|
ZX Spectrum Graphic Modes
The original ZX Spectrum computer produces a one bit per pixel, bitmapped colour graphics video output. A composite video signal is generated through an RF modulator, and was designed for use with contemporary 1980s television sets. The image size of the framebuffer is 256 × 192 pixels, with a palette of 15 non-modifiable colours, where the entire colour palette is extremely saturated. The resolution of the colour output is 64 times lower than the resolution of the pixel bitmap. The extremely low colour resolution was used to conserve memory, totaling just 768 bytes for colour attributes. Colour is stored separate from the pixel bitmap, as a 32 × 24 cell grid, using one byte per each of the character cells. One character cell is composed of 8 × 8 pixels. In practice, this means any character cell can only use two selected colours for colouring the contained 64 pixels. Since the machine was designed for usage with a standard television s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZX Spectrum Graphics Showcase
ZX may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Kamen Rider ZX (pronounced "Zed-Cross"), the tenth fictional superhero in the "Kamen Rider" franchise * ''Mega Man ZX'', a video game for the Nintendo DS * ''ZX Tunes'', remastered soundtracks of the "Mega Man ZX" game * '' Z/X'', Japanese collectible card game Science * ZX-calculus, in quantum computing, a graphical language for reasoning about linear maps between qubits Technology * Chinasat, a family of communications satellites (from the transliteration, Zhongxing) * Walkman ZX Series, a series of digital audio players made by Sony * ZX80, ZX81 and ZX Spectrum, home computers produced by Sinclair Transport * ZX Auto, also known as Zitsubishi, a Chinese SUV and truck manufacturer * Citroën ZX, a car model * Nissan 300ZX, a car model * Kawasaki Ninja series motorcycles (model designation codes ZX and ZX-R) * Air Georgian (IATA airline code ZX, 1994–2020) * Zoom Airlines Limited Zoom Airlines Ltd was a British scheduled, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blitter
A blitter is a circuit, sometimes as a coprocessor or a logic block on a microprocessor, dedicated to the rapid movement and modification of data within a computer's memory. A blitter can copy large quantities of data from one memory area to another relatively quickly, and in parallel with the CPU, while freeing up the CPU's more complex capabilities for other operations. A typical use for a blitter is the movement of a bitmap, such as windows and icons in a graphical user interface or images and backgrounds in a 2D video game. The name comes from the bit blit operation of the 1973 Xerox Alto, which stands for bit-block transfer. A blit operation is more than a memory copy, because it can involve data that's not byte aligned (hence the ''bit'' in ''bit blit''), handling transparent pixels (pixels which should not overwrite the destination), and various ways of combining the source and destination data. Blitters have largely been superseded by programmable graphics process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gate Array
A gate array is an approach to the design and manufacture of application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) using a semiconductor device fabrication, prefabricated chip with components that are later interconnected into logic devices (e.g. NAND gates, Flip-flop (electronics), flip-flops, etc.) according to custom order by adding metal interconnect layers in the factory. It was popular during the upheaval in the semiconductor industry in the 1980s, and its usage declined by the end of the 1990s. Similar technologies have also been employed to design and manufacture analog, analog-digital, and structured arrays, but, in general, these are not called gate arrays. Gate arrays have also been known as uncommitted logic arrays ('ULAs'), which also offered linear circuit functions, and ''semi-custom chips''. History Development Gate arrays had several concurrent development paths. Ferranti in the UK pioneered commercializing bipolar transistor, bipolar ULA technology, offering c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Address
In computing, a memory address is a reference to a specific memory location in memory used by both software and hardware. These addresses are fixed-length sequences of digits, typically displayed and handled as unsigned integers. This numerical representation is based on the features of CPU (such as the instruction pointer and incremental address registers). Programming language constructs often treat the memory like an array. Types Physical addresses A digital computer's main memory consists of many memory locations, each identified by a unique physical address (a specific code). The CPU or other devices can use these codes to access the corresponding memory locations. Generally, only system software (such as the BIOS, operating systems, and specialized utility programs like memory testers) directly addresses physical memory using machine code instructions or processor registers. These instructions tell the CPU to interact with a hardware component called the memory c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random-access Memory
Random-access memory (RAM; ) is a form of Computer memory, electronic computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working Data (computing), data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read (computer), read or written in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory, in contrast with other direct-access data storage media (such as hard disks and Magnetic tape data storage, magnetic tape), where the time required to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their physical locations on the recording medium, due to mechanical limitations such as media rotation speeds and arm movement. In today's technology, random-access memory takes the form of integrated circuit (IC) chips with MOSFET, MOS (metal–oxide–semiconductor) Memory cell (computing), memory cells. RAM is normally associated with Volatile memory, volatile types of memory where s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Screen Tearing
Screen tearing is a visual artifact in video display where a display device shows information from multiple frames in a single screen draw. The artifact occurs when the video feed to the device is not synchronized with the display's refresh rate. That can be caused by non-matching refresh rates, and the tear line then moves as the phase difference changes (with speed proportional to the difference of frame rates). It can also occur simply from a lack of synchronization between two equal frame rates, and the tear line is then at a fixed location that corresponds to the phase difference. During video motion, screen tearing creates a torn look as the edges of objects (such as a wall or a tree) fail to line up. Tearing can occur with most common display technologies and video cards and is most noticeable in horizontally-moving visuals, such as in slow camera pans in a movie or classic side-scrolling video games. Screen tearing is less noticeable when more than two frames finish r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Television
Analog television is the original television technology that uses analog signals to transmit video and audio. In an analog television broadcast, the brightness, colors and sound are represented by amplitude, instantaneous phase and frequency, phase and frequency of an analog signal. Analog signals vary over a continuous range of possible values which means that electronic noise and interference may be introduced. Thus with analog, a moderately weak signal becomes Noise (video), snowy and subject to interference. In contrast, picture quality from a digital television (DTV) signal remains good until the signal level drops below digital cliff, a threshold where reception is no longer possible or becomes intermittent. Analog television may be wireless (terrestrial television and satellite television) or can be distributed over a cable network as cable television. All broadcast television systems used analog signals before the arrival of DTV. Motivated by the lower bandwidth requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zilog Z80
The Zilog Z80 is an 8-bit computing, 8-bit microprocessor designed by Zilog that played an important role in the evolution of early personal computing. Launched in 1976, it was designed to be Backward compatibility, software-compatible with the Intel 8080, offering a compelling alternative due to its better Integrated circuit, integration and increased performance. Along with the 8080's seven Processor register, registers and flags register, the Z80 introduced an alternate register set, two 16-bit index registers, and additional instructions, including bit manipulation and block copy/search. Originally intended for use in embedded systems like the 8080, the Z80's combination of compatibility, affordability, and superior performance led to widespread adoption in video game systems and home computers throughout the late 1970s and early 1980s, helping to fuel the personal computing revolution. The Z80 was used in iconic products such as the Osborne 1, TRS-80, Radio Shack TRS-80, Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interrupt
In digital computers, an interrupt (sometimes referred to as a trap) is a request for the processor to ''interrupt'' currently executing code (when permitted), so that the event can be processed in a timely manner. If the request is accepted, the processor will suspend its current activities, save its state, and execute a function called an '' interrupt handler'' (or an ''interrupt service routine'', ISR) to deal with the event. This interruption is often temporary, allowing the software to resume normal activities after the interrupt handler finishes, although the interrupt could instead indicate a fatal error. Interrupts are commonly used by hardware devices to indicate electronic or physical state changes that require time-sensitive attention. Interrupts are also commonly used to implement computer multitasking and system calls, especially in real-time computing. Systems that use interrupts in these ways are said to be interrupt-driven. History Hardware interrupts wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASIC
Basic or BASIC may refer to: Science and technology * BASIC, a computer programming language * Basic (chemistry), having the properties of a base * Basic access authentication, in HTTP Entertainment * Basic (film), ''Basic'' (film), a 2003 film * Basic, one of the Galactic Basic, languages in ''Star Wars'' Music * Basic (Glen Campbell album), ''Basic'' (Glen Campbell album), 1978 * Basic (Robert Quine and Fred Maher album), ''Basic'' (Robert Quine and Fred Maher album), 1984 * B.A.S.I.C. (Alpinestars album), ''B.A.S.I.C.'' (Alpinestars album), 2000 * Basic (Brown Eyed Girls album), ''Basic'' (Brown Eyed Girls album), 2015 * B.A.S.I.C. (The Basics album), ''B.A.S.I.C.'' (The Basics album), 2019 Places * Basic, Mississippi, a community in the US * BASIC countries, Brazil, South Africa, India and China in climate change negotiations Organizations * BASIC Bank Limited, government owned bank in Bangladesh * Basic Books, an American publisher Other uses * Basic (cigarette), a brand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Frame
In filmmaking, video production, animation, and related fields, a frame is one of the many '' still images'' which compose the complete ''moving picture''. The term is derived from the historical development of film stock, in which the sequentially recorded single images look like a framed picture when examined individually. The term may also be used more generally as a noun or verb to refer to the edges of the image as seen in a camera viewfinder or projected on a screen. Thus, the camera operator can be said to keep a car in frame by panning with it as it speeds past. Overview When the moving picture is displayed, each frame is flashed on a screen for a short time (nowadays typically , , or of a second) and then immediately replaced by the next one. Persistence of vision blends the frames together, producing the illusion of a moving image. The frame is also sometimes used as a unit of time, so that a momentary event might be said to last six frames, the actual duration of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
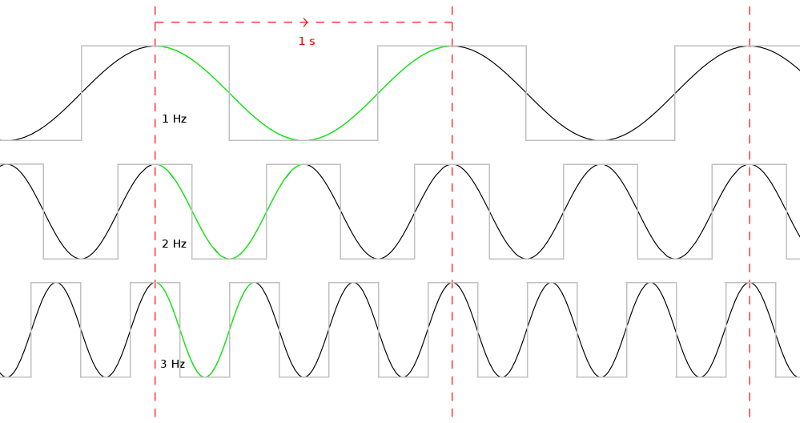
Clock Rate
Clock rate or clock speed in computing typically refers to the frequency at which the clock generator of a processor can generate pulses used to synchronize the operations of its components. It is used as an indicator of the processor's speed. Clock rate is measured in the SI unit of frequency hertz (Hz). The clock rate of the first generation of computers was measured in hertz or kilohertz (kHz), the first personal computers from the 1970s through the 1980s had clock rates measured in megahertz (MHz). In the 21st century the speed of modern CPUs is commonly advertised in gigahertz (GHz). This metric is most useful when comparing processors within the same family, holding constant other features that may affect performance. Determining factors Binning Manufacturers of modern processors typically charge higher prices for processors that operate at higher clock rates, a practice called binning. For a given CPU, the clock rates are determined at the end of the manufact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |