|
Wehha Of East Anglia
Wehha of East Anglia is listed by Anglo-Saxon records as a king of the East Angles. If he existed, Wehha ruled the East Angles as a pagan king during the 6th century, when the region was being established as a kingdom by migrants arriving from what is now Frisia and the southern Jutland peninsula. Early sources identify him as a member of the Wuffingas dynasty, which was established around the east coast of Suffolk. Nothing of his reign is known. According to the East Anglian tally from the ''Textus Roffensis'', Wehha was the son of Wilhelm. The 9th century ''History of the Britons'' lists Wehha, named as 'Guillem Guercha', as the first king of the East Angles, as well as his son and heir Wuffa, after whom the dynasty was named. It has been claimed that the name ''Wehha'' is a hypocoristic version of '' Wihstān'', from the Anglo-Saxon poem ''Beowulf''. This claim, along with evidence from finds discovered at Sutton Hoo since 1939, suggests a connection between the Wuffingas and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of The East Angles
The Kingdom of East Anglia, also known as the Kingdom of the East Angles, was a small independent Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon kingdom that comprised what are now the England, English counties of Norfolk and Suffolk and perhaps the eastern part of The Fens. The kingdom was one of the seven traditional members of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. The East Angles were initially ruled (from the 6th century until 749) by members of the Wuffingas dynasty, named after Wuffa of East Anglia, Wuffa, whose name means 'descendants of the wolf'. The last king was Guthrum II, who ruled in the 10th century. After 749 East Anglia was ruled by kings whose genealogy is not known, or by underkings who were subject to the control of the kings of Mercia. East Anglia briefly recovered its independence after the death of Offa of Mercia in 796, but Mercian hegemony was soon restored by his successor, Coenwulf of Mercia, Coenwulf. Between 826 and 869, following an East Anglian revolt in which the Mercian king, Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to Germanic peoples, Germanic settlers who became one of the most important cultural groups in Britain by the 5th century. The Anglo-Saxon period in Britain is considered to have started by about 450 and ended in 1066, with the Norman conquest of England, Norman Conquest. Although the details of Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, their early settlement and History of Anglo-Saxon England, political development are not clear, by the 8th century an Anglo-Saxon cultural identity which was generally called had developed out of the interaction of these settlers with the existing Romano-British culture. By 1066, most of the people of what is now England spoke Old English, and were considered English. Viking and Norman invasions chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newmarket, Suffolk
Newmarket is a market town and civil parish in the West Suffolk (district), West Suffolk district of Suffolk, England, 14 miles west of Bury St Edmunds and 14 miles northeast of Cambridge. In 2021, it had a population of 16,772. It is a global centre for thoroughbred horse race, thoroughbred horse racing, racehorse training, breeding, and horse health. Two Classic races and three British Champions Series races are held at Newmarket every year. The town has had close royal connections since the time of James I of England, James I, who built a palace there, and was also a base for Charles I of England, Charles I, Charles II of England, Charles II, and most monarchs since. Elizabeth II visited the town often to see her horses in training. Newmarket has over fifty horse training stables, two large racetracks, the Rowley Mile and the Newmarket Racecourse, July Course, and one of the most extensive and prestigious horse training grounds in the world. The town is home to over 3,500 rac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devil's Dyke, Cambridgeshire
Devil's Dyke or Devil's Ditch is a linear earthen barrier, thought to be of Anglo-Saxon origin, in eastern Cambridgeshire and Suffolk. It runs for in an almost straight line from Reach, Cambridgeshire, Reach to Woodditton, with a ditch and bank system facing southwestwards, blocking the open chalkland between the marshy The Fens, fens to the north and the formerly wooded hills to the south. It is a Scheduled Monument, a biological Site of Special Scientific Interest and a Special Area of Conservation. Description The name ''Devil's Ditch'' or ''Dyke'' is a post-Middle Ages, medieval one. In medieval times it was simply called the ''dic'' ("the ditch"), or ''le Micheldyche'' or ''magnum fossatum'' ("great ditch"). Devil's Dyke is over long and is the largest of a series of ancient Levee, dykes in Cambridgeshire. In some places the bank measures high and across. The highest point along the Devil's Dyke is at Gallows Hill, where it measures from the bottom of the ditch to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Angles
The Middle Angles were an important ethnic or cultural group within the larger kingdom of Mercia in England in the Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon period. Origins and territory It is likely that Angles (tribe), Angles broke into the English Midlands, Midlands from East Anglia and the Wash early in the 6th century. Those who established their control first came to be called ''Middil Engli'' (Middle Angles). Their territory was centred in modern Leicestershire and East Staffordshire, but probably extended as far as the Cambridgeshire uplands and the Chilterns. This gave them a strategically important place within both Mercia and England as a whole, dominating both the great land routes of Watling Street and Fosse Way, and the major river route of the River Trent, together with its tributaries, the River Tame, West Midlands, Tame and River Soar, Soar. Mercia The Middle Angles were incorporated into the wider kingdom of Mercia, apparently well before the reign of Penda (c.626–655), wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Essex
The Kingdom of the East Saxons (; ), referred to as the Kingdom of Essex , was one of the seven traditional kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was founded in the 6th century and covered the territory later occupied by the counties of Essex, Middlesex, much of Hertfordshire and (for a short while) west Kent. The last king of Essex was Sigered of Essex, who in 825 ceded the kingdom to Ecgberht, King of Wessex. Extent The Kingdom of Essex was bounded to the north by the River Stour and the Kingdom of East Anglia, to the south by the River Thames and Kent, to the east lay the North Sea and to the west Mercia. The territory included the remains of two provincial Roman capitals, Colchester and London. The kingdom included the Middle Saxon Province, which included the area of the later County of Middlesex and most, if not all, of Hertfordshire Although the province is ever recorded only as part of the East Saxon Kingdom, charter evidence shows that it was not part of its co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icknield Way
The Icknield Way is an ancient trackway in southern and eastern England that runs from Norfolk to Wiltshire. It follows the chalk escarpment that includes the Berkshire Downs and Chiltern Hills. Background It is generally said to be, within Great Britain, one of the oldest roads the route of which can still be traced, being one of the few long-distance trackways to have existed before the Romans occupied the country. However, this has been disputed, and the evidence for its being a prehistoric route has been questioned. The name is Celto-British in derivation, and may be named after the Iceni tribe. They may have established this route to permit trade with other parts of the country from their base in East Anglia. It has also been suggested that the road has older prehistoric origins. The name is also said to have been initially used for the part to the west and south (i.e. south of the River Thames) but now refers usually to the track or traces north of the Thames. From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Fens
The Fens or Fenlands in eastern England are a naturally marshy region supporting a rich ecology and numerous species. Most of the fens were drained centuries ago, resulting in a flat, dry, low-lying agricultural region supported by a system of drainage channels and man-made rivers (Ditch, dykes and drains) and automated pumping stations. There have been unintended consequences to this reclamation, as the land level has continued to sink and the dykes have been built higher to protect it from flooding. ''Fen'' is the local term for an individual area of marshland or former marshland. It also designates the type of marsh typical of the area, which has pH, neutral or alkaline water and relatively large quantities of dissolved minerals, but few other plant nutrition, plant nutrients. The Fens are a National Character Area, based on their landscape, biodiversity, geodiversity and economic activity. The Fens lie inland of the Wash, and are an area of nearly in the south east of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Sea in the north. It is more than long and wide, covering . It hosts key north European shipping lanes and is a major fishery. The coast is a popular destination for recreation and tourism in bordering countries, and a rich source of energy resources, including wind energy, wind and wave power. The North Sea has featured prominently in geopolitical and military affairs, particularly in Northern Europe, from the Middle Ages to the modern era. It was also important globally through the power northern Europeans projected worldwide during much of the Middle Ages and into the modern era. The North Sea was the centre of the Viking Age, Vikings' rise. The Hanseatic League, the Dutch Golden Age, Dutch Republic, and Kingdom of Great Britain, Brita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
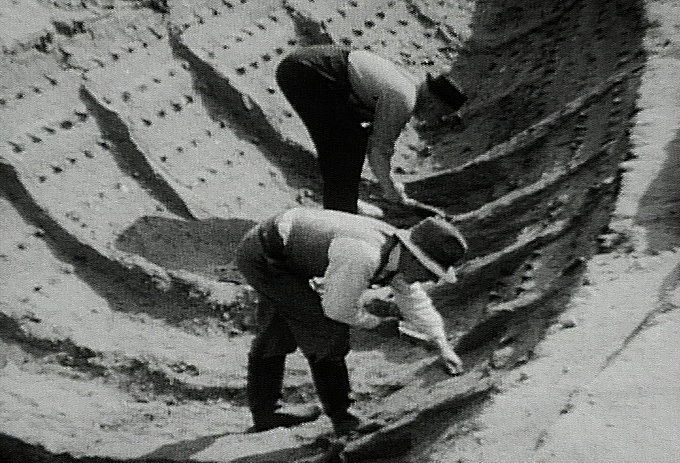
Ship Burial
A ship burial or boat grave is a burial in which a ship or boat is used either as the tomb for the dead and the grave goods, or as a part of the grave goods itself. If the ship is very small, it is called a boat grave. This style of burial was practiced by various seafaring cultures in Asia and Europe. Notable ship burial practices include those by the Germanic peoples, particularly by Viking Age Norsemen, as well as the pre-colonial ship burials described in the Boxer Codex (c. 15th century) in the Philippines. Asia-Pacific China The extinct Bo people of China's Sichuan and Yunnan provinces are known for their hanging coffins. The ancestors of the Bo people were instrumental in helping the Western Zhou overthrow the ruling Yin at the end of the Shang dynasty. Apart from this, the Bo people differed from other ethnic minorities in China through their burial traditions. Instead of the more common burial on the ground, the coffins of the Bo people were found hanging on cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sutton Hoo Helmet
The Sutton Hoo helmet is a decorated Anglo-Saxon helmet found during a 1939 excavation of the Sutton Hoo ship burial, ship-burial. It was thought to be buried around the years and is widely associated with an Anglo-Saxon leader, King Rædwald of East Anglia; its elaborate decoration may have given it a secondary function akin to a crown. The helmet was both a functional piece of armour and a decorative piece of metalwork. An iconic object from an archaeological find hailed as the "British Tutankhamen", it has become a symbol of the Early Middle Ages, "of Archaeology in general", and of England. The visage contains eyebrows, a nose, and moustache, creating the image of a man joined by a dragon's head to become a soaring dragon with outstretched wings. It was excavated as hundreds of rusted fragments; first displayed following an initial reconstruction in 1945–46, it took its present form after a second reconstruction in 1970–71. The helmet and the other artefacts from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature dates from the mid-7th century. After the Norman Conquest of 1066, English was replaced for several centuries by Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman (a langues d'oïl, type of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during the subsequent period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into what is now known as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles (tribe), Angles, Saxons and Jutes. As the Germanic settlers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |