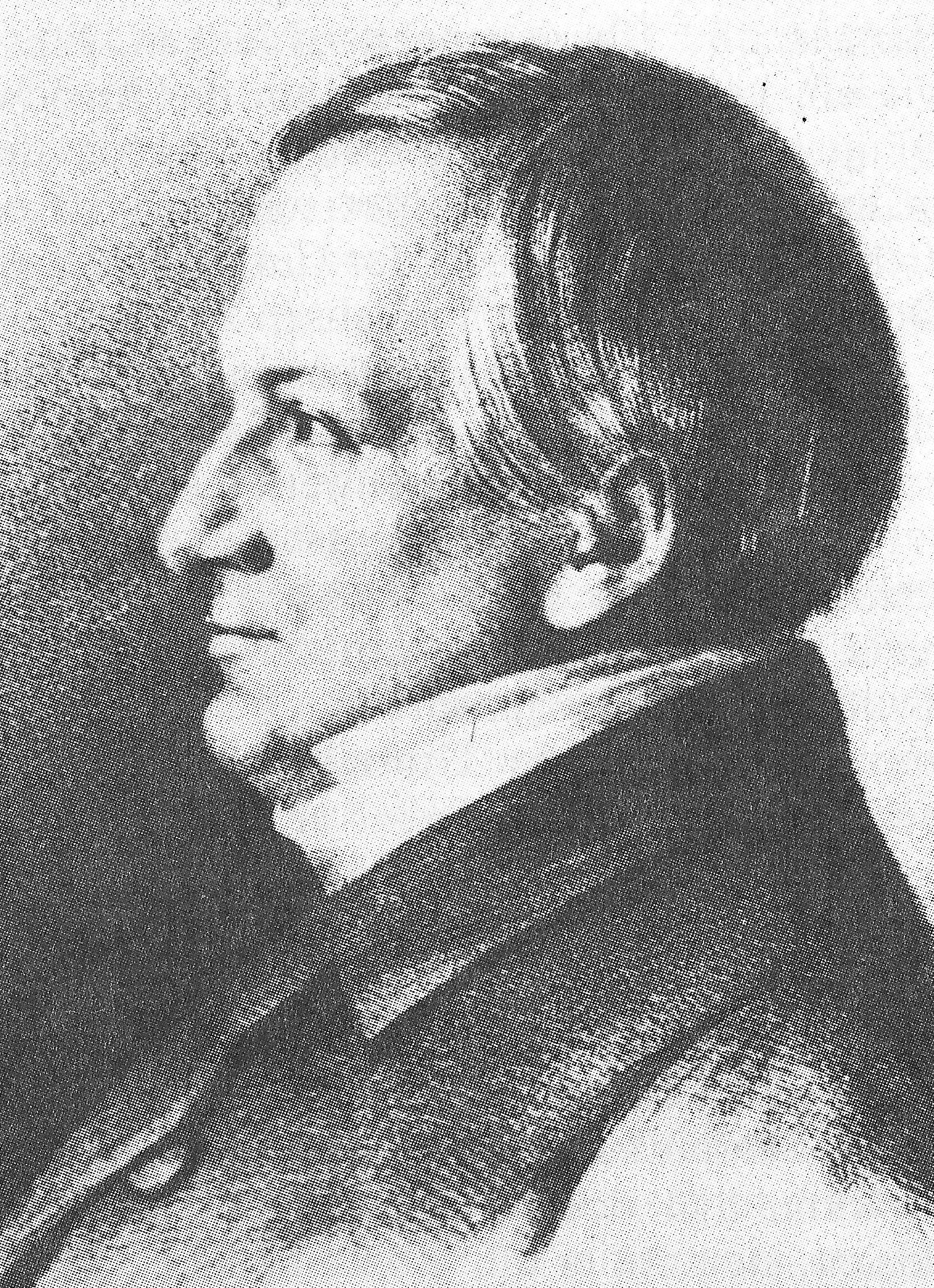|
Wilhelm Von Gloeden
Wilhelm Iwan Friederich August von Gloeden (September 16, 1856 – February 16, 1931), commonly known as Baron von Gloeden, was a German photographer who worked mainly in Italy. He is mostly known for his pastoral nude studies of Sicilian boys, which usually featured props such as wreaths or amphoras, suggesting a setting in the Greece or Italy of antiquity. His work demonstrates the controlled use of lighting as well utilizing elegant poses of his models. His innovations include the use of photographic filters and special body makeup (a mixture of milk, olive oil, and glycerin) to disguise skin blemishes. His work, both landscapes and nudes, drew wealthy tourists to Sicily, particularly gay men uncomfortable in northern Europe. Early life Wilhelm von Gloeden was self-invented. He claimed to be the son of an officer and baron from Mecklenburg, and gave a "Schloss Volkshagen near Wismar" as his place of birth. However, there was no such castle. He was indeed born into a Meckle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freiherr
(; male, abbreviated as ), (; his wife, abbreviated as , ) and (, his unmarried daughters and maiden aunts) are designations used as titles of nobility in the German-speaking areas of the Holy Roman Empire, the Austro-Hungarian Empire and in its various successor states, including Austria, Prussia, Bavaria, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, etc. Traditionally, it denotes the titled rank within the nobility above ' (knight) and ' (nobility without a specific title) and below ' ( count or earl). The title superseded the earlier medieval form, '. It corresponds approximately to the English baron in rank. The Duden orthography of the German language references the French nobility title of ''Baron'', deriving from the Latin-Germanic combination ''liber baro'' (which also means "free lord"), as corresponding to the German "Freiherr"; and that ''Baron'' is a corresponding salutation for a ''Freiherr''. Duden; Definition of ''Baron, der'' (in German)/ref> ' in the feudal system The title ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duke Of Mecklenburg
This list of dukes and grand dukes of Mecklenburg dates from the origins of the Germany, German princely state of Mecklenburg's royal house in the High Middle Ages to the monarchy's abolition at the end of World War I. Strictly speaking, Mecklenburg's princely dynasty was descended linearly from the princes (or kings) of a Slavic tribe, the Obotrites, and had its original residence in a castle (Mecklenburg Castle, Mecklenburg) in Dorf Mecklenburg (Mikelenburg) close to Wismar."Fürsten und Gutsherren..." As part of a feudal union under German law from 1160—at first under the Saxons—Mecklenburg was granted imperial immediacy in 1348 and its princely rulers styled Dukes of Mecklenburg. Despite several Main partititons of Mecklenburg, partitions, Mecklenburg remained an integral state until the end of the monarchy. The First Partition of Mecklenburg came in 1234, causing the principality to lose land. Thus arose the partial principalities (lordships) of Werle, Parchim-Richenberg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capri
Capri ( , ; ) is an island located in the Tyrrhenian Sea off the Sorrento Peninsula, on the south side of the Gulf of Naples in the Campania region of Italy. A popular resort destination since the time of the Roman Republic, its natural beauty, historic sites, and upscale tourism have made it famous worldwide. The island is characterized by its rugged limestone landscape, sea stacks (Faraglioni), coastal grottoes including the renowned Blue Grotto (Capri), Blue Grotto, and high cliffs overlooking the sea. Notable features include the harbours of Marina Grande, Capri, Marina Grande and Marina Piccola, the panoramic Belvedere of Tragara, the ruins of Roman imperial villas such as Villa Jovis, and the towns of Capri (town), Capri and Anacapri, the latter situated higher up the slopes of Monte Solaro, the island's highest point. Administratively, Capri is part of the Metropolitan City of Naples within the Campania region. The island is divided into two municipalities (''comuni''): ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naples
Naples ( ; ; ) is the Regions of Italy, regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 908,082 within the city's administrative limits as of 2025, while its Metropolitan City of Naples, province-level municipality is the third most populous Metropolitan cities of Italy, metropolitan city in Italy with a population of 2,958,410 residents, and the List of urban areas in the European Union, eighth most populous in the European Union. Naples metropolitan area, Its metropolitan area stretches beyond the boundaries of the city wall for approximately . Naples also plays a key role in international diplomacy, since it is home to NATO's Allied Joint Force Command Naples and the Parliamentary Assembly of the Mediterranean. Founded by Greeks in the 1st millennium BC, first millennium BC, Naples is one of the oldest continuously inhabited urban areas in the world. In the eighth century BC, a colony known as Parthenope () was e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sokołowsko
Sokołowsko is a village and traditional climatic health resort in Gmina Mieroszów, within Wałbrzych County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It lies approximately north-east of Mieroszów, south of Wałbrzych, and south-west of the regional capital Wrocław. Geography Sokołowsko is the largest village within the Stone Mountains of the Central Sudetes. It is situated in a deep forest-covered hollow traversed by the ''Sokołowiec'' and ''Dziczy'' streams, at an altitude of above sea level. The border with the town of Meziměstí in the Czech Republic is about in the south. Sokołowsko is surrounded by several forested mountains, predominantly made up from porphyry rocks: ''Stożek Mały'' () in the north-west and ''Masyw Bukowca'' () in the north-east, as well as ''Garbatka'' () in the south-west, ''Włostowa'' () in the south and south-east and ''Radosno'' () in the east. The range offers numerous trails for hiking and cross-country skiing in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanatorium
A sanatorium (from Latin '' sānāre'' 'to heal'), also sanitarium or sanitorium, is a historic name for a specialised hospital for the treatment of specific diseases, related ailments, and convalescence. Sanatoriums are often in a healthy climate, usually in the countryside. The idea of healing was an important reason for the historical wave of establishments of sanatoria, especially at the end of the 20th and early 21th centuries. One sought, for instance, the healing of consumptives especially tuberculosis (before the discovery of antibiotics) or alcoholism, but also of more obscure addictions and longings of hysteria, masturbation, fatigue and emotional exhaustion. Facility operators were often charitable associations, such as the Order of St. John and the newly founded social welfare insurance companies. Sanatoriums should not be confused with the Russian sanatoriums from the time of the Soviet Union, which were a type of sanatorium resort residence for workers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as inactive or latent tuberculosis. A small proportion of latent infections progress to active disease that, if left untreated, can be fatal. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with hemoptysis, blood-containing sputum, mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is Human-to-human transmission, spread from one person to the next Airborne disease, through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with latent TB do not spread the disease. A latent infection is more likely to become active in those with weakened I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weimar Saxon-Grand Ducal Art School
The Grand-Ducal Saxon Art School, Weimar (German:Großherzoglich-Sächsische Kunstschule Weimar) was founded on 1 October 1860, in Weimar, Germany, by a decree of Charles Alexander, Grand Duke of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach. It existed until 1910, when it merged with several other art schools to become the ''Großherzoglich Sächsische Hochschule für Bildende Kunst'' ("Grand-Ducal Saxon School for Fine Arts"). It should not be confused with the Weimar Princely Free Drawing School, which existed from 1776 to 1930 and, after 1860, served as a preparatory school. History From 1870 to 1900, the students and teachers of the school turned away from the academic tradition of idealized compositions. Inspired by the Barbizon School, they went directly to nature for their inspiration, in genre as well as landscape painting. This approach set the school apart and attracted attention throughout Europe. Grand-Ducal Saxon School for Fine Arts, Weimar In 1910, William Ernest, Grand Duke of Saxe-W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rostock
Rostock (; Polabian language, Polabian: ''Roztoc''), officially the Hanseatic and University City of Rostock (), is the largest city in the German States of Germany, state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and lies in the Mecklenburgian part of the state, close to the border with Pomerania. With around 210,000 inhabitants, it is the third-largest city on the German Baltic Sea, Baltic coast after Kiel and Lübeck, the eighth-largest city in the area of former East Germany, as well as the List of cities in Germany by population, 39th-largest city of Germany. Rostock was the largest coastal and most important port city in East Germany. Rostock stands on the estuary of the Warnow, River Warnow into the Bay of Mecklenburg of the Baltic Sea. The city stretches for about along the river. The river flows into the sea in the very north of the city, between the boroughs of Warnemünde and Hohe Düne. The city center lies further upstream, in the very south of the city. Most of Rostock's inhabita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kreuzzeitung
The ''Kreuzzeitung'' was a national daily newspaper published between 1848 and 1939 in the Kingdom of Prussia and then during the German Empire, the Weimar Republic and into the first part of the Third Reich. The paper was a voice of the conservative upper class, although it was never associated with any political party and never had more than 10,000 subscribers. Its target readership was the nobility, military officers, high-ranking officials, industrialists and diplomats. Because its readers were among the elite, the ''Kreuzzeitung'' was often quoted and at times very influential. It had connections to officials in the highest levels of government and business and was especially known for its foreign reporting. Most of its content consisted of carefully researched foreign and domestic news reported without commentary. Its original name was officially the (''New Prussian Newspaper''), although because of the Iron Cross as its emblem in the title, it was simply called the ‘''Kr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Conservative Party
The German Conservative Party (, DkP) was a Right-wing politics, right-wing political party of the German Empire founded in 1876. It largely represented the wealthy landowning German nobility and the Prussian Junker (Prussia), Junker class. The party was a response to German unification, Universal suffrage, universal and equal franchise in national elections and rapid industrialization. It changed from a diffuse party of broad ideology into an interest party in Bismarckian Germany. In the early 1870s, Otto von Bismarck formed his majority with the base in the National Liberal Party (Germany), National Liberal Party which emphasized free trade and anti-Catholicism. Bismarck broke with them in the late 1870s, by which time the German Conservative Party and the Free Conservative Party had brought together the landed Junkers in the East and the rapidly growing industrial leadership in the major cities. They now became the main base of Bismarck's support and successive Chancellor of Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |