbati'', a nickname which Tarif carried. It is thought that he was born in the area of Barbate, near Cádiz in Spain. However, Jérôme Carcopino and other historians think the name is much older and the tribe is the same as that which the Ancient Rome, Romans called ''Baquates'', who up until the 7th century lived near Volubilis. History Few deta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hintata
The Hintata or Hin Tata were a Berbers, Berber tribal confederation belonging to the tribal group Masmuda of the High Atlas, Morocco. They were historically known for their political power in the region of Marrakesh between the twelfth century and sixteenth century. Having helped the Almohad Caliphate, Almohads come to power, the Hintata have always been very close to the Almohad Caliphate, Almohad caliphs and during the Marinid Sultanate, Marinid period, controlled the region of Marrakesh from the ''Jabal'' Hintata, in the High Atlas, coming to reign independently on fifteenth century and early sixteenth century. The Hafsid dynasty of Tunis were a descendant of the Hintata. Branches The hintata were composed of nine clans. These clans were the Banu (Ait) Galgaʾiya, the Banu (Ait) Lamazdur, the Banu (Ait) Tagurtant, the Banu (Ait) Taklawwuh-tin, the Banu (Ait) Talwuh-rit, the Banu (Ait) Tumsidin, the Banu (Ait) Wawazgit, the Banu (Ait) Yigaz, and their allies the Mazala. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghomaras
The Ghomara (, ''Ighmaren'') are a group of tribes in northern Morocco belonging to the Berbers. They live in the western Rif, in the area of Chefchaouen and Tetouan.G. Camps & J. Vignet-Zunz, "Ghomâra", in ''Encyclopédie berbère'', vol. 20, 1998 Originally, Ghomaras were a Berber tribal group belonging to the Masmuda confederacy. While most have shifted to speaking Arabic, a minority continue to speak the Berber Berber or Berbers may refer to: Ethnic group * Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa * Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages Places * Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile People with the surname * Ady Berber (1913–196 ... Ghomara language. Tribes The Ghomaras are traditionally divided into nine tribes: *Beni Bouzra *Beni Grir *Beni Khaled *Beni Mansour *Beni Rezin *Beni Selman *Beni Smih *Beni Zejel *Beni Ziat Bibliography * G. Camps & J. Vignet-Zunz"Ghomâra" ''Encyclopédie berbère, vol.20'', 1998, pp. 3110–3119 * Jama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almoravid Dynasty
The Almoravid dynasty () was a Berber Muslim dynasty centered in the territory of present-day Morocco. It established an empire that stretched over the western Maghreb and Al-Andalus, starting in the 1050s and lasting until its fall to the Almohads in 1147. The Almoravids emerged from a coalition of the Lamtuna, Gudala, and Massufa, nomadic Berber tribes living in what is now Mauritania and the Western Sahara, traversing the territory between the Draa, the Niger, and the Senegal rivers. During their expansion into the Maghreb, they founded the city of Marrakesh as a capital, . Shortly after this, the empire was divided into two branches: a northern one centered in the Maghreb, led by Yusuf ibn Tashfin and his descendants, and a southern one based in the Sahara, led by Abu Bakr ibn Umar and his descendants. The Almoravids expanded their control to al-Andalus (the Muslim territories in Iberia) and were crucial in temporarily halting the advance of the Christian kingdoms in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tebu Languages
Tebu is a small family of two Saharan languages, consisting of Daza and Teda. It is spoken by the two groups of Toubou people, the ''Daza'' and ''Teda''. Tebu is predominantly spoken in Chad and in southern Libya by around 580,000 people. Daza and Teda have an estimated 537,000 and 42,500 speakers, respectively.SIL Ethnologue ''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It w ... estimatesDazagaTedaga. References Saharan languages Languages of Chad Languages of Libya Languages of Niger Toubou people {{ns-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toubou People
The Toubou or Tubu (from Old Tebu, meaning "rock people") are an ethnic group native to the Tibesti Mountains that inhabit the central Sahara in northern Chad, southern Libya, northeastern Niger, and northwestern Sudan. They live either as herders and nomads or as farmers near oases. Their society is clan-based, with each clan having certain oases, pastures and wells. The Toubou are generally divided into two closely related groups: the Teda (or Tuda, Téda, Toda, Tira) and the Daza (or Dazzaga, Dazagara, Dazagada). They are believed to share a common origin and speak the Tebu languages, which are from the Saharan branch of the Nilo-Saharan language family. Tebu is divided further into two closely related languages, called '' Tedaga'' (Téda Toubou) and '' Dazaga'' (Daza Toubou). Of the two groups, the Daza, found to the south of the Teda, are more numerous. The Toubou people are also referred to as the Tabu, Tebu, Tebou, Tibu, 'Tibbu, Toda, Todga, Todaga, Tubu, Tuda, Tudag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godala
The Godala or Gudāla is a Berber tribe in Western Africa that lived along the Atlantic coast in present-day Mauritania and participated in the Saharan salt trade and the salt mines of Ijiil. The Godala may be linked to or the same as the ancient Gaetuli tribe of Berbers. According to a 1985 study of West African history, the area along both sides of the mouth of the Senegal River was controlled by the Godala group of Berbers. They mined the Awlil salt deposits along the coast just north of the mouth of the Senegal, and controlled a coastal trade route that linked southern Morocco Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc .... Godala territory bordered that of Takrur, and Godala caravans traded salt mined at Awlil along the north bank of the Senegal. Guezula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamtuna
The Lamtuna () are a nomadic Berber tribe belonging to the Iẓnagen / Sanhaja (Zenaga) confederation, who traditionally inhabited areas from Sous to Adrar Plateau. During the Almoravid period, many Lamtunas emigrated northwards. Currently, the Lemtuna Tribe is based in the South of Mauritania (Monguel and Agueilat). The chief of this Tribe is Mr. Limam Ould Teguedi (former Minister of Justice, former Minister of Culture and former Attorney General of Mauritania). Among notable families are the family of Ehl Aly Ibn Ibrahim, the family of Ehel Sidelemine, Ehl Abdawa, Ehl Mohamed El-Emine and Ehl Mohammed Ghali. Sahrawi Tajakant as well as Messouma tribes are of the most recognisable offshoots of the Lamtunas. They inhabit areas in Algeria, Morocco, Mauritania and Western Sahara. The Banu Ghaniya, the successors of this dynasty in Tripoli and the Nafusa Mountains and the governors of the Spanish Balearic Islands until about the middle of the 13th century, originated from this tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
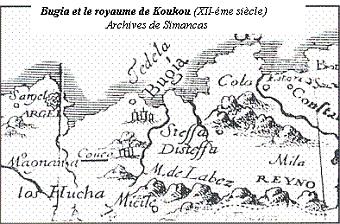
Kingdom Of Kuku
The Kingdom of Kuku was a kingdom in North Africa North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t .... It was established around 1515 CE and ruled by the Ath l-Qadi dynasty until 1632 or 1638 CE. Ahmed ou el Kadhi (Ou l-Qadi) is acknowledged as the founder. Origins The Ath l-Qadi are generally accepted to have been from the Ath Ghoubri region and having a maraboutic lineage. According to Laurent-Charles Féraud (1829–1888), the dynasty possessed parchments which attributed their genealogy to a certain Ammar ben Idris, hence relating them to the Sharifian Idrisids of Fez, while Joseph Nil Robin associates them with a non-Sharifian Fassi ancestry. References 1515 establishments in Africa Berber dynasties Early modern history of Algeria States and territories dise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Beni Abbas
The Kingdom of Beni Abbas or Sultanate of Beni Abbas () was a state in North Africa, then a fief and a principality, controlling Lesser Kabylie in Kabylia and its surroundings from the sixteenth century to the nineteenth century. It is referred to in the Spanish historiography as "reino de Labes". Sometimes more commonly referred to by its ruling family, the Mokrani dynasty (). Its capital was the Kalâa of Ait Abbas, an impregnable citadel in the Biban mountain range. The kingdom was for a long time a bastion of resistance to the Spanish Empire, then to the Regency of Algiers. Strategically located on the road from Algiers to Constantine and from the Mediterranean Sea to the Sahara, the Kalâa of Ait Abbas, attracted Andalusians, both Christians and Jews, in the sixteenth century, fleeing Spain or Algiers. Their know-how enriched a local industrial fabric whose legacy is the handicraft of the Ait Abbas tribe. The surrounding tribes were also home to intense intellectual ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |