|
Woolly Mouse
The woolly mouse refers to a variety of genetically modified laboratory mice developed in 2025 by Colossal Biosciences as part of efforts toward the de-extinction of the woolly mammoth. The mice feature mammoth-inspired traits which include woolly coats and other genetic modifications aimed at cold tolerance. Background Colossal Biosciences, an American biotechnology company, initiated the woolly mouse project as part of their broader woolly mammoth de-extinction program. The company made efforts to restore woolly mammoths through genetic engineering of Asian elephants by introducing mammoth-like traits that would allow the resulting species to survive in cold environments. The company proposed that herds of genetically modified elephants with mammoth-like traits could help mitigate climate change through their impact on Arctic ecosystems. According to the company's hypothesis, these creatures would graze in ways that promote grassland development in tundra regions and redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mus Musculus
The house mouse (''Mus musculus'') is a small mammal of the rodent family Muridae, characteristically having a pointed snout, large rounded ears, and a long and almost hairless tail. It is one of the most abundant species of the genus ''Mus (genus), Mus''. Although a wild animal, the house mouse has benefited significantly from associating with human habitation to the point that truly wild populations are significantly less common than the synanthropic populations near human activity. The house mouse has been domestication, domesticated as the pet or fancy mouse, and as the laboratory mouse, which is one of the most important model organisms in biology and medicine. The complete mouse reference genome was Whole genome sequencing, sequenced in 2002. Characteristics House mice have an adult body length (nose to base of tail) of and a tail length of . The weight is typically . In the wild they vary in color from grey and light brown to black (individual hairs are actually Agouti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome Editing
Genome editing, or genome engineering, or gene editing, is a type of genetic engineering in which DNA is inserted, deleted, modified or replaced in the genome of a living organism. Unlike early genetic engineering techniques that randomly insert genetic material into a host genome, genome editing targets the insertions to site-specific locations. The basic mechanism involved in genetic manipulations through programmable nucleases is the recognition of target genomic loci and binding of effector DNA-binding domain (DBD), double-strand breaks (DSBs) in target DNA by the restriction endonucleases (FokI and CRISPR associated protein, Cas), and the repair of DSBs through homology-directed recombination (HDR) or non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). History Genome editing was pioneered in the 1990s, before the advent of the common current nuclease-based gene-editing platforms, but its use was limited by low efficiencies of editing. Genome editing with engineered nucleases, i.e. all three m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endangered Species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, invasive species, and climate change. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List lists the global conservation status of many species, and various other agencies assess the status of species within particular areas. Many nations have laws that protect conservation-reliant species which, for example, forbid hunting, restrict land development, or create protected areas. Some endangered species are the target of extensive conservation efforts such as captive breeding and habitat restoration. Human activity is a significant cause in causing some species to become endangered. Conservation status The conservation status of a species indicates the likelihood that it will become extinct. Multiple factors are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can change into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type. In mammals, roughly 50 to 150 cells make up the inner cell mass during the blastocyst stage of embryonic development, around days 5–14. These have stem-cell capability. '' In vivo'', they eventually differentiate into all of the body's cell types (making them pluripotent). This process starts with the differentiation into the three germ layers – the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm – at the gastrulation stage. However, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developmental Biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which animals and plants grow and develop. Developmental biology also encompasses the biology of Regeneration (biology), regeneration, asexual reproduction, metamorphosis, and the growth and differentiation of stem cells in the adult organism. Perspectives The main processes involved in the embryogenesis, embryonic development of animals are: tissue patterning (via regional specification and patterned cellular differentiation, cell differentiation); tissue growth; and tissue morphogenesis. * Regional specification refers to the processes that create the spatial patterns in a ball or sheet of initially similar cells. This generally involves the action of cytoplasmic determinants, located within parts of the fertilized egg, and of inductive signals emitted from signaling centers in the embryo. The early stages of regional specification do not generate functional differentiated cells, but cell populations committed to developing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Crick Institute
The Francis Crick Institute (formerly the UK Centre for Medical Research and Innovation) is a biomedical research centre in London, which was established in 2010 and opened in 2016. The institute is a partnership between Cancer Research UK, Imperial College London, King's College London (KCL), the Medical Research Council, University College London (UCL) and the Wellcome Trust. The institute has 1,500 staff, including 1,250 scientists, and an annual budget of over £100 million, making it the biggest single biomedical laboratory in Europe. The institute is named after the molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist Francis Crick, co-discoverer of the structure of DNA, who shared the 1962 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with James Watson and Maurice Wilkins. Unofficially, the Crick has been called ''Sir Paul's Cathedral'', a reference to Sir Paul Nurse and St Paul's Cathedral in London. History Background In 2003, the Medical Research Council decided that its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
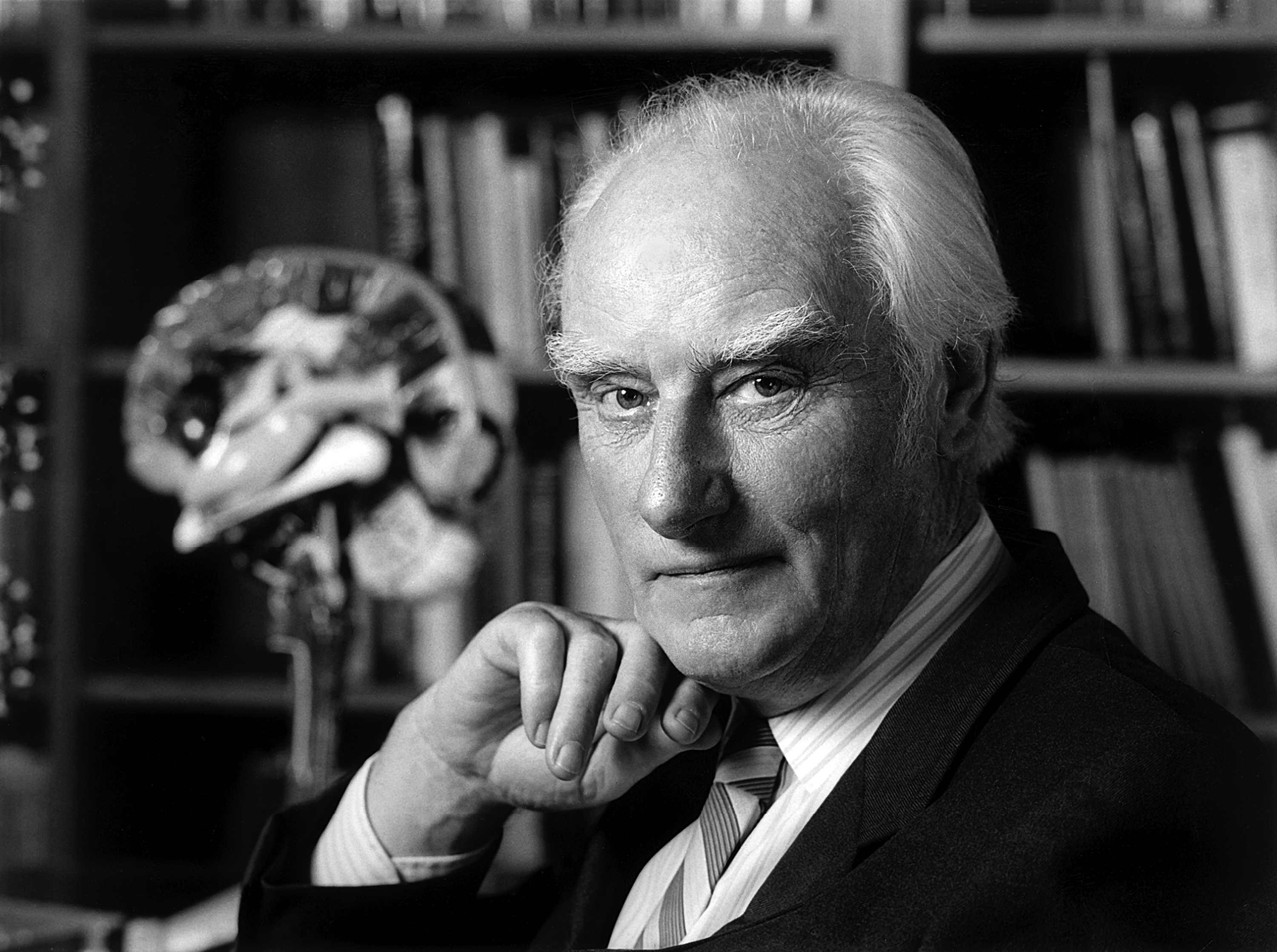
Robin Lovell-Badge
Robin Howard Lovell-Badge is a British scientist most famous for his discovery, along with Peter Goodfellow, of the SRY gene on the Y-chromosome that is the determinant of sex in mammals. They shared the 1995 Louis-Jeantet Prize for Medicine for their discovery. He was awarded the 2022 Genetics Society Medal. He is currently a Senior Group Leader and Head of the Laboratory of Stem Cell Biology and Developmental Genetics at the Francis Crick Institute The Francis Crick Institute (formerly the UK Centre for Medical Research and Innovation) is a biomedical research centre in London, which was established in 2010 and opened in 2016. The institute is a partnership between Cancer Research UK, Im ... in Central London. One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from the royalsociety.org website where: References Living people 20th-century British biologists 21st-century British biologists Commanders of the Order of the British Empire Fellows of the Roya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beth Shapiro
Beth Alison Shapiro (born January 14, 1976) is an American evolutionary molecular biologist, associate director for conservation genomics at the UC Santa Cruz Genomics Institute, and a Howard Hughes Medical Institute investigator. She also teaches in the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at the University of California, Santa Cruz. In March 2024, Shapiro began a three year sabbatical to become the chief scientific officer of Colossal Biosciences. Shapiro's work has centered on the analysis of ancient DNA. TEDx talk She was awarded a Royal Society University Research Fellowship in 2006 and a MacArthur Fellowship in 2009. She was elected a Member of the National Academy of Sciences in 2025. Early life and education On January 14, 1976, Shapiro was born in Allentown, Pennsylvania. She grew up in Rome, Georgia, where she served as a local news presenter while attending Rome High School. In 1994, Shapiro graduated from Rome High School with a GPA of 4.0, and enter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
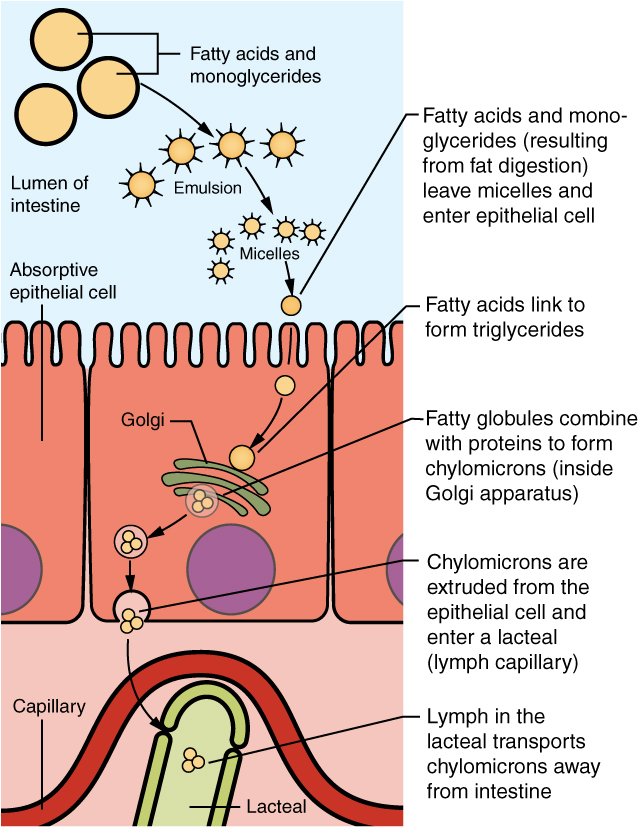
Lipid Metabolism
Lipid metabolism is the synthesis and degradation of lipids in cells, involving the breakdown and storage of fats for energy and the synthesis of structural and functional lipids, such as those involved in the construction of cell membranes. In animals, these fats are obtained from food and are synthesized by the liver. Lipogenesis is the process of synthesizing these fats. The majority of lipids found in the human body from ingesting food are triglycerides and cholesterol. Other types of lipids found in the body are fatty acids and membrane lipids. Lipid metabolism is often considered the digestion and absorption process of dietary fat; however, there are two sources of fats that organisms can use to obtain energy: from consumed dietary fats and from stored fat. Vertebrates (including humans) use both sources of fat to produce energy for organs such as the heart to function. Since lipids are hydrophobic molecules, they need to be solubilized before their metabolism can begin. Lipid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanin
Melanin (; ) is a family of biomolecules organized as oligomers or polymers, which among other functions provide the pigments of many organisms. Melanin pigments are produced in a specialized group of cells known as melanocytes. There are five basic types of melanin: eumelanin, pheomelanin, neuromelanin, allomelanin and pyomelanin. Melanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino acid tyrosine is followed by polymerization. Pheomelanin is a cysteinated form containing poly benzothiazine portions that are largely responsible for the red or yellow tint given to some skin or hair colors. Neuromelanin is found in the brain. Research has been undertaken to investigate its efficacy in treating neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinson's. Allomelanin and pyomelanin are two types of nitrogen-free melanin. The phenotypic color variation observed in the epidermis and hair of mammals is primarily determi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melanocortin 1 Receptor
The melanocortin 1 receptor (MC1R), also known as melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptor (MSHR), melanin-activating peptide receptor, or melanotropin receptor, is a G protein–coupled receptor that binds to a class of pituitary peptide hormones known as the melanocortins, which include adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and the different forms of melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). It is coupled to Gαs and upregulates levels of cAMP by activating adenylyl cyclase in cells expressing this receptor. It is normally expressed in skin and melanocytes, and to a lesser degree in periaqueductal gray matter, astrocytes and leukocytes. In skin cancer, MC1R is highly expressed in melanomas but not carcinomas. MC1R is one of the key proteins involved in regulating mammalian skin color and hair color. It is located on the plasma membrane of specialized cells known as melanocytes, which produce the pigment melanin through the process of melanogenesis. It controls the type o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |