|
Zawi Ben Ziri
Zawi ibn Ziri as-Sanhaji or Al-Mansur Zawi ibn Ziri ibn Manad as-Sanhaji (), was a chief in the Berber Sanhaja tribe. He arrived in Spain in 1000 (391) during the reign of Almanzor. He took part in the rebellion against the Caliphate of Córdoba and settled in the Cora of Elvira with followers from his Sanhaja tribe. He founded the Taifa of Granada, and founded the Zirid dynasty of Granada as its first Emir, reigning from 1013 to 1019. Early Zirid dynasty Zawi's father, Ziri ibn Manad (Ziri) was the leader of the Berber Sanhaja tribe, with allegiance to al-Mansur bi-Nasr Allah, leader of the Fatimid Caliphate. Ziri founded the Zirid dynasty in the Maghreb with the permission of al-Mansur bi-Nasr Allah in 944 and built the city of El Achir. During the ongoing revolt of the Zenata tribe against Fatimid rule, Ziri marched against the Zenata forces in 970. Following a bloody battle, the Sanhaja army was routed and Ziri's horse fell on him. With his troops having abandoned the bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
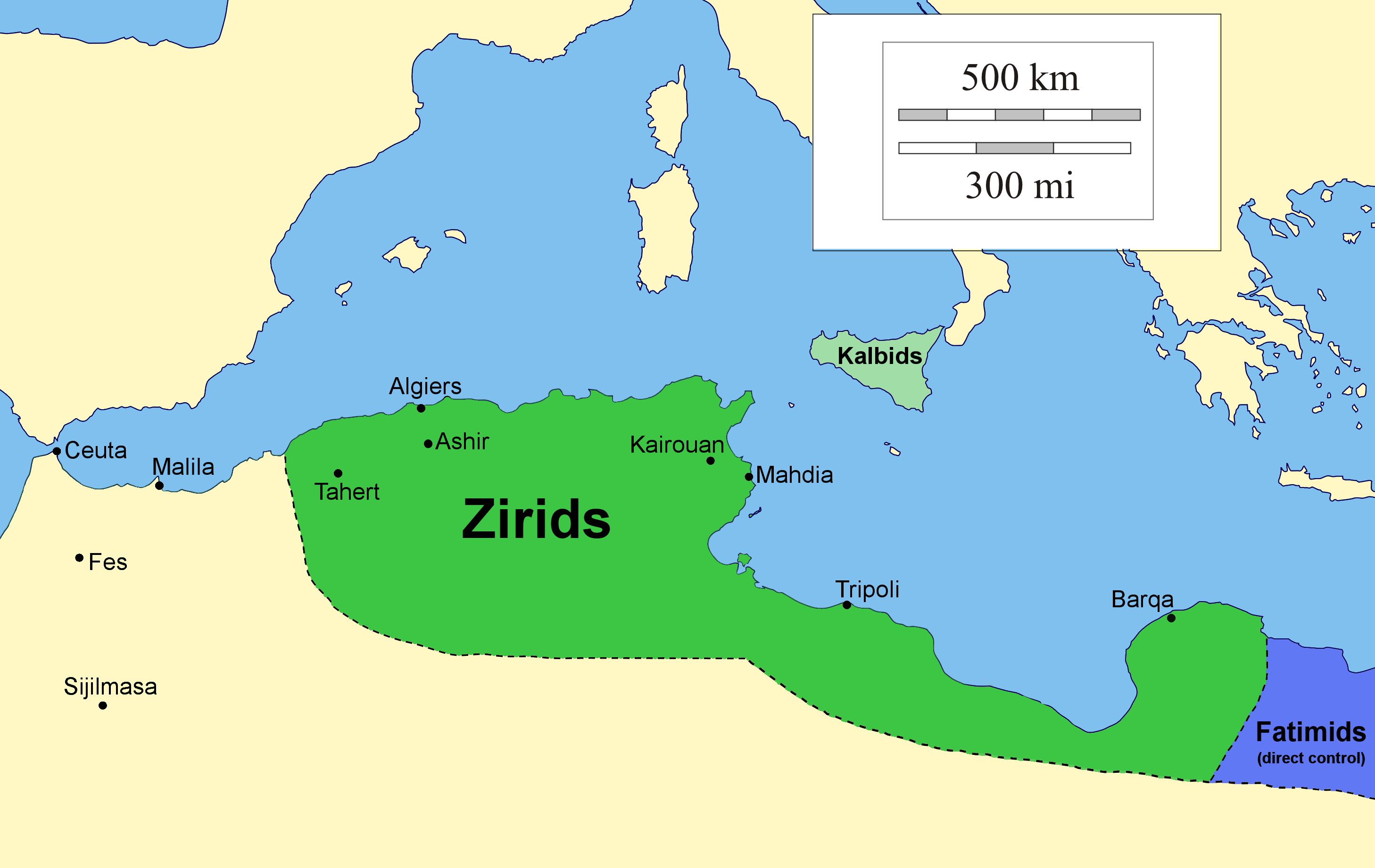
Zirids
The Zirid dynasty (), Banu Ziri (), was a Sanhaja Berber dynasty from what is now Algeria which ruled the central Maghreb from 972 to 1014 and Ifriqiya (eastern Maghreb) from 972 to 1148. Descendants of Ziri ibn Manad, a military leader of the Fatimid Caliphate and the eponymous founder of the dynasty, the Zirids were emirs who ruled in the name of the Fatimids. The Zirids gradually established their autonomy in Ifriqiya through military conquest until officially breaking with the Fatimids in the mid-11th century. The rule of the Zirid emirs opened the way to a period in North African history where political power was held by Berber dynasties such as the Almoravid dynasty, Almohad Caliphate, Zayyanid dynasty, Marinid Sultanate and Hafsid dynasty. Under Buluggin ibn Ziri the Zirids extended their control westwards and briefly occupied Fez and much of present-day Morocco after 980, but encountered resistance from the local Zenata Berbers who gave their allegiance to the Calip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Achir
El Achir is a town and commune in Bordj Bou Arréridj Province, Algeria Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger .... According to the 1998 census it has a population of 18,149. References Communes of Bordj Bou Arréridj Province {{BordjBouArréridj-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus () was the Muslim-ruled area of the Iberian Peninsula. The name refers to the different Muslim states that controlled these territories at various times between 711 and 1492. At its greatest geographical extent, it occupied most of the peninsula as well as Septimania under Umayyad rule. These boundaries changed through a series of conquests Western historiography has traditionally characterized as the ''Reconquista'',"Para los autores árabes medievales, el término Al-Andalus designa la totalidad de las zonas conquistadas – siquiera temporalmente – por tropas arabo-musulmanas en territorios actualmente pertenecientes a Portugal, España y Francia" ("For medieval Arab authors, Al-Andalus designated all the conquered areas – even temporarily – by Arab-Muslim troops in territories now belonging to Spain, Portugal and France"), García de Cortázar, José Ángel. ''V Semana de Estudios Medievales: Nájera, 1 al 5 de agosto de 1994'', Gobie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Badis Ibn Mansur
Bādīs ibn al-Manṣūr (; 14 August 984 - 10 May 1016), known fully as ʾAbū Manād Bādīs Nāṣir al-Dawla (), was the third ruler of the Zirids in Ifriqiya from 996 to 1016. Badis ibn Mansur succeeded his father al-Mansur ibn Buluggin () as viceroy of Ifriqiya on 8 April 996. At the outset of his reign he faced a revolt by the Zenata Berbers, who threatened the Zirid domains from Tiaret to Tripoli. To focus on them, he left the eastern parts of his emirate in the hands of a deputy. Throughout his reign, Badis also had to fend off Fatimid forays into Tripolitania. He stayed very close to his overlords, the Fatimids of Egypt,Talbi (1970) notes that he sent the poet ar-Raqiq on a diplomatic mission to Cairo. on account of a power struggle amongst the Zirids - his right to rule was challenged by his great-uncle Zawi ibn Ziri, who was ultimately driven into Andalusia where he founded the Zirid dynasty of Granada (1012–1090). By 1001, Badis had secured his position with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketama, Morocco
Issaguen Ketama is a small town and rural commune in Al Hoceïma Province of the Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima region of Morocco Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc .... At the time of the 2004 census, the commune had a total population of 15,924 people living in 2,444 households. References Populated places in Al Hoceïma Province Rural communes of Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceima {{TazaAlHoceimaTaounate-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sijilmassa
Sijilmasa (; also transliterated Sijilmassa, Sidjilmasa, Sidjilmassa and Sigilmassa) was a medieval Moroccan city and trade entrepôt at the northern edge of the Sahara in Morocco. The ruins of the town extend for five miles along the River Ziz in the Tafilalt oasis near the town of Rissani. The town's history was marked by several successive invasions by Berber dynasties. Up until the 14th century, as the northern terminus for the western trans-Sahara trade route, it was one of the most important trade centres in the Maghreb during the Middle Ages. History Foundation and early Middle Ages According to al-Bakri's ''Book of Routes and Places'', Sufrite Kharijites first settled the town in the wake of the Berber revolts against the Umayyads. Al-Bakri recounts that others joined these early settlers there, until they numbered around four thousand, at which point they laid the groundwork for the city. They elected a leader, 'Isa bin Mazid al-Aswad (the Black), to handle their af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiaret
Tiaret () or Tahert () is a major city in northwestern Algeria that gives its name to the wider farming region of Tiaret Province. Both the town and region lie south-west of the capital of Algiers in the western region of the Hautes Plaines, in the Tell Atlas, and about from the Mediterranean coast. It is served by Abdelhafid Boussouf Bou Chekif Airport. Etymology The name means "Lioness" in the Berber language, a reference to the Barbary lions that lived in this region. Maghrebian place names like Oran (''Wahran'') which means "lion", and Souk Ahras which means "Market of Lions" have the same etymological source. Population The town had a population of 178,915 in 2008. The town covered around 20.086.62 km2. Infrastructure and industry A 1992 study by the University of Nice Sophia Antipolis reported significant areas contaminated by industrial pollution, and growing squatter settlements on the periphery. The region is predominantly one of agriculture. There is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammad Ibn Buluggin
Hammad ibn Buluggin () (died August 1029) was the first ruler of the Hammadid dynasty in what is now Algeria (1014–1029). Life After the death of his father Buluggin ibn Ziri, al-Mansur ibn Buluggin (984–995), Hammad's brother, became the head of the Zirid dynasty in Ifriqiya, and installed Hammad as governor of the central Maghreb (grossly corresponding to the modern northern Algeria). He took on the Zanata tribes and eventually drove them into what is now modern-day Morocco. In 1007 Hammad founded the residence of al-Qala ("the Fortress") in the Hodna mountains west of Setif and embarked on an extensive building programme, which included a palace and mosque that became famous amongst contemporaries. Following this Hammad gained ever more influence in the western Zirid realm. In 1014 he adopted Sunni Islam, declared his independence from the Zirids and recognised the Sunni Abbasids in Baghdad as being the rightful Caliphs (not the Shia Fatimids in Egypt, on whose behalf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Mansur Ibn Buluggin
al-Mansûr ibn Buluggin () (died 26 March 996 ) was the second ruler of the Zirids in Ifriqiya (r. 984–995). Life Al-Mansur succeeded his father Buluggin ibn Ziri (r. 972–984) in Ifriqiya. Despite further campaigns by the Zirids against the Berber tribes of Morocco, he was forced to abandon the attempt at a permanent conquest of Fez and Sijilmasa. Still, he was able to consolidate Zirid rule in the central Maghreb when he defeated the Kutama Berbers in 988, and when his brother Hammad ibn Buluggin, as governor of Algeria, drove the Zanata Berbers into Morocco. The vassal relationship to the Fatimids became increasingly loose under al-Mansur, not least because their focus of attention was on the overthrow of the Abbasids in Iraq Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maghrawa
The Maghrawa or Meghrawa () were a large Berber tribal confederation in North Africa. They are the largest branch of the Zenata confederation. Their traditional territories around the time of Muslim expansion into the Maghreb in the 7th century were around present-day northeastern Algeria. They ruled parts of the western Maghreb on behalf of the Umayyad Caliphate of Cordoba at the end of the 10th century and during the first half of the 11th century. Origins The origins of the Maghrawa are uncertain. Ibn 'Abd al-Barr, an 11th-century writer, claimed that they arrived to the Maghreb in ancient times. Medieval Berber writers traced the ancestry of the Maghrawa to a leader named Maghrāw. According to Ibn Khaldun (d. 1406), they were related to the Banu Ifran, the Banu Jarawa, and the Banu Irniyan. Several tribes descend from the Maghrawa, including the Bani bou Said, Bani Ilit (Ilent), Bani Zendak, Bani Urac (Urtezmir, Urtesminn), Bani Urcifan, Bani Laghouat, Bani Righa, Ban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of largest cities in the Arab world, the Arab world, and List of largest metropolitan areas of the Middle East, the Middle East. The Greater Cairo metropolitan area is List of largest cities, one of the largest in the world by population with over 22.1 million people. The area that would become Cairo was part of ancient Egypt, as the Giza pyramid complex and the ancient cities of Memphis, Egypt, Memphis and Heliopolis (ancient Egypt), Heliopolis are near-by. Located near the Nile Delta, the predecessor settlement was Fustat following the Muslim conquest of Egypt in 641 next to an existing ancient Roman empire, Roman fortress, Babylon Fortress, Babylon. Subsequently, Cairo was founded by the Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid dynasty in 969. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |