|
Zawiya Of Sidi Sahib
The Zawiya of Sidi Sahib, also known as the Zawiya of Abu al-Balawi or Mosque of the Barber, is a Zawiya (institution), zawiya (religious shrine and complex) in Kairouan, Tunisia. Its origins date to the early era of the city's history, but the current complex largely dates to a major renovation and expansion in the 17th century. It is one of the most important religious sites in the city. History According to tradition, Abu Zama'a al-Balawi (also known as Sidi Sahib), the barber and a Companions of the Prophet, Companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, was buried here in 654 after dying in battle. Tradition also holds that he was buried with three hairs from Muhammad's beard. Today, he is also considered the town's patron saint. By the 11th century, the tomb had become a pilgrimage site and a cemetery developed around it. By the 14th century, it was considered one of the most important shrines in Kairouan. A first zawiya or mausoleum was first built here in the 14th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance Architecture
Renaissance architecture is the European architecture of the period between the early 15th and early 16th centuries in different regions, demonstrating a conscious revival and development of certain elements of ancient Greek and Roman thought and material culture. Stylistically, Renaissance architecture followed Gothic architecture and was succeeded by Baroque architecture. Developed first in Florence, with Filippo Brunelleschi as one of its innovators, the Renaissance style quickly spread to other Italian cities. The style was carried to Spain, France, Germany, England, Russia and other parts of Europe at different dates and with varying degrees of impact. Renaissance style places emphasis on symmetry, proportion, geometry and the regularity of parts, as demonstrated in the architecture of classical antiquity and in particular ancient Roman architecture, of which many examples remained. Orderly arrangements of columns, pilasters and lintels, as well as the use of semici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squinch
In architecture, a squinch is a triangular corner that supports the base of a dome. Its visual purpose is to translate a rectangle into an octagon. See also: pendentive. Construction A squinch is typically formed by a masonry arch that spans a square corner. History in the Middle East The dome chamber in the Palace of Ardashir, the Sassanid king, in Firuzabad, Iran is the earliest surviving example of the use of the squinch, suggesting that the squinch may have been invented in Persia. After the rise of Islam, it was used in the Middle East in both eastern Romanesque and Islamic architecture. It remained a feature of Islamic architecture, especially in Iran, and was often covered by corbelled stalactite-like structures known as muqarnas. History in Western Europe It spread to the Romanesque architecture of western Europe, one example being the Normans' 12th-century church of San Cataldo, Palermo in Sicily. This has three domes, each supported by four doubled squinch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital (architecture)
In architecture the capital (from the Latin ''caput'', or "head") or chapiter forms the topmost member of a column (or a pilaster). It mediates between the column and the load thrusting down upon it, broadening the area of the column's supporting surface. The capital, projecting on each side as it rises to support the abacus, joins the usually square abacus and the usually circular shaft of the column. The capital may be convex, as in the Doric order; concave, as in the inverted bell of the Corinthian order; or scrolling out, as in the Ionic order. These form the three principal types on which all capitals in the classical tradition are based. The Composite order established in the 16th century on a hint from the Arch of Titus, adds Ionic volutes to Corinthian acanthus leaves. From the highly visible position it occupies in all colonnaded monumental buildings, the capital is often selected for ornamentation; and is often the clearest indicator of the architectu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinthian Order
The Corinthian order ( Greek: Κορινθιακός ρυθμός, Latin: ''Ordo Corinthius'') is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order which was the earliest, followed by the Ionic order. In Ancient Greek architecture, the Corinthian order follows the Ionic in almost all respects other than the capitals of the columns. When classical architecture was revived during the Renaissance, two more orders were added to the canon: the Tuscan order and the Composite order. The Corinthian, with its offshoot the Composite, is the most ornate of the orders. This architectural style is characterized by slender fluted columns and elaborate capitals decorated with acanthus leaves and scrolls. There are many variations. The name ''Corinthian'' is derived from the ancient Greek city of Corinth, although the style had its own model in Roman practice, following precedents set by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horseshoe Arch
The horseshoe arch (; Spanish: "arco de herradura"), also called the Moorish arch and the keyhole arch, is an emblematic arch of Islamic architecture, especially Moorish architecture. Horseshoe arches can take rounded, pointed or lobed form. History Origins and early uses The origins of the horseshoe arch are controversial. It appeared in pre-Islamic Sasanian architecture such as the Taq-i Kasra in present-day Iraq and the Palace of Ardashir in southwestern Iran (3rd century CE). It also appeared in Late Roman or Byzantine architecture in pre-Islamic Syria, where the form was used in the Baptistery of Saint Jacob at Nusaybin (4th century CE) and in Qasr Ibn Wardan (564 CE). However, the horseshoe arch allowed more height than the classical (semi-circular) arch as well as better aesthetic and decorative use. Muslims used this arch to develop their famous ultra-semicircular arch, around which the whole of Islamic architecture evolved, thus more likely suggesting that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mihrab
Mihrab ( ar, محراب, ', pl. ') is a niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the '' qibla'', the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca towards which Muslims should face when praying. The wall in which a ''mihrab'' appears is thus the "qibla wall". The '' minbar'', which is the raised platform from which an imam (leader of prayer) addresses the congregation, is located to the right of the mihrab. Etymology The origin of the word ''miḥrāb'' is complicated and multiple explanations have been proposed by different sources and scholars. It may come from Old South Arabian (possibly Sabaic) ''mḥrb'' meaning a certain part of a palace, as well as "part of a temple where ''tḥrb'' (a certain type of visions) is obtained," from the root word ''ḥrb'' "to perform a certain religious ritual (which is compared to combat or fighting and described as an overnight retreat) in the ''mḥrb'' of the temple." It may also possibly be related to Ethiopic ''məkʷrab'' "temple, sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypostyle
In architecture, a hypostyle () hall has a roof which is supported by columns. Etymology The term ''hypostyle'' comes from the ancient Greek ὑπόστυλος ''hypóstȳlos'' meaning "under columns" (where ὑπό ''hypó'' means below or underneath and στῦλος ''stŷlos'' means column). Technical options The roof may be constructed with bridging lintels of stone, wood or other rigid material such as cast iron, steel or reinforced concrete. There may be a ceiling. The columns may be all the same height or, as in the case of the Great Hypostyle Hall at Karnak, the columns flanking the central space may be of greater height rather than those of the side aisles, allowing openings in the wall above the smaller columns, through which light is admitted over the aisle roof, through clerestory windows. Applications The architectural form has many applications, occurring in the ''cella'' of ancient Greek temples and in many Asian buildings, particularly of wood construction. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cultures, including most Western cultures. Some noteworthy examples of porticos are the East Portico of the United States Capitol, the portico adorning the Pantheon in Rome and the portico of University College London. Porticos are sometimes topped with pediments. Palladio was a pioneer of using temple-fronts for secular buildings. In the UK, the temple-front applied to The Vyne, Hampshire, was the first portico applied to an English country house. A pronaos ( or ) is the inner area of the portico of a Greek or Roman temple, situated between the portico's colonnade or walls and the entrance to the '' cella'', or shrine. Roman temples commonly had an open pronaos, usually with only columns and no walls, and the pronaos could be as lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waqf
A waqf ( ar, وَقْف; ), also known as hubous () or ''mortmain'' property is an inalienable charitable endowment under Islamic law. It typically involves donating a building, plot of land or other assets for Muslim religious or charitable purposes with no intention of reclaiming the assets. A charitable trust may hold the donated assets. The person making such dedication is known as a ''waqif'' (a donor). In Ottoman Turkish law, and later under the British Mandate of Palestine, a ''waqf'' was defined as usufruct state land (or property) from which the state revenues are assured to pious foundations. Although the ''waqf'' system depended on several hadiths and presented elements similar to practices from pre-Islamic cultures, it seems that the specific full-fledged Islamic legal form of endowment called ''waqf'' dates from the 9th century AD (see below). Terminology In Sunni jurisprudence, ''waqf'', also spelled ''wakf'' ( ar, وَقْف; plural , ''awqāf''; tr, va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
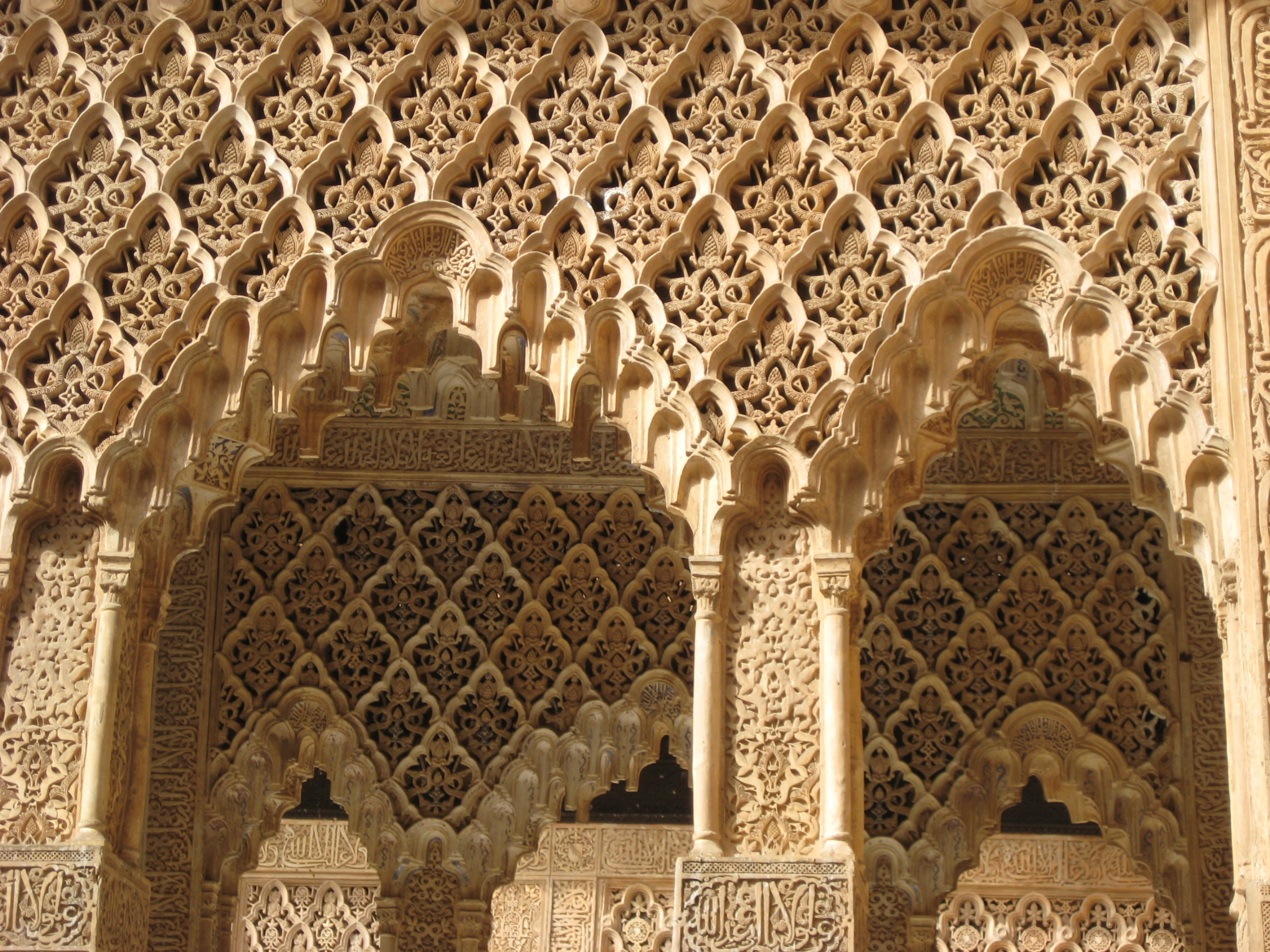
Islamic Geometric Patterns
Islamic geometric patterns are one of the major forms of Islamic ornament, which tends to avoid using figurative images, as it is forbidden to create a representation of an important Islamic figure according to many holy scriptures. The geometric designs in Islamic art are often built on combinations of repeated squares and circles, which may be overlapped and interlaced, as can arabesques (with which they are often combined), to form intricate and complex patterns, including a wide variety of tessellations. These may constitute the entire decoration, may form a framework for floral or calligraphic embellishments, or may retreat into the background around other motifs. The complexity and variety of patterns used evolved from simple stars and lozenges in the ninth century, through a variety of 6- to 13-point patterns by the 13th century, and finally to include also 14- and 16-point stars in the sixteenth century. Geometric patterns occur in a variety of forms in Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stucco Decoration In Islamic Architecture
Stucco decoration in Islamic architecture refers to carved or molded stucco and plaster. The terms "stucco" and "plaster" are used almost interchangeably in this context to denote most types of stucco or plaster decoration with slightly varying compositions. This decoration was mainly used to cover walls and surfaces and the main motifs were those predominant in Islamic art: geometric, arabesque (or vegetal), and calligraphic, as well as three-dimensional ''muqarnas''. Plaster of gypsum composition was extremely important in Islamic architectural decoration as the relatively dry climate throughout much of the Islamic world made it easy to use this cheap and versatile material in a variety of spaces. Stucco decoration was already used in ancient times in the region of Iran and the Greco-Roman Mediterranean. In Islamic architecture, stucco decoration appeared during the Umayyad period (late 7th–8th centuries) and underwent further innovations and generalization during the 9t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpg)




