|
YedZ Family
YedZTC# 5.B.7 of ''E. coli'' has been examined topologically and has 6 transmembrane segments (TMSs) with both the N- and C-termini localized to the cytoplasm. von Rozycki ''et al.'' 2004 identified homologues of YedZ in bacteria and animals. YedZ homologues exhibit conserved histidyl residues in their transmembrane domains that may function in heme binding. Some of the homologues encoded in the genomes of various bacteria have YedZ domains fused to transport, electron transfer and biogenesis proteins. One of the animal homologues is the 6 TMS epithelial plasma membrane antigen of the prostate (STAMP1) that is over-expressed in prostate cancer. Some animal homologues have YedZ domains fused C-terminal to homologues of NADP oxidoreductases. YedZ homologues arose by intragenic triplication of a 2 TMS-encoding element. They exhibit statistically significant sequence similarity to two families of putative heme export systems and one family of cytochrome-containing electron carriers and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut, where they constitute about 0.1%, along with other facultative anaerobes. These bacteria are mostly harmless or even beneficial to humans. For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by harmful pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. coli'' and humans are a type of mutualistic biological relationship—where both the humans and the ''E. coli'' are benefitting each other. ''E. coli'' is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, abbreviated NADP or, in older notation, TPN (triphosphopyridine nucleotide), is a Cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor used in anabolic reactions, such as the Calvin cycle and lipid and nucleic acid syntheses, which require NADPH as a reducing agent ('hydrogen source'). NADPH is the redox, reduced form, whereas NADP is the redox, oxidized form. NADP is used by all forms of cellular life. NADP is essential for life because it is needed for cellular respiration. NADP differs from NAD+, NAD by the presence of an additional phosphate group on the 2' position of the ribose ring that carries the adenine Moiety (chemistry), moiety. This extra phosphate is added by NAD+ kinase, NAD+ kinase and removed by NADP+ phosphatase. Biosynthesis NADP In general, NADP+ is synthesized before NADPH is. Such a reaction usually starts with NAD+, NAD+ from either the de-novo or the salvage pathway, with NAD+ kinase, NAD+ kinase adding the extra phosphate g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidoreductase
In biochemistry, an oxidoreductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of electrons from one molecule, the reductant, also called the electron donor, to another, the oxidant, also called the electron acceptor. This group of enzymes usually utilizes NADP+ or NAD+ as cofactors. Transmembrane oxidoreductases create electron transport chains in bacteria, chloroplasts and mitochondria, including respiratory complexes I, II and III. Some others can associate with biological membranes as peripheral membrane proteins or be anchored to the membranes through a single transmembrane helix. in Membranome database Reactions For e ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetotactic Bacteria
Magnetotactic bacteria (or MTB) are a polyphyletic group of bacteria that orient themselves along the magnetic field lines of Earth's magnetic field. Discovered in 1963 by Salvatore Bellini and rediscovered in 1975 by Richard Blakemore, this alignment is believed to aid these organisms in reaching regions of optimal oxygen concentration. To perform this task, these bacteria have organelles called magnetosomes that contain magnetic crystals. The biological phenomenon of microorganisms tending to move in response to the environment's magnetic characteristics is known as magnetotaxis. However, this term is misleading in that every other application of the term taxis involves a stimulus-response mechanism. In contrast to the magnetoreception of animals, the bacteria contain fixed magnets that force the bacteria into alignment—even dead cells are dragged into alignment, just like a compass needle. Introduction The first description of magnetotactic bacteria was in 1963 by Salv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteria's informal common name, blue-green algae. Cyanobacteria are probably the most numerous taxon to have ever existed on Earth and the first organisms known to have produced oxygen, having appeared in the middle Archean eon and apparently originated in a freshwater or terrestrial environment. Their photopigments can absorb the red- and blue-spectrum frequencies of sunlight (thus reflecting a greenish color) to split water molecules into hydrogen ions and oxygen. The hydrogen ions are used to react with carbon dioxide to produce complex organic compounds such as carbohydrates (a process known as carbon fixation), and the oxygen is released as a byproduct. By continuously producing and releasing oxygen over billions of years, cyanobacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetosome
Magnetosomes are membranous structures present in magnetotactic bacteria (MTB). They contain iron-rich magnetic particles that are enclosed within a lipid bilayer membrane. Each magnetosome can often contain 15 to 20 magnetite crystals that form a chain which acts like a compass needle to orient magnetotactic bacteria in geomagnetic fields, thereby simplifying their search for their preferred microaerophilic environments. Recent research has shown that magnetosomes are invaginations of the inner membrane and not freestanding vesicles. Magnetite-bearing magnetosomes have also been found in eukaryotic magnetotactic algae, with each cell containing several thousand crystals. Overall, magnetosome crystals have high chemical purity, narrow size ranges, species-specific crystal morphologies and exhibit specific arrangements within the cell. These features indicate that the formation of magnetosomes is under precise biological control and is mediated biomineralization. Magnetotactic b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Families
A protein family is a group of evolutionarily related proteins. In many cases, a protein family has a corresponding gene family, in which each gene encodes a corresponding protein with a 1:1 relationship. The term "protein family" should not be confused with family as it is used in taxonomy. Proteins in a family descend from a common ancestor and typically have similar three-dimensional structures, functions, and significant sequence similarity. Sequence similarity (usually amino-acid sequence) is one of the most common indicators of homology, or common evolutionary ancestry. Some frameworks for evaluating the significance of similarity between sequences use sequence alignment methods. Proteins that do not share a common ancestor are unlikely to show statistically significant sequence similarity, making sequence alignment a powerful tool for identifying the members of protein families. Families are sometimes grouped together into larger clades called superfamilies based on stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Proteins
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane (Transmembrane protein, transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane (Integral monotopic protein, integral monotopic). Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane. Membrane proteins are common, and medically important—about a third of all human proteins are membrane proteins, and these are targets for more than half of all drugs. Nonetheless, compared to other classes of proteins, determining membrane protein structures remains a challenge in large part due to the difficulty in establishing experimental conditions that can preserve the correct (Native state, native) Protein structure, conformation of the protein in isolation from its native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
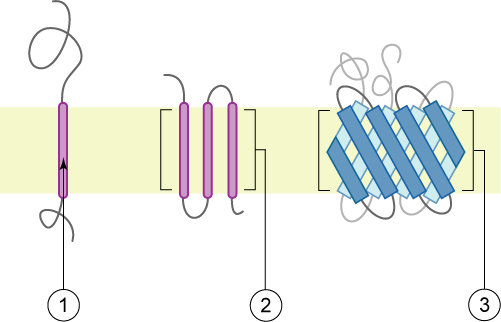
Transmembrane Proteins
A transmembrane protein is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them ( beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents. The peptide sequence that spans the membrane, or the transmembrane segment, is largely hydrophobic and can be visualized using the hydropathy plot. Depending on the number of transmembrane segments, transmembrane proteins can be classified as single-pass membrane proteins, or as multipass membrane proteins. Some other integral membrane proteins are called monotopic, meaning that they are also permanently attached to the membrane, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmembrane Transporters
A transmembrane protein is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them (beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents. The peptide sequence that spans the membrane, or the transmembrane segment, is largely hydrophobic and can be visualized using the hydropathy plot. Depending on the number of transmembrane segments, transmembrane proteins can be classified as single-pass membrane proteins, or as multipass membrane proteins. Some other integral membrane proteins are called monotopic, meaning that they are also permanently attached to the membrane, but do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport Proteins
A transport protein (variously referred to as a transmembrane pump, transporter, escort protein, acid transport protein, cation transport protein, or anion transport protein) is a protein that serves the function of moving other materials within an organism. Transport proteins are vital to the growth and life of all living things. There are several different kinds of transport proteins. Carrier proteins are proteins involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, or macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane. Carrier proteins are integral membrane proteins; that is, they exist within and span the membrane across which they transport substances. The proteins may assist in the movement of substances by facilitated diffusion (i.e., passive transport) or active transport. These mechanisms of movement are known as carrier-mediated transport. Each carrier protein is designed to recognize only one substance or one group of very similar substances. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |