|
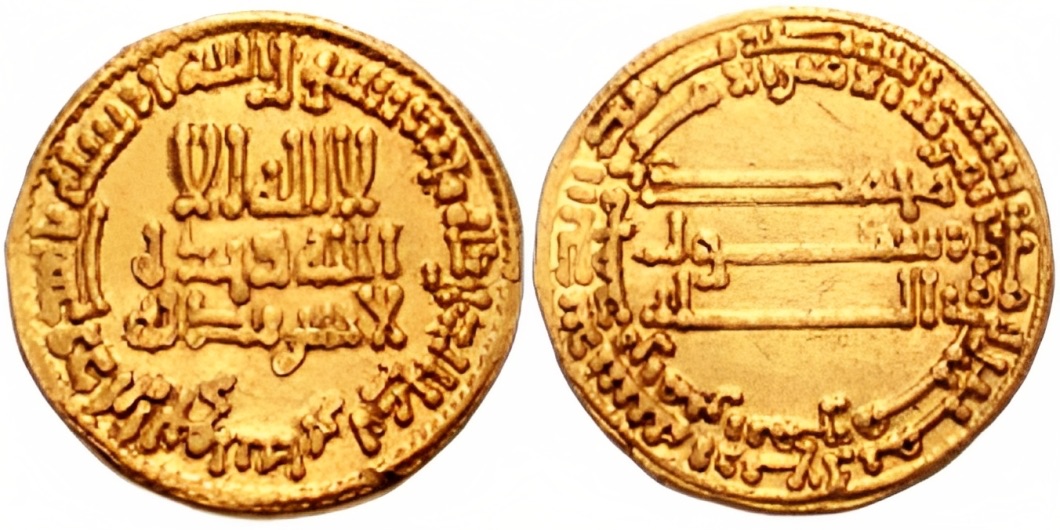
Yazid Ibn Jarir Al-Qasri
Yazid ibn Jarir ibn Yazid ibn Khalid ibn Abdallah al-Qasri ( ar, يزيد بن جرير بن يزيد بن خالد بن عبد الله القسري) was a provincial governor for the Abbasid Caliphate, serving as governor of the Yemen from 812 to 813. Career Yazid was a descendant of Khalid ibn Abdallah al-Qasri (died 743), the powerful governor of Iraq on behalf of the Umayyads. He is possibly to be identified with a Yazid ibn Jarir who twice served as governor of Sistan during the caliphate of Harun al-Rashid (r. 786–809), first as deputy to al-Fadl ibn Yahya in 794 and then under Ali ibn Isa ibn Mahan in 797. During the civil war between the rival caliphs al-Amin (r. 809–813) and al-Ma'mun (r. 813–833), Yazid was appointed governor of the Yemen by al-Ma'mun's general Tahir ibn al-Husayn, with a directive to bring the province under al-Ma'mun's control. He accordingly set off for the Yemen with a large body of horsemen, and upon his arrival he convinced the Yemeni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Ibn Sa'id Al-Kinani
Muhammad ibn Sa'id ibn al-Sarh al-Kinani ( ar, محمد بن سعيد بن السرح الكناني), alternatively given as Sa'id ibn Sarh, was a ninth century governor of the Yemen for the Abbasid Caliphate. A member of the ''ahl Filastin'' ("people of Palestine __NOTOC__ Palestine may refer to: * State of Palestine, a state in Western Asia * Palestine (region), a geographic region in Western Asia * Palestinian territories, territories occupied by Israel since 1967, namely the West Bank (including East ..."), Ibn al-Sarh was appointed to the Yemen during the caliphate of al-Amin (r. 809–813). Although little is known of his administration, by the time he left office he had accumulated a large amount of wealth, which he took with him when he departed from the province during the Fourth Fitna. He then returned to Palestine, and is subsequently mentioned as seizing control of al-Ramlah during the chaos of the Fitna.; ; . Notes References * * * * * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Fitna
The Fourth Fitna or Great Abbasid Civil War resulted from the conflict between the brothers al-Amin and al-Ma'mun over the succession to the throne of the Abbasid Caliphate. Their father, Caliph Harun al-Rashid, had named al-Amin as the first successor, but had also named al-Ma'mun as the second, with Khurasan granted to him as an appanage. Later a third son, al-Qasim, had been designated as third successor. After Harun died in 809, al-Amin succeeded him in Baghdad. Encouraged by the Baghdad court, al-Amin began trying to subvert the autonomous status of Khurasan, and al-Qasim was quickly sidelined. In response, al-Ma'mun sought the support of the provincial élites of Khurasan and made moves to assert his own autonomy. As the rift between the two brothers and their respective camps widened, al-Amin declared his own son Musa as his heir and assembled a large army. In 811, al-Amin's troops marched against Khurasan, but al-Ma'mun's general Tahir ibn Husayn defeated them in the Battl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th-century Arabs
The 9th century was a period from 801 ( DCCCI) through 900 ( CM) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Carolingian Renaissance and the Viking raids occurred within this period. In the Middle East, the House of Wisdom was founded in Abbasid Baghdad, attracting many scholars to the city. The field of algebra was founded by the Muslim polymath al-Khwarizmi. The most famous Islamic Scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal was tortured and imprisoned by Abbasid official Ahmad ibn Abi Du'ad during the reign of Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim and caliph al-Wathiq. In Southeast Asia, the height of the Mataram Kingdom happened in this century, while Burma would see the establishment of the major kingdom of Pagan. Tang China started the century with the effective rule under Emperor Xianzong and ended the century with the Huang Chao rebellions. While the Maya experienced widespread political collapse in the central Maya region, resulting in internecine warfare, the abandonment of cities, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid Governors Of Yemen
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. They ruled as caliphs for most of the caliphate from their capital in Baghdad in modern-day Iraq, after having overthrown the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 AH). The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph Al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad, near the ancient Babylonian capital city of Babylon. Baghdad became the center of science, culture and invention in what became known as the Golden Age of Islam. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. They ruled as caliphs for most of the caliphate from their capital in Baghdad in modern-day Iraq, after having overthrown the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 AH). The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph Al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad, near the ancient Babylonian capital city of Babylon. Baghdad became the center of science, culture and invention in what became known as the Golden Age of Islam. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sana'a
Sanaa ( ar, صَنْعَاء, ' , Yemeni Arabic: ; Old South Arabian: 𐩮𐩬𐩲𐩥 ''Ṣnʿw''), also spelled Sana'a or Sana, is the capital and largest city in Yemen and the centre of Sanaa Governorate. The city is not part of the Governorate, but forms the separate administrative district of "ʾAmānat al-ʿĀṣima" (). Under the Yemeni constitution, Sanaa is the capital of the country, although the seat of the Yemeni government moved to Aden, the former capital of South Yemen in the aftermath of the Houthi occupation. Aden was declared as the temporary capital by President Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi in March 2015. At an elevation of , Sanaa is one of the highest capital cities in the world and is next to the Sarawat Mountains of Jabal An-Nabi Shu'ayb and Jabal Tiyal, considered to be the highest mountains in the country and amongst the highest in the region. Sanaa has a population of approximately 3,937,500 (2012), making it Yemen's largest city. As of 2020, the gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abna Al-dawla
The ''abnāʾ al-dawla'' ( ar, أبناء الدولة, meaning "sons of the regime/dynasty"), often simply " the ''Abnāʾ''", is a term for the Khorasani Arabs who had participated in the Abbasid Revolution of 749–750 and their descendants, who settled in Baghdad and Iraq. They became the ruling elite of the Abbasid Caliphate and formed the mainstay of the caliphal army. However, the term appears rarely in the sources until the time of the Fourth Fitna civil war in the 810s, when it is applied to the Khurasanis of Baghdad, who overwhelmingly supported Caliph al-Amin against his brother al-Ma'mun. The terms ''ahl Khurāsān'' ("people of Khurasan") and ''abnāʾ ahl Khurāsān'' ("sons of the people of Khurasan") are more frequently used for the Khurasanis who formed the mainstay of the Abbasid regime in general. Following al-Ma'mun's victory in the civil war, the ''abnāʾ al-dawla'' were largely replaced by the latter's Persian followers, and under his successor al-Mu'tasim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
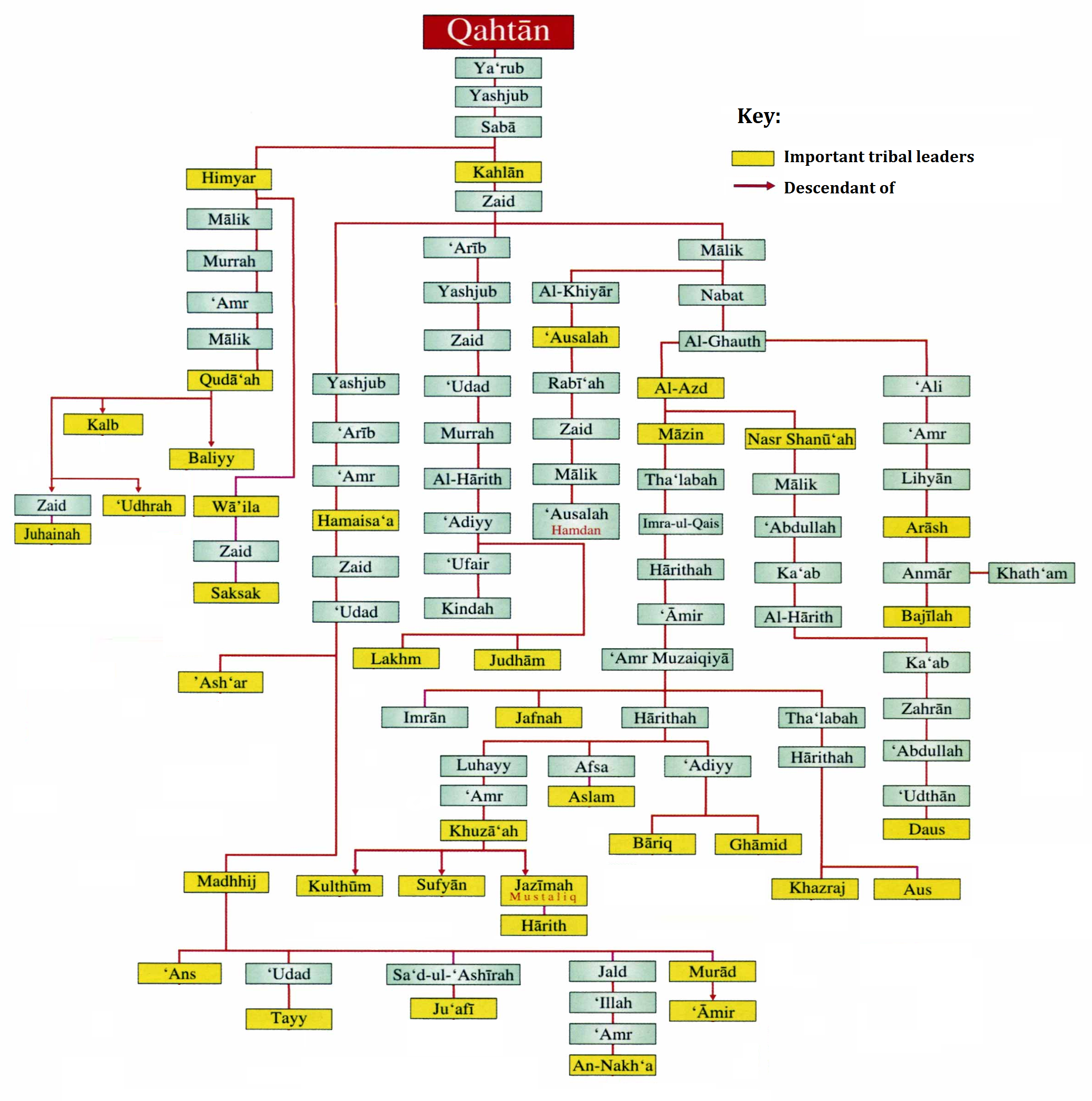
Qahtanite
The terms Qahtanite and Qahtani ( ar, قَحْطَانِي; transliterated: Qaḥṭānī) refer to Arabs who originate from South Arabia. The term "Qahtan" is mentioned in multiple ancient Arabian inscriptions found in Yemen. Arab traditions believe that they are the original Arabs. Traditional Arab genealogy According to Arab tradition, the Qahtanites are from South Arabia, unlike the Adnanites who are from the north of Arabia descended from Ishmael through Adnan. "The 'arabized or arabizing Arabs', on the contrary, are believed to be the descendants of Ishmael through Adnan, but in this case the genealogy does not match the Biblical line exactly. The label 'arabized' is due to the belief that Ishmael spoke Hebrew until he got to Mecca, where he married a Yemeni woman and learnt Arabic. Both genealogical lines go back to Sem, son of Noah, but only Adnanites can claim Abraham as their ascendant, and the lineage of Mohammed, the Seal of Prophets (khatim al-anbiya'), can the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tahir Ibn Al-Husayn
Ṭāhir ibn Ḥusayn ( fa, طاهر ابن حسین, ''Tāher ebn-e Hoseyn''; ar, طاهر بن الحسين, ''Tahir bin al-Husayn''), also known as Dhul-Yamīnayn ( ar, ذو اليمينين, "the ambidextrous"), and al-Aʿwar ( ar, الأعور, "the one-eyed"), was a Persian general and governor during the Abbasid Caliphate. Specifically, he served under al-Ma'mun during the Fourth Fitna and led the armies that would defeat al-Amin, making al-Ma'mun the ''caliph''. He was then rewarded as governor of Khorasan, which marked the beginning of the Tahirids. Early life Tahir was born in Pushang which was a village near the ancient city of Herat in Khorasan. He was from a ''dehqan'' noble family who had distinguished themselves since the Abbasid Revolution, and were previously awarded minor governorships in eastern Khorasan for their service to the Abbasids. His grandfather Ruzaiq was a ''mawla'' of Talha ibn Abd Allah al-Khuza'i, an Arab nobleman from the Khuza'a tribe, who s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Ma'mun
Abu al-Abbas Abdallah ibn Harun al-Rashid ( ar, أبو العباس عبد الله بن هارون الرشيد, Abū al-ʿAbbās ʿAbd Allāh ibn Hārūn ar-Rashīd; 14 September 786 – 9 August 833), better known by his regnal name Al-Ma'mun ( ar, المأمون, al-Maʾmūn), was the seventh Abbasid caliph, who reigned from 813 until his death in 833. He succeeded his half-brother al-Amin after a civil war, during which the cohesion of the Abbasid Caliphate was weakened by rebellions and the rise of local strongmen; much of his domestic reign was consumed in pacification campaigns. Well educated and with a considerable interest in scholarship, al-Ma'mun promoted the Translation Movement, the flowering of learning and the sciences in Baghdad, and the publishing of al-Khwarizmi's book now known as "Algebra". He is also known for supporting the doctrine of Mu'tazilism and for imprisoning Imam Ahmad ibn Hanbal, the rise of religious persecution ('' mihna''), and for the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Amin
Abu Musa Muhammad ibn Harun al-Rashid ( ar, أبو موسى محمد بن هارون الرشيد, Abū Mūsā Muḥammad ibn Hārūn al-Rashīd; April 787 – 24/25 September 813), better known by his laqab of Al-Amin ( ar, الأمين, al-Amīn), was the sixth Arab Abbasid caliph from 809 to 813. Al-Amin succeeded his father, Harun al-Rashid, in 809 and ruled until he was deposed and killed in 813, during the civil war by his half-brother, al-Ma'mun. Early life and the issue of succession Muhammad, the future al-Amin, was born in April 787 to the Abbasid caliph Harun al-Rashid () and Zubayda, herself descended from the second Abbasid caliph, al-Mansur (). Muhammad had an elder half-brother, Abdallah, the future al-Ma'mun (), who had been born in September 786. However, Abdallah's mother was a Persian slave concubine, and his pure Abbasid lineage gave Muhammad seniority over his half-brother. Indeed, he was the only Abbasid caliph to claim such descent. Already in 792, Har ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Ibn Isa Ibn Mahan
Ali ibn Isa ibn Mahan ( ar, علي بن عيسى بن ماهان, ʿAlī ibn ʿĪsā ibn Māhān; ) was a prominent Iranian military leader of the Abbasid Caliphate in the late 8th and early 9th centuries. Origin and early career Ali's father, Isa ibn Mahan, was an early follower and ''da'i'' of the Abbasids; he mutinied after the Abbasid Revolution and was executed by Abu Muslim. Ali himself appears first in 779/80, under Caliph al-Mahdi (), as commander of the caliphal guard (''ḥaras''). He then served as commander of the guard of the heir-apparent al-Hadi (), and continued in the post after the latter's accession. Under al-Hadi, he also occupied the posts of secretary of the army department ('' diwan al-jund''), the powerful post of chamberlain (''hajib'') and director of the treasures. Governorship of Khurasan under Harun al-Rashid Under Harun al-Rashid () he continued to serve as commander of the guard until 796, when he was named governor of Khurasan, over the objections o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)