|
Western Wall
The Western Wall (; ; Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: ''HaKosel HaMa'arovi'') is an ancient retaining wall of the built-up hill known to Jews and Christians as the Temple Mount of Jerusalem. Its most famous section, known by the same name, often shortened by Jews to the Kotel or Kosel, is known in the West as the Wailing Wall, and in Arab world and Islamic world as the Buraq Wall (; ). In a Jewish religious context, the term Western Wall and its variations is used in the narrow sense, for the section used for Jewish prayer; in its broader sense it refers to the entire retaining wall on the western side of the Temple Mount. At the prayer section, just over half the wall's total height, including its 17 courses located below street level, dates from the end of the Second Temple period, and is believed to have been begun by Herod the Great. The very large stone blocks of the lower courses are Herodian, the courses of medium-sized stones above them were added during the Um ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old City (Jerusalem)
The Old City of Jerusalem (; ) is a Walls of Jerusalem, walled area in Jerusalem. In a tradition that may have begun with an 1840–41 Royal Engineers maps of Palestine, Lebanon and Syria, 1840s British map of the city, the Old City is divided into four uneven quarters: the Muslim Quarter (Jerusalem), Muslim Quarter, the Christian Quarter, the Armenian Quarter, and the Jewish Quarter (Jerusalem), Jewish Quarter. A fifth area, the Temple Mount, known to Muslims as Al-Aqsa or ''Haram al-Sharif'', is home to the Dome of the Rock, the Al-Aqsa Mosque, and was once the site of Temple in Jerusalem, the Jewish Temple. The Old City's Walls of Jerusalem, current walls and city gates were built by the Ottoman Empire from 1535 to 1542 under Suleiman the Magnificent. The Old City is home to several sites of key importance and holiness to the three major Abrahamic religions: the Temple Mount and the Western Wall for Judaism, the Church of the Holy Sepulchre for Christianity, and the Dome o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
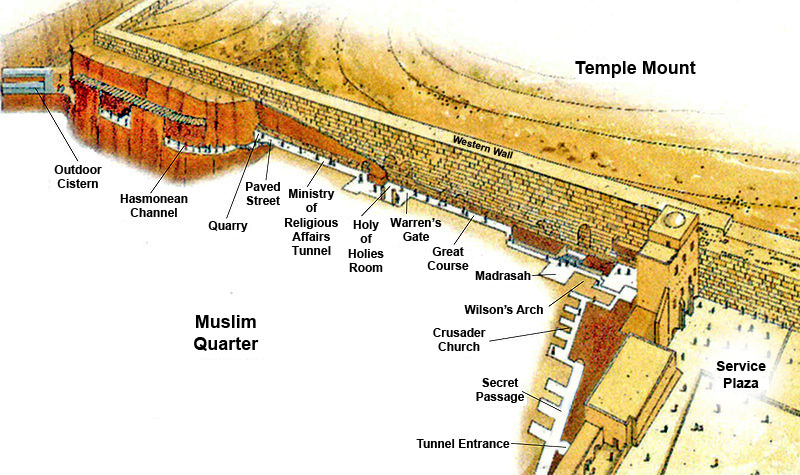
Western Wall Tunnel
The Western Wall Tunnel (, translit.: ''Minharat Hakotel'') is a tunnel exposing the Western Wall slightly north from where the traditional, open-air prayer site ends and up to the Wall's northern end. Most of the tunnel is in continuation of the open-air Western Wall and is located under buildings of the Muslim Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem. While the open-air portion of the Western Wall is approximately long, the majority of its original length of is hidden underground. The tunnel allows access to the remainder of the Wall in a northerly direction. The tunnel is connected to several adjacent excavated underground spaces, many of which can be visited together with the main tunnel. For this reason the plural form, Western Wall Tunnels, is often used. History In 19 BCE, King Herod undertook a project to double the area of the Temple Mount in Jerusalem by incorporating part of the hill on the Northwest. In order to do so, four retaining walls were constructed, and the T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and is considered Holy city, holy to the three major Abrahamic religions—Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Both Israel and Palestine claim Jerusalem as their capital city; Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions there, while Palestine ultimately foresees it as its seat of power. Neither claim is widely Status of Jerusalem, recognized internationally. Throughout History of Jerusalem, its long history, Jerusalem has been destroyed at least twice, Siege of Jerusalem (other), besieged 23 times, captured and recaptured 44 times, and attacked 52 times. According to Eric H. Cline's tally in Jerusalem Besieged. The part of Jerusalem called the City of David (historic), City of David shows first signs of settlement in the 4th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haram Esh-Sharif
Al-Aqsa (; ) or al-Masjid al-Aqṣā () and also is the compound of Islamic religious buildings that sit atop the Temple Mount, also known as the Haram al-Sharif, in the Old City (Jerusalem), Old City of Jerusalem, including the Dome of the Rock, many mosques and prayer halls, madrasas, zawiya (prayer space), zawiyas, khalwa (structure), khalwas and other domes and religious structures, as well as the four encircling Minarets of the Al-Aqsa Mosque compound, minarets. It is considered the third Holiest sites in Islam, holiest site in Islam. The compound's main congregational mosque or Musalla, prayer hall is variously known as ''Al-Aqsa Mosque'', ''Qibli Mosque'' or ''al-Jāmiʿ al-Aqṣā'', while in some sources it is also known as ''al-Masjid al-Aqṣā''; the wider compound is sometimes known as Al-Aqsa Mosque compound in order to avoid confusion. During the rule of the Rashidun caliph Umar () or the Umayyad caliph Mu'awiya I (), a small prayer house on the compound was ere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isra And Mi'raj
The Israʾ and Miʿraj (, ') are the names given to the narrations that the prophet Muhammad ascended to the sky during a night journey, saw Allah and the afterlife, and returned. It is believed that expressions without a subject in verses 1-18 of surah An-Najm and some verses of 17th surah of the Quran, commonly called ''al-Isra''', allude to the story. Framework and the details are elaborated and developed in the Miraj Nameh, miraculous accounts, some of which are based on hadith, the reports, teachings, deeds and sayings of Muhammad collected later centuries attributed after him. The story of the journey and ascent are marked as one of the most celebrated in the Islamic calendar—27th of the Islamic month of Rajab. Ibn Sa'd summarizes the earliest version of the written stories under the title "Ascension and the Order of Prayer" and dated the event to a Saturday, the 17th of Ramadan, eighteen months before Muhammad's Hijrah. According to him, the angels Gabriel and Michael (ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
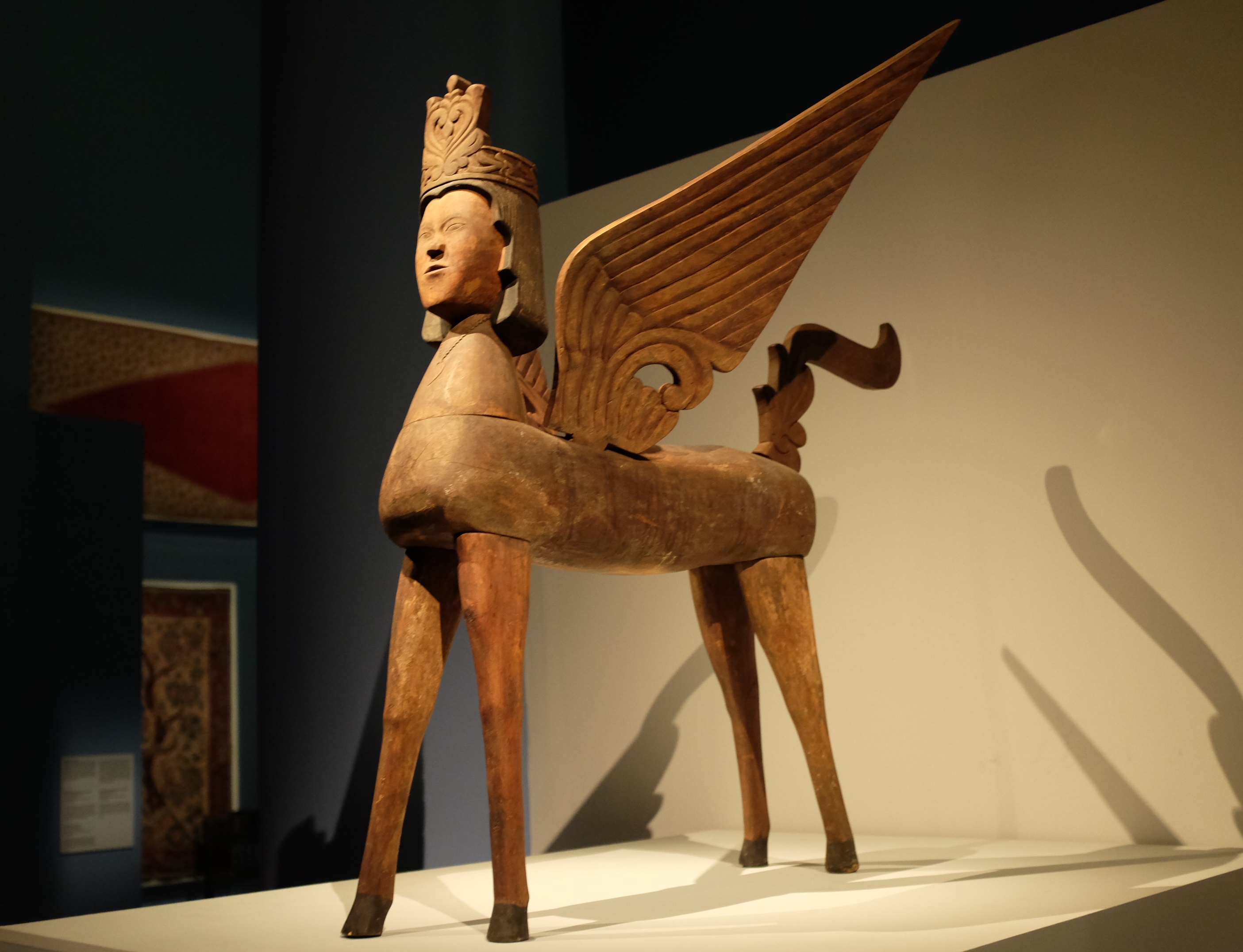
Burāq
The Buraq ( "lightning") is a supernatural Equinae, equine-esque creature in Islamic tradition that served as the mount of the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad during his Isra and Mi'raj journey from Mecca to Jerusalem and up through the Seven Heavens, heavens and back by night. Although never stated to have wings, it is almost always depicted as a pegasus-like being. The Buraq is also said to have transported certain Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets such as Abraham over long distances within a moment's duration. Etymology The ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'', referring to the writings of Al-Damiri (d.1405), considers ''al-burāq'' to be a derivative and adjective of ''barq'' "lightning/emitted lightning" or various general meanings stemming from the verb: "to beam, flash, gleam, glimmer, glisten, glitter, radiate, shimmer, shine, sparkle, twinkle". The name is thought to refer to the creature's lightning-like speed. According to ''Encyclopædia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of Adam in Islam, Adam, Noah in Islam, Noah, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Moses in Islam, Moses, Jesus in Islam, Jesus, and other Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets. He is believed to be the Seal of the Prophets in Islam, and along with the Quran, his teachings and Sunnah, normative examples form the basis for Islamic religious belief. Muhammad was born in Mecca to the aristocratic Banu Hashim clan of the Quraysh. He was the son of Abdullah ibn Abd al-Muttalib and Amina bint Wahb. His father, Abdullah, the son of tribal leader Abd al-Muttalib ibn Hashim, died around the time Muhammad was born. His mother Amina died when he was six, leaving Muhammad an orphan. He was raised under the care of his grandfather, Abd al-Muttalib, and paternal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Haram Al-Sharif
Al-Aqsa (; ) or al-Masjid al-Aqṣā () and also is the compound of Islamic religious buildings that sit atop the Temple Mount, also known as the Haram al-Sharif, in the Old City (Jerusalem), Old City of Jerusalem, including the Dome of the Rock, many mosques and prayer halls, madrasas, zawiya (prayer space), zawiyas, khalwa (structure), khalwas and other domes and religious structures, as well as the four encircling Minarets of the Al-Aqsa Mosque compound, minarets. It is considered the third Holiest sites in Islam, holiest site in Islam. The compound's main congregational mosque or Musalla, prayer hall is variously known as ''Al-Aqsa Mosque'', ''Qibli Mosque'' or ''al-Jāmiʿ al-Aqṣā'', while in some sources it is also known as ''al-Masjid al-Aqṣā''; the wider compound is sometimes known as Al-Aqsa Mosque compound in order to avoid confusion. During the rule of the Rashidun caliph Umar () or the Umayyad caliph Mu'awiya I (), a small prayer house on the compound was ere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warren's Gate
Warren's Gate () is an ancient entrance into the Temple platform in Jerusalem. Located about into the Western Wall Tunnel, the gate was first described by and later named after nineteenth century British surveyor Charles Warren. During the Second Temple period, Warren's Gate led to a tunnel and staircase at the Temple Mount. Following the Rashidun Caliphate conquest of Jerusalem from the Byzantines, Jews were allowed to pray inside the tunnel, turning the location into a Jewish synagogue. When the synagogue was destroyed in the First Crusade during the siege of Jerusalem in 1099, the tunnel ended up becoming a water cistern, thus its later name being ''Cistern 30''. The area is surrounded by a vaulted tunnel. Rabbi Yehuda Getz, the late official Rabbi of the Western Wall, believed that the Gate represented the point west of the Wall closest to the Holy of Holies. An underground dispute broke out in July 1981 between Jewish explorers who were inside Warren's Gate and Arab g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shechina
Shekhinah () is the English transliteration of a Hebrew word meaning "dwelling" or "settling" and denotes the presence of God in a place. This concept is found in Judaism from Talmudic literature. The word "Shekhinah" is found in the Bible only as a "Shechaniah", a masculine proper name. The Hebrew root “shakan” appears in numerous conjugations, it can be found 128 times. (See Strong’s Hebrew dictionary 7931.) It also appears in the Mishnah, the Talmud, and Midrash. Etymology The word ''shekhinah'' is first encountered in the rabbinic literature. S. G. F. Brandon, ed., ''Dictionary of Comparative Religion'' (New York: Charles Scribner's Sons 1970), p. 573: "Shekhinah". The Semitic root from which ''shekhinah'' is derived, ''š-k-n'', means "to settle, inhabit, or dwell". In the verb form, it is often used to refer to the dwelling of a person or animal in a place, or to the dwelling of God. Nouns derived from the root included ''shachen'' ("neighbor") and ''mishkan'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |