|
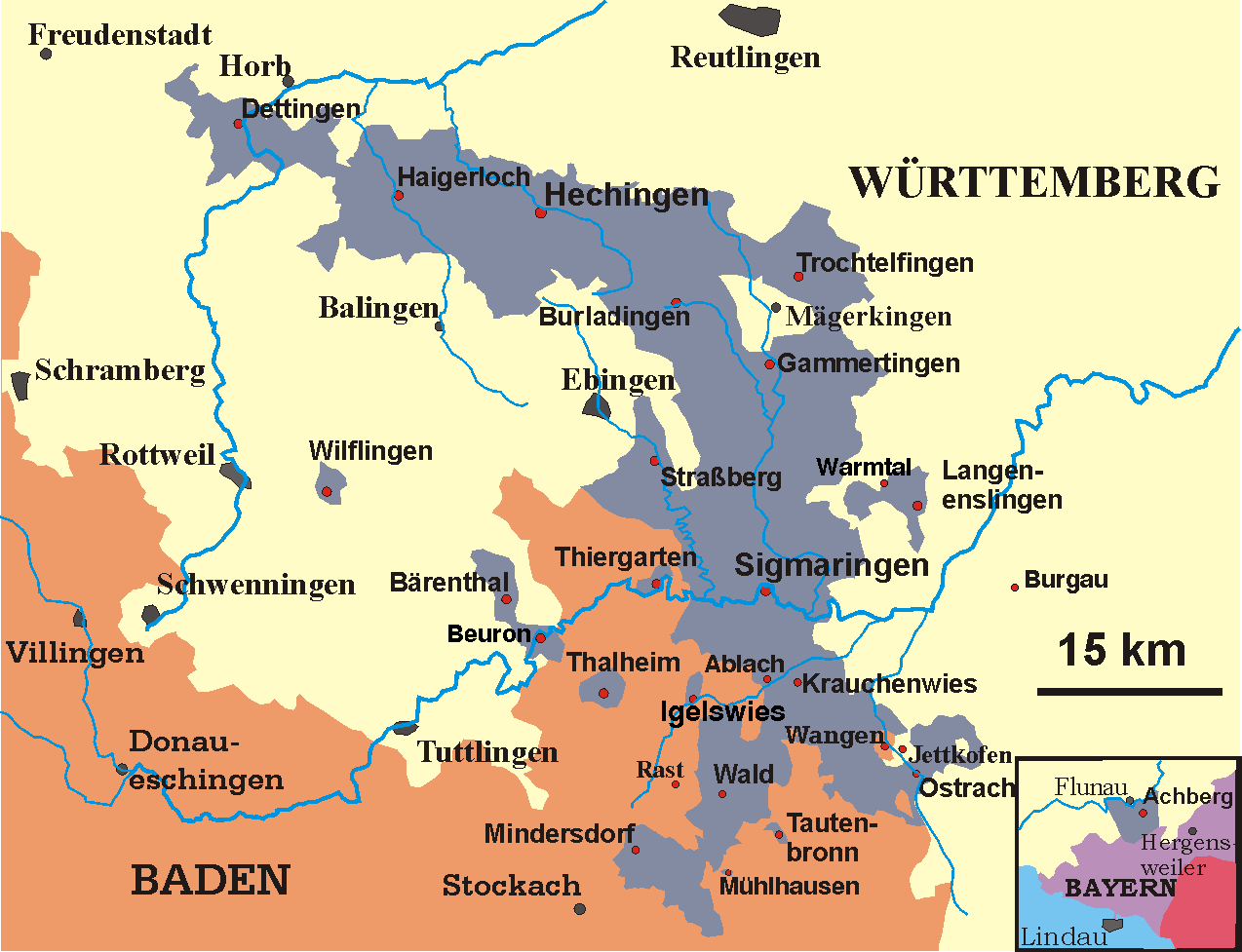
Württemberg-Hohenzollern
Württemberg-Hohenzollern was a West Germany, West German state created in 1945 as part of the French Allied Occupation Zones in Germany, post-World War II occupation zone. Its capital was Tübingen. In 1952, it was merged into the newly founded state of Baden-Württemberg. History Württemberg-Hohenzollern should not be confused with the larger ''Gau Württemberg-Hohenzollern, Gau'' ("shire") of the same name that was formed briefly during the Third Reich. Württemberg-Hohenzollern consisted of the southern half of the former state of Free People's State of Württemberg, Württemberg, the Prussian administrative region of Province of Hohenzollern, Hohenzollern and the Bavaria, Bavarian district of Lindau (district), Lindau. The northern half of Württemberg became part of the state of Württemberg-Baden under US-administration. The division between north and south was set so that the Autobahn connecting Karlsruhe and Munich (today the Bundesautobahn 8, A8) was completely contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Landtag Of Württemberg-Hohenzollern
The Landtag of Württemberg-Hohenzollern was the first freely elected Parliament of the state of Württemberg-Hohenzollern following the states formation after the Second World War inside of the French zone of occupation. The Landtag was the body succeeding the , the convention composed of municipal delegates that was tasked with drafting a constitution for the state. The first election to the Landtag was held simultaneously with the referendum over the adoption of the constitution drafted by the Advisory State Assembly on 18 May 1947. The Landtag first met on 3 June 1947 in Tübingen. It was elected for a term of four years; therefore the next state election should have been in early 1951. However, due to the planned unification of the three German states Württemberg-Hohenzollern, Baden and Württemberg-Baden, the President of Württemberg-Hohenzollern Gebhard Müller extended the term of the Landtag by decree until the three states unified. The constitutional amendment required ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gau Württemberg-Hohenzollern
The Gau Württemberg-Hohenzollern, formed on 8 July 1925, was an administrative division of Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945 in the German state of Württemberg and the Prussian province of Hohenzollern. Before that, from 1925 to 1933, it was the regional subdivision of the Nazi Party in that area. History The Nazi Gau (plural Gaue) system was originally established in a party conference on 22 May 1926, in order to improve administration of the party structure. From 1933 onward, after the Nazi seizure of power, the ''Gaue'' increasingly replaced the German states as administrative subdivisions in Germany. At the head of each Gau stood a Gauleiter, a position which became increasingly more powerful, especially after the outbreak of the Second World War, with little interference from above. Local Gauleiters often held government positions as well as party ones and were in charge of, among other things, propaganda and surveillance and, from September 1944 onward, the Volkssturm The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
German State
The Federal Republic of Germany is a federation and consists of sixteen partly sovereign ''states''. Of the sixteen states, thirteen are so-called area-states ('Flächenländer'); in these, below the level of the state government, there is a division into local authorities (counties and county-level cities) that have their own administration. Two states, Berlin and Hamburg, are city-states, in which there is no separation between state government and local administration. The state of Bremen is a special case: the state consists of the cities of Bremen, for which the state government also serves as the municipal administration, and Bremerhaven, which has its own local administration separate from the state government. It is therefore a mixture of a city-state and an area-state. Three states, Bavaria, Saxony, and Thuringia, use the appellation ("free state"); this title is merely stylistic and carries no legal or political significance (similar to the US states that call them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Carlo Schmid (German Politician)
Carlo Schmid (3 December 1896 – 11 December 1979) was a German academic and politician of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD). Schmid is one of the most important authors of both the Grundgesetz, German Basic Law and the Godesberg Program of the SPD. He was intimately involved in German-French relations and served as "Federal Minister for the Affairs of the Federal Council and States" from 1966 to 1969. Biography and profession Schmid was born in Perpignan, France, and lived there for five years before his family moved to Germany. In 1908, the family moved to Stuttgart, where Schmid attended the prestigious humanist , where he passed his Abitur in 1914. From 1914 to 1918, Schmid fought in the German army. After the war he studied law at the University of Tübingen after which he successfully sat the first (1921) and second (1924) Legal State Exam. In 1923, he completed a doctoral dissertation under the supervision of the renowned legal scholar Hugo Sinzheimer. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Province Of Hohenzollern
The Province of Hohenzollern (, ''Hohenzollern Lands'') was a district of Prussia from 1850 to 1946. It was located in Swabia, the region of southern Germany that was the ancestral home of the House of Hohenzollern, to which the kings of Prussia belonged. The Hohenzollern Lands were formed in 1850 from two principalities that had belonged to members of the Catholic branch of the Hohenzollern family. They were united to create a unique type of administrative district (''Regierungsbezirk'') that was not a true province – a was normally a part of a province – but that had almost all the rights of a Prussian province. The Hohenzollern Lands lost their separate identity in 1946 when they were made part of the state of Württemberg-Hohenzollern following World War II. History The Catholic ruling houses of Hohenzollern-Hechingen and Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen had hereditary treaties with Prussia that went back to 1695 and 1707 respectively. During the German Revolutions of 1848� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg ( ; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a states of Germany, German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million inhabitants across a total area of nearly , it is the third-largest German state by both List of German states by area, area (behind Bavaria and Lower Saxony) and List of German states by population, population (behind North Rhine-Westphalia and Bavaria). The List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, largest city in Baden-Württemberg is the state capital of Stuttgart, followed by Mannheim and Karlsruhe. Other major cities are Freiburg im Breisgau, Heidelberg, Heilbronn, Konstanz, Pforzheim, Reutlingen, Tübingen, and Ulm. Modern Baden-Württemberg includes the historical territories of Baden, Prussian Province of Hohenzollern, Hohenzollern, and Württemberg. Baden-Württemberg became a state of West Germany in April 1952 through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Free People's State Of Württemberg
The Free People's State of Württemberg () was a state which existed in the Weimar Republic and from 1933 in Nazi Germany. History Revolution in Württemberg With the German revolution near the end of World War I, the Kingdom of Württemberg was transformed from a monarchy to a democratic republic without bloodshed; its borders and internal administration remained unchanged. King William II of Württemberg abdicated on 30 November 1918. Following the introduction of a new constitution (significantly amended later in the year) by an assembly elected in January, and the Weimar Constitution in 1919, Württemberg was re-established as a member state of the German Reich.Article 1 of the Württemberg constitution (25 September 1919) states: "Württemberg is a democratic republic and member of the German Reich. Its state authority is exerted in accordance with both this constitution and German national law". Article 2 of the Weimar Constitution (11 August 1919) states: "The territ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lorenz Bock
Lorenz Bock (August 12, 1883, in Nordstetten – August 3, 1948, in Rottweil) was a German lawyer and politician. He was first with the Center Party, later with the Christian Democratic Union (CDU). Life and career Lorenz Bock was born on August 12, 1883, in Nordstetten, (today district of Horb am Neckar). After visiting the schools in Horb am Neckar and Rottweil he studied from 1902 to 1907 jurisprudence at the Munich and at the University of Tübingen. He graduated from the clerkship at the Amtsgericht in Riedlingen, the Landgericht in Ravensburg and with the public prosecution in Stuttgart. He worked since 1910 as a lawyer in Rottweil. From 1915 to 1918 he was a participant in the First World War. After the war Bock continued his career as a lawyer. In August 1944 he was arrested by the Gestapo. Lorenz Bock died on the evening of August 3, 1948, in Rottweil from the effects of intestinal paralysis. Politics Bock joined already before the First World War, the Centre Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Allied-occupied Germany
The entirety of Germany was occupied and administered by the Allies of World War II, from the Berlin Declaration on 5 June 1945 to the establishment of West Germany on 23 May 1949. Unlike occupied Japan, Nazi Germany was stripped of its sovereignty and its government was entirely dissolved. After Germany formally surrendered on Tuesday, 8 May 1945, the four countries representing the Allies (the United States, United Kingdom, Soviet Union, and France) asserted joint authority and sovereignty through the Allied Control Council (ACC). Germany after the war was a devastated country – roughly 80 percent of its infrastructure was in need of repair or reconstruction – which helped the idea that Germany was entering a new phase of history (" zero hour"). At first, Allied-occupied Germany was defined as all territories of Germany before the 1938 Nazi annexation of Austria. The Potsdam Agreement on 2 August 1945 defined the new eastern German border by giving Poland and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gebhard Müller
Gebhard Müller (17 April 1900 – 7 August 1990) was a German lawyer and politician ( CDU). He was President of Württemberg-Hohenzollern (1948–1952), Minister President of Baden-Württemberg (1953–1958) and President of the Federal Constitutional Court of Germany (1959-1971). He was born in Füramoos and died in Stuttgart. Early life Gebhard Müller was the fifth child of a teacher from Oberschwaben and lived in his birthplace Füramoos until 1906, from then in his father's new place of work Ludwigsburg. He attended the Catholic elementary school in Ludwigsburg and later the Gymnasium in Rottweil. In the last year of World War I he was drafted and served in the Ludwigsburg barracks without having to march out. In 1919 Müller started studying theology, history and philosophy at the University of Tübingen. He later switched to law and political science and passed his doctoral degree exam in the latter. Career Müller served as a legal clerk at the local district court in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lindau (district)
Lindau is a Districts of Germany, ''Landkreis'' (district) in Swabia (Bavaria), Swabia, Bavaria, Germany; its capital is the city of Lindau. It is bounded by (from the east and clockwise) the district of Oberallgäu, Austria (federal state of Vorarlberg), Lake Constance and the state of Baden-Württemberg (districts of Bodensee (district), Bodensee and Ravensburg (district), Ravensburg). History The city of Lindau became a Free Imperial City in the 13th century; it was directly subordinate to the Holy Roman Emperor, emperor. The rural areas around Lindau were the property of monasteries or tiny counties, that rose and fell in the region. When Napoleon I of France, Napoleon gained influence in the area, all these entities were dissolved in the German Mediatisation and Lindau fell to Bavaria. The district of Lindau was established in 1938. After the World War II, Second World War it became — like the Circle of the Rhine, Rhenish Palatinate — part of the French zone of occupation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Württemberg-Baden
Württemberg-Baden was a state of the Federal Republic of Germany. It was created in 1945 by the United States occupation forces, after the previous states of Baden and Württemberg had been split up between the US and French occupation zones. Its capital was Stuttgart. In 1952, Württemberg-Baden merged with Württemberg-Hohenzollern and Baden into the present state of Baden-Württemberg. History Württemberg-Baden consisted of the northern halves of the former states of Württemberg and Baden. The southern border of this part of the US-administered zone was set so that the autobahn connecting Karlsruhe and Munich (today the A8) was completely contained within the American zone. The three major subdivisions of the American zone ( Greater Hesse, Bavaria and Württemberg-Baden) were declared on 19 September 1945. On 24 November 1946, a new constitution was enacted and Württemberg-Baden's first parliament was elected. On 23 May 1949, the state became a founding member of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |