|
Wijkanderberget
Wijkanderberget is a mountain in Wedel Jarlsberg Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It is named after Swedish physicist and astronomer August Wijkander, who joined Nordenskiöld's expedition of 1872. The mountain has two peaks of equal height, 562 m.a.s.l. and is situated between Scottbreen Scottbreen is a glacier in Wedel Jarlsberg Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. The glacier has a length of about 4.5 kilometers. It is located between Wijkanderberget and the ridge of Bohlinryggen, which separates Scottbreen from the glacier of Renardbr ..., Blomlibreen and Blomlidalen. References Mountains of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-mountain-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottbreen
Scottbreen is a glacier in Wedel Jarlsberg Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. The glacier has a length of about 4.5 kilometers. It is located between Wijkanderberget and the ridge of Bohlinryggen, which separates Scottbreen from the glacier of Renardbreen. References Glaciers of Spitsbergen {{spitsbergen-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
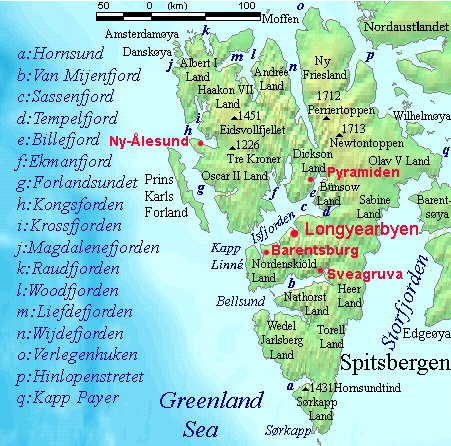
Wedel Jarlsberg Land
Wedel Jarlsberg Land is the land area between Van Keulenfjorden and Hornsund on the southwestern part of Spitsbergen Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern N ..., Svalbard. The area is largely covered with glaciers, and is completely within the Sør-Spitsbergen National Park. Named after Baron Fritz Wedel Jarlsberg (1855-1942), Norwegian minister in Paris, to whose initiative and labour it was greatly due that Norway succeeded in acquiring the sovereignty of Svalbard by a treaty signed in Paris on February 9, 1920. Until then it had been regarded as no-man's-land. The northwestern part of the area was earlier called Orvin Land. References Peninsulas of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway. Constituting the westernmost bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea, and the Greenland Sea. Spitsbergen covers an area of , making it the largest island in Norway and the 36th-largest in the world. The administrative centre is Longyearbyen. Other settlements, in addition to research outposts, are the Russian mining community of Barentsburg, the research community of Ny-Ålesund, and the mining outpost of Sveagruva. Spitsbergen was covered in of ice in 1999, which was approximately 58.5% of the island's total area. The island was first used as a whaling base in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which it was abandoned. Coal mining started at the end of the 19th century, and several permanent com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norway, Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of continental Europe, mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74th parallel north, 74° to 81st parallel north, 81° north latitude, and from 10th meridian east, 10° to 35th meridian east, 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the Whaling, whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wedel Jarlsberg Land
Wedel Jarlsberg Land is the land area between Van Keulenfjorden and Hornsund on the southwestern part of Spitsbergen, Svalbard Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range .... The area is largely covered with glaciers, and is completely within the Sør-Spitsbergen National Park. Named after Baron Fritz Wedel Jarlsberg (1855-1942), Norwegian minister in Paris, to whose initiative and labour it was greatly due that Norway succeeded in acquiring the sovereignty of Svalbard by a treaty signed in Paris on February 9, 1920. Until then it had been regarded as no-man's-land. The northwestern part of the area was earlier called Orvin Land. References Peninsulas of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld
Nils Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld (18 November 183212 August 1901) was a Finland-Swedish aristocrat, geologist, mineralogist and Arctic explorer. He was a member of the Fenno-Swedish Nordenskiöld family of scientists and held the title of a friherre (baron). Born in the Grand Duchy of Finland at the time it was a part of the Russian Empire, he was later, due to his political activity, forced to move to Sweden, where he later became a member of the Parliament of Sweden and of the Swedish Academy. He led the ''Vega'' Expedition along the northern coast of Eurasia in 1878–1879. This was the first complete crossing of the Northeast Passage. Initially a troubled enterprise, the successful expedition is considered to be among the highest achievements in the history of Swedish science. Nordenskiöld family The Nordenskiölds were an old Fenno-Swedish family, and members of the nobility. Nordenskiöld's father, Nils Gustaf Nordenskiöld, was a Finnish mineralogist, civil servant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Polar Institute
The Norwegian Polar Institute (NPI; no, Norsk Polarinstitutt) is Norway's central governmental institution for scientific research, mapping and environmental monitoring in the Arctic and the Antarctic. The NPI is a directorate under Norway's Ministry of Climate and Environment. The institute advises Norwegian authorities on matters concerning polar environmental management and is the official environmental management body for Norwegian activities in Antarctica. Activities The institute's activities are focused on environmental research and management in the polar regions. The NPI's researchers investigate biodiversity, climate and environmental toxins in the Arctic and Antarctic, and in this context the institute equips and organizes large-scale expeditions to both polar regions. The institute contributes to national and international climate work, and is an active contact point for the international scientific community. The institute collects and analyses data on the environ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |