|
Yotsugana
are a set of four specific kana, じ, ぢ, ず, づ (in the Nihon-shiki romanization system: ''zi'', ''di'', ''zu'', ''du''), used in the Japanese writing system. They historically represented four distinct voiced morae (syllables) in the Japanese language. However, most dialects, such as Standard Japanese-speakers, have undergone mergers and now pronounce two sounds. Modern sound usage in various dialects Most of the far northern dialects ( Tōhoku dialects and Hokkaidō) and far southern dialects (notably Okinawan Japanese) and the Ryukyuan languages (the other Japonic languages) have also mostly merged the four sounds to one sound. However, a few dialects, mainly around Shikoku and Kyushu is the third-largest island of Japan's Japanese archipelago, four main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands (i.e. excluding Okinawa Island, Okinawa and the other Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Ryukyu Islands, Islands ... in the southwest, still dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kagoshima Dialect
The , often referred to as the , is a group of dialects or dialect continuum of the Japanese language spoken mainly within the area of the former Ōsumi and Satsuma provinces now incorporated into the southwestern prefecture of Kagoshima. It may also be collectively referred to as the Satsuma dialect ( or ), owing to both the prominence of the Satsuma Province and the region of the Satsuma Domain which spanned the former Japanese provinces of Satsuma, Ōsumi and the southwestern part of Hyūga. The Satsugū dialect is commonly cited for its mutual unintelligibility to even its neighboring Kyūshū variants, prompting the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology to classify it as a distinct language in the Japanesic branch in its Glottolog database. It shares over three-quarters of the Standard Japanese vocabulary corpus and some areal features of Kyūshū. Distribution and subdialects The boundaries of the Satsugū dialect are traditionally defined as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tōhoku Dialect
The , commonly called 東北弁 ''Tōhoku-ben'', is a group of the Japanese dialects spoken in the Tōhoku region, the northeastern region of Honshū. Toward the northern part of Honshū, the Tōhoku dialect can differ so dramatically from standard Japanese that it is sometimes rendered with subtitles in the nationwide media and it has been treated as the typical rural accent in Japanese popular culture. Phonetics A notable linguistic feature of the Tōhoku dialect is its neutralization of the high vowels "i" and "u" (Standard and ) after coronal obstruents, so that the words ''sushi'', ''susu'' ('soot'), and ''shishi'' ('lion') are rendered homophonous, where they would have been distinct in other dialects. In light of this, Tōhoku dialect is sometimes referred to as ''Zūzū-ben''. The vowels tend to be neutralized to in Northern Tōhoku dialect and in Southern Tōhoku dialect. In addition, all unvoiced stops become voiced intervocalically, rendering the pronunciation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yotsugana
are a set of four specific kana, じ, ぢ, ず, づ (in the Nihon-shiki romanization system: ''zi'', ''di'', ''zu'', ''du''), used in the Japanese writing system. They historically represented four distinct voiced morae (syllables) in the Japanese language. However, most dialects, such as Standard Japanese-speakers, have undergone mergers and now pronounce two sounds. Modern sound usage in various dialects Most of the far northern dialects ( Tōhoku dialects and Hokkaidō) and far southern dialects (notably Okinawan Japanese) and the Ryukyuan languages (the other Japonic languages) have also mostly merged the four sounds to one sound. However, a few dialects, mainly around Shikoku and Kyushu is the third-largest island of Japan's Japanese archipelago, four main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands (i.e. excluding Okinawa Island, Okinawa and the other Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Ryukyu Islands, Islands ... in the southwest, still dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gendai Kanazukai
is the present official '' kanazukai'' (system of spelling the Japanese syllabary). Also known as , it is derived from historical usage. History As long ago as the Meiji Restoration, there had been dissatisfaction regarding the growing discrepancy between spelling and speech. On November 16, 1946, soon after World War II, the cabinet instituted the modern Japanese orthography as part of a general orthographic reform. The system was further amended in 1986. General differences There were no small kana in the pre-reform system; thus, for example, would be ambiguous between ''kiyo'' and ''kyo'' while could be either ''katsuta'' or ''katta''. The pronunciation of medial ''h''-row kana as ''w''-row kana in the pre-reform system does not extend to compound words; thus, was pronounced ''nihon'', not ''nion'' (via **''niwon''). There are a small number of counterexamples; e.g., "duck", pronounced ''ahiru'' rather than ''airu'', or , pronounced Fujiwara, despite being a compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Phonology
Japanese phonology is the system of sounds used in the pronunciation of the Japanese language. Unless otherwise noted, this article describes the standard variety of Japanese based on the Tokyo dialect. There is no overall consensus on the number of contrastive sounds (phonemes), but common approaches recognize at least 12 distinct consonants (as many as 21 in some analyses) and 5 distinct vowels, . Phonetic length is contrastive for both vowels and consonants, and the total length of Japanese words can be measured in a unit of timing called the mora (from Latin "delay"). Only limited types of consonant clusters are permitted. There is a pitch accent system where the position or absence of a pitch drop may determine the meaning of a word: (), (), (). Japanese phonology has been affected by the presence of several layers of vocabulary in the language: in addition to native Japanese vocabulary, Japanese has a large amount of Chinese-based vocabulary (used especially to fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tosa Dialect
The Tosa dialect (Japanese: 土佐弁 ''tosa-ben'') is a Japanese Shikoku dialect spoken in central and eastern Kochi Prefecture (former Tosa Province), including Kochi City. The dialect of the Western region of Kochi Prefecture is called the Hata dialect (Japanese: 幡多弁 ''hata-ben'') and is drastically different from the Central and Eastern dialect. Classification Shikoku dialects are divided into Western (Tokushima, Kagawa and Ehime), Southern (Kochi), and also occasionally Southwest (western Kochi and southern Ehime). The Tosa dialect exists in a somewhat unique position due to being historically isolated from other prefectures because of the Shikoku Mountains. Kochi Prefecture dialects are broadly divided into Western and Eastern-Central. * Western dialect - Shimanto (city), Tosashimizu, Sukumo, Otsuki, Mihara, Kuroshio (excluding the former town of Saga), Shimanto (town) (excluding the former town of Kubokawa), Yusuhara. Possesses a Tokyo standard pitch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kansai Dialect
The is a group of Japanese dialects in the Kansai region (Kinki region) of Japan. In Japanese, is the common name and it is called in technical terms. The dialects of Kyoto and Osaka are known as , and were particularly referred to as such in the Edo period. The Kansai dialect is typified by the speech of Osaka, the major city of Kansai, which is referred to specifically as . It is characterized as being both more melodic and harsher by speakers of the standard language.Omusubi: Japan's Regional Diversity , retrieved January 23, 2007 Background Since Osaka is the largest city in the region and its speakers received the most media exposure over the last century, non-Kansai-dialect speakers tend to associate the dialect of Osaka with the entire Kansai region. However, technic ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rendaku
is a pronunciation change seen in some compound words in Japanese. When rendaku occurs, a voiceless consonant (such as ) is replaced with a voiced consonant (such as ) at the start of the second (or later) part of the compound. For example, the morpheme starts with the voiceless consonant when used as an independent word or as the first part of a compound word, but this is replaced with the corresponding voiced consonant in the compound word , from + . Although rendaku is common, it does not occur in all compound words. A rule known as Lyman's law blocks rendaku when the second element already contains a voiced obstruent phoneme (, , , or ). For instance, in , the in remains voiceless because contains . Rendaku is also blocked almost always when the second element of a compound is a recent loan into Japanese. Furthermore, rendaku may fail to occur even in contexts where no definite blocking factor is present. In the Japanese writing system, rendaku affects how a morp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kana
are syllabary, syllabaries used to write Japanese phonology, Japanese phonological units, Mora (linguistics), morae. In current usage, ''kana'' most commonly refers to ''hiragana'' and ''katakana''. It can also refer to their ancestor , which were Kanji, Chinese characters used phonetically to transcribe Japanese language, Japanese (e.g. ''man'yōgana''); and ''hentaigana'', which are historical variants of the now-standard hiragana. Katakana, with a few additions, are also used to write Ainu language, Ainu. A Okinawan scripts, number of systems exist to write the Ryūkyūan languages, in particular Okinawan language, Okinawan, in hiragana. Taiwanese kana were used in Taiwanese Hokkien as ruby text for Chinese characters in Taiwan when it was Taiwan under Japanese rule, under Japanese rule. Each syllabogram, kana character corresponds to one phoneme or syllable, unlike kanji, which generally each logogram, corresponds to a morpheme. Apart from the five vowels, it is always ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
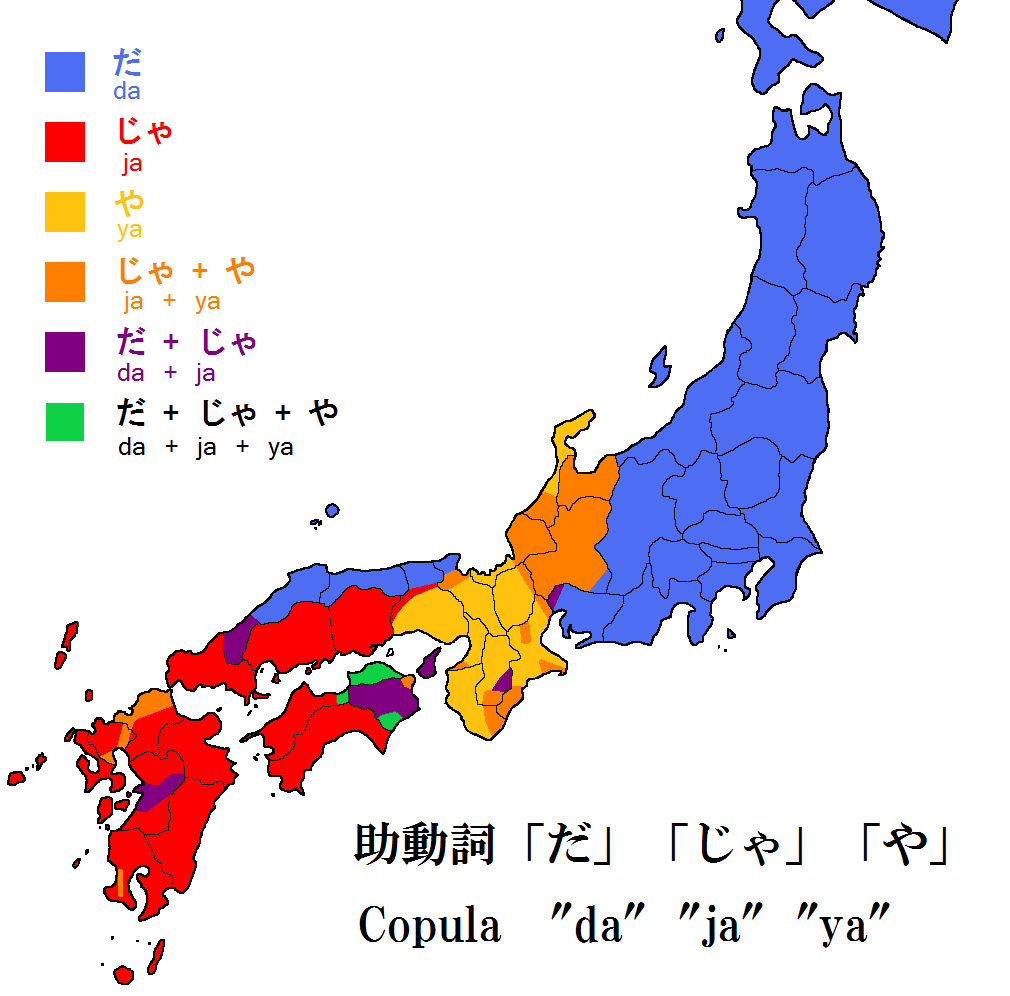
Japanese Dialects
The of the Japanese language fall into two primary clades, Eastern (including modern capital Tokyo) and Western (including old capital Kyoto), with the dialects of Kyushu and Hachijō Island often distinguished as additional branches, the latter perhaps the most divergent of all. The Ryukyuan languages of Okinawa Prefecture and the southern islands of Kagoshima Prefecture form a separate branch of the Japonic family, and are not Japanese dialects, although they are sometimes referred to as such. The setting of Japan with its numerous islands and mountains has the ideal setting for developing many dialects. History Regional variants of Japanese have been confirmed since the Old Japanese era. The '' Man'yōshū'', the oldest existing collection of Japanese poetry, includes poems written in dialects of the capital (Nara) and eastern Japan, but other dialects were not recorded. The compiler included ''azuma uta'' ("eastern songs") that show that eastern dialect traits were dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hata Dialect
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Hata may refer to: Places * Hata, Nagano, a former town in Nagano Prefecture, Japan *Hata District, Kōchi, a district in Kōchi Prefecture, Japan * Hata, India, a town and municipal council in Uttar Pradesh, India * Hata (Assembly constituency), a constituency of the Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly *Hata, a former village that is now the site of Ahta Indian Reserve No. 3 *Hata, Purvi Singhbhum, a village in Jharkhand, India Other uses * Hata (surname), a Japanese surname *Hata clan, a former immigrant clan to Japan See also * Hata Station (other), multiple railway stations in Japan *Hatamoto A was a high ranking samurai in the direct service of the Tokugawa shogunate of feudal Japan. While all three of the Shōgun, shogunates in History of Japan, Japanese history had official retainers, in the two preceding ones, they were referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kōchi Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Shikoku. Kōchi Prefecture has a population of 669,516 (1 April 2023) and has a geographic area of 7,103 km2 (2,742 sq mi). Kōchi Prefecture borders Ehime Prefecture to the northwest and Tokushima Prefecture to the northeast. Kōchi is the capital and largest city of Kōchi Prefecture, with other major cities including Nankoku, Shimanto, and Kōnan. Kōchi Prefecture is located on Japan's Pacific coast surrounding a large bay in the south of Shikoku, with the southernmost point of the island located at Cape Ashizuri in Tosashimizu. Kōchi Prefecture is home to Kōchi Castle, considered the most intact Japanese castle, and the Shimanto River, one of the few undammed rivers in Japan. History Antiquity Before the Ritsuryō System In the Kujiki, first recorded governments in Kōchi Prefecture were Hata (in the west) and Tosa (in the center). Hata was established first, so it is thought that it had more influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |