|
William Miller (Australian Presbyterian Minister)
The Rev William Miller (sometimes Millar) (1815–1874) was a Scots-born minister of the Free Presbyterian Church of Victoria who served the John Knox Church, cnr Little Lonsdale Street, Melbourne, Little Lonsdale and Swanston Street, Melbourne, Swanston Streets, Melbourne, Victoria, Melbourne 1851–64, and was the first Chairman of the council of Scotch College, Melbourne, Scotch College in Melbourne. Miller should not to be confused with his contemporary Rev William Baird Millar/er, who belonged to the United Presbyterian Church of Victoria 1851–53, and never held a charge but engaged chiefly in teaching. Life and ministry He was born on 4 August 1815 in East Kilpatrick the son of John Miller and Isabella Wilson. He studied Divinity at New College, Edinburgh.Ewing, William ''Annals of the Free Church'' Miller was licensed by the Free Church of Scotland (1843-1900), Free Church of Scotland Presbytery (church polity), Presbytery of Linlithgow on 14 August 1849, and was or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Presbyterian Church Of Victoria
The Free Presbyterian Church of Victoria, also known as the Free Church of Australia Felix, was an Australian Presbyterian denomination founded in Melbourne, Victoria in 1846 as a result of the Disruption of 1843 in the Church of Scotland. The first Presbyterian minister in Melbourne, James Forbes and one of his three elders at Scots' Church, Melbourne adhered to the position also adopted by those who withdrew from the 'Synod of Australian in connection with the Established Church of Scotland' and formed the Presbyterian Church of Eastern Australia in New South Wales on 10 October 1846. Forbes and his elder withdrew from the Presbytery of Melbourne of the Synod and organised a distinct body on similar lines to the Presbyterian Church of Eastern Australia, although spelling out the constitution afresh rather than simply adhering to the existing constitution. There was no difference of principle between the two bodies. Forbes gave up his handsome stipend (£200 from the govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Assembly Of The Church Of Scotland
The General Assembly of the Church of Scotland is the sovereign and highest court of the Church of Scotland, and is thus the Church's governing body.''An Introduction to Practice and Procedure in the Church of Scotland'' by A. Gordon McGillivray, 2nd Edition (2006 updated text) It generally meets each year and is chaired by a Moderator elected at the start of the Assembly. Church courts As a Presbyterian church, the Church of Scotland is governed by courts of elders rather than by bishops. At the bottom of the hierarchy of courts is the Kirk Session, the court of the parish; representatives of Kirk Sessions form the Presbytery, the local area court. Formerly there were also Synods at regional level, with authority over a group of presbyteries, but these have been abolished. At national level, the General Assembly stands at the top of this structure. Meetings General Assembly meetings are usually held in the Assembly Hall on the Mound, Edinburgh. This was originally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Presbyterian Ministers
Australian(s) may refer to: Australia * Australia, a country * Australians, citizens of the Commonwealth of Australia ** European Australians ** Anglo-Celtic Australians, Australians descended principally from British colonists ** Aboriginal Australians, indigenous peoples of Australia as identified and defined within Australian law * Australia (continent) ** Indigenous Australians * Australian English, the dialect of the English language spoken in Australia * Australian Aboriginal languages * ''The Australian'', a newspaper * Australiana, things of Australian origins Other uses * Australian (horse), a racehorse * Australian, British Columbia, an unincorporated community in Canada See also * The Australian (other) * Australia (other) * * * Austrian (other) Austrian may refer to: * Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent ** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen, see Austrian nationality law * Austrian German dialect * S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1874 Deaths
Events January–March * January 1 – New York City annexes The Bronx. * January 2 – Ignacio María González becomes head of state of the Dominican Republic for the first time. * January 3 – Third Carlist War – Battle of Caspe: Campaigning on the Ebro in Aragon for the Spanish Republican Government, Colonel Eulogio Despujol surprises a Carlist force under Manuel Marco de Bello at Caspe, northeast of Alcañiz. In a brilliant action the Carlists are routed, losing 200 prisoners and 80 horses, while Despujol is promoted to Brigadier and becomes Conde de Caspe. * January 20 – The Pangkor Treaty (also known as the Pangkor Engagement), by which the British extended their control over first the Sultanate of Perak, and later the other independent Malay States, is signed. * January 23 **Prince Alfred, Duke of Edinburgh, second son of Queen Victoria, marries Grand Duchess Maria Alexandrovna of Russia, only daughter of Tsar Alexander III of Rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1815 Births
Events January * January 2 – Lord Byron marries Anna Isabella Milbanke in Seaham, county of Durham, England. * January 3 – Austria, Britain, and Bourbon-restored France form a secret defensive alliance treaty against Prussia and Russia. * January 8 – Battle of New Orleans: American forces led by Andrew Jackson defeat British forces led by Sir Edward Pakenham. American forces suffer around 60 casualties and the British lose about 2,000 (the battle lasts for about 30 minutes). * January 13 – War of 1812: British troops capture Fort Peter in St. Marys, Georgia, the only battle of the war to take place in the state. * January 15 – War of 1812: Capture of USS ''President'' – American frigate , commanded by Commodore Stephen Decatur, is captured by a squadron of four British frigates. February * February – The Hartford Convention arrives in Washington, D.C. * February 3 – The first commercial cheese factory is fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Calder
West Calder ( sco, Wast Cauder, gd, Caladar an Iar) is a village in the council area of West Lothian, Scotland, located four miles west of Livingston. Historically it is within the County of Midlothian. The village was an important centre in the oil shale industry in the 19th and 20th Centuries. West Calder has its own railway station. The surrounding villages that take West Calder's name in their address - Polbeth, Addiewell, Loganlea, Harburn and Westwood - outline the area that this village encompasses, and they all have played an important part in the history of the village as well as West Lothian. The village is a 10-minute drive from Livingston, which is host to two large shopping centres. The village lies along the ridge above the Calder burn. History Early evidence of settlement in the area of West Calder is indicated by the presence of Castle Greg, an Roman fortlet to the south-east of the village in neighboring Harburn. In the medieval period, the area was pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paisley, Renfrewshire
Paisley ( ; sco, Paisley, gd, Pàislig ) is a large town situated in the west central Lowlands of Scotland. Located north of the Gleniffer Braes, the town borders the city of Glasgow to the east, and straddles the banks of the White Cart Water, a tributary of the River Clyde. Paisley serves as the administrative centre for the Renfrewshire council area, and is the largest town in the historic county of the same name. It is often cited as "Scotland's largest town" and is the fifth largest settlement in the country, although it does not have city status. The town became prominent in the 12th century, with the establishment of Paisley Abbey, an important religious hub which formerly had control over other local churches. By the 19th century, Paisley was a centre of the weaving industry, giving its name to the Paisley shawl and the Paisley pattern. The town's associations with political radicalism were highlighted by its involvement in the Radical War of 1820, with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callander Railway Station
Callander was a railway station located in Callander, in the council area of Stirling, Scotland. History The first station at Callander was a terminus opened by the Dunblane, Doune and Callander Railway on 1 July 1858. It was closed on 1 June 1870 when the second station was opened along with the first section of the Callander and Oban Railway, between Callander and Glenoglehead (originally named 'Killin'). The original terminal station of the Dunblane, Doune and Callander Railway become a goods yard. The station underwent expansion in 1882. Closure came on 1 November 1965, when the service between Callander and Dunblane ended as part of the Beeching Axe. The section between Callander and Crianlarich (lower) was closed on 27 September that year following a landslide at Glen Ogle. The track to the west of the station was lifted in early 1967, and the track through the station was lifted in late 1968 and some demolition work was carried out. The station building itself was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callander
Callander (; gd, Calasraid) is a small town in the council area of Stirling, Scotland, situated on the River Teith. The town is located in the historic county of Perthshire and is a popular tourist stop to and from the Highlands. The town serves as the eastern gateway to the Loch Lomond and the Trossachs National Park, the first National Park in Scotland, and is often referred to as the "Gateway to the Highlands". Dominating the town to the north are the Callander Crags, a visible part of the Highland Boundary Fault, rising to at the cairn. Ben Ledi () lies north-west of Callander. Popular local walks include Bracklinn Falls, The Meadows, Callander Crags and the Wood Walks. The Rob Roy Way passes through Callander. The town sits on the Trossachs Bird of Prey Trail. The River Teith is formed from the confluence of two smaller rivers, the Garbh Uisge (River Leny) and Eas Gobhain about west of the bridge at Callander. A 19th-century Gothic church stands in the town squa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
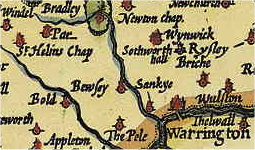
St Helens, Lancashire
St Helens () is a town in Merseyside, England, with a population of 102,629. It is the administrative centre of the Metropolitan Borough of St Helens, which had a population of 176,843 at the 2001 Census. St Helens is in the south-west of the historic county of Lancashire, north of the River Mersey. The town historically lay within the ancient Lancashire division of West Derby known as a ''hundred''. The town initially started as a small settlement in the township of Windle but, by the mid 1700s, the town had become synonymous with a wider area; by 1838, it was formally made responsible for the administration of the four townships of Eccleston, Parr, Sutton and Windle. In 1868, the town was created by incorporation as a municipal borough and later became a county borough in 1887; it became a metropolitan borough in 1974, with an expanded administrative responsibility for towns and villages in close proximity. The area developed rapidly in the Industrial Revolution of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Presbyterian Church
The United Reformed Church (URC) is a Protestant Christian church in the United Kingdom. As of 2022 it has approximately 40,000 members in 1,284 congregations with 334 stipendiary ministers. Origins and history The United Reformed Church resulted from the 1972 union of the Presbyterian Church of England and the Congregational Church in England and Wales. In introducing the United Reformed Church Bill in the House of Commons on 21 June 1972, Alexander Lyon called it "one of the most historic measures in the history of the Christian churches in this country". About a quarter of English Congregational churches chose not to join the new denomination; in England, there are three main groups of continuing Congregationalists: the Congregational Federation, the Evangelical Fellowship of Congregational Churches and the Fellowship of Independent Evangelical Churches. The URC subsequently united with the Re-formed Association of Churches of Christ in 1981 and the Congregational Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)