|
Weaver Rail Mount
A Weaver rail mount is a system to connect telescopic sights (often via a scope mount) and other accessories to firearms and certain crossbows. It uses a pair of parallel rails and several slots perpendicular to these rails. The later Picatinny rail, developed by the US military, is a development of the key concepts of the Weaver system, and they are partially compatible. History The Weaver mount was developed by William Ralph Weaver (1905 – 8 November 1975) at his telescopic sight company W.R. Weaver Co., which he founded in 1930. Previous systems included the Leupold & Stevens, Leupold/Redfield mounts. Compared to the Leupold mount, the Weaver rail is not as strong and cannot be adjusted for windage. W.R. Weaver Co. became Weaver Optics, and was a subsidiary of Meade Instruments, Meade Instruments Corporation from 2002 to 2008, when it was on-sold to become part of Alliant Techsystems's Security and Sporting division in Onalaska, Wisconsin. Features Older Weaver system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telescopic Sight
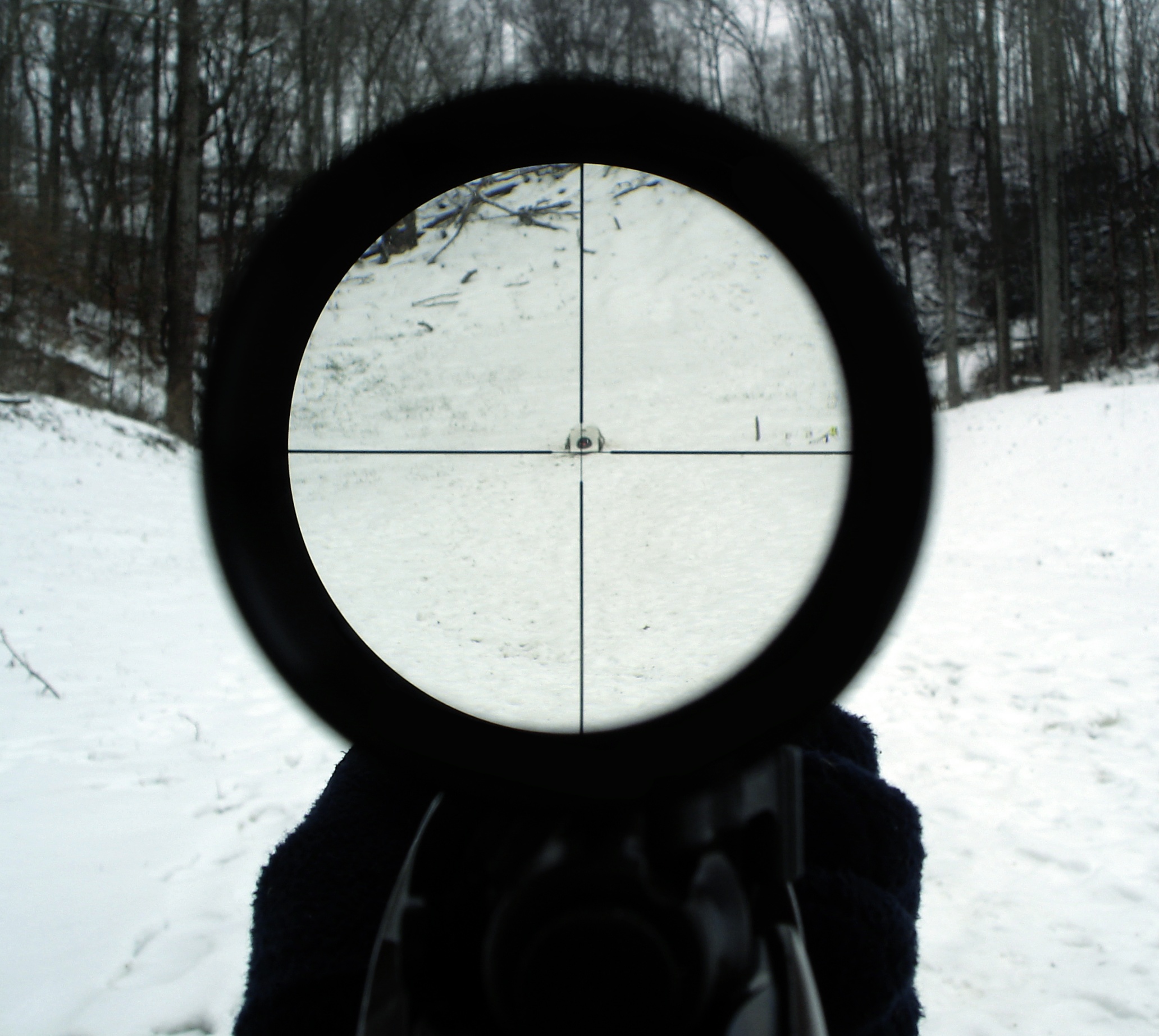
A telescopic sight, commonly called a scope informally, is an optical sighting device based on a refracting telescope. It is equipped with some form of a referencing pattern – known as a ''reticle'' – mounted in a focally appropriate position in its optical system to provide an accurate point of aim. Telescopic sights are used with all types of systems that require magnification in addition to reliable visual aiming, as opposed to non-magnifying iron sights, reflector (reflex) sights, holographic sights or laser sights, and are most commonly found on long-barrel firearms, particularly rifles, usually via a scope mount. Similar devices are also found on other platforms such as artillery, tanks and even aircraft. The optical components may be combined with optoelectronics to add night vision or smart device features. History The first experiments directed to give shooters optical aiming aids go back to the early 17th century. For centuries, different optical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scope Mount
Scope mounts are rigid implements used to attach (typically) a telescopic sight or other types of optical sights onto a firearm. The mount can be made integral to the scope body (such as the Zeiss rail) or, more commonly, an external fitting that clamp onto the scope tube via screw-tightened rings (similar to pipe shoes). The scope and mount are then fastened onto compatible interfaces on the weapon. Words such as ''mounts'' and ''bases'' are used somewhat loosely, and can refer to several different parts which are either used together or in place of each other as ways to mount optical sights to firearms. Attachment interfaces for scope mounts vary according to weapon design and user choice. Traditionally scope mounts are fastened onto firearms via tapped screw holes (usually on the receiver) and/or clamps (onto the barrel or stock). Since the mid-20th century, dovetail rails, where the mount is slided over a straight dovetail bracket with an inverted isosceles trapezoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firearms
A firearm is any type of gun that uses an explosive charge and is designed to be readily carried and operated by an individual. The term is legally defined further in different countries (see legal definitions). The first firearms originated in 10th-century China, when bamboo tubes containing gunpowder and pellet projectiles were mounted on spears to make the portable fire lance, operable by a single person, which was later used effectively as a shock weapon in the siege of De'an in 1132. In the 13th century, fire lance barrels were replaced with metal tubes and transformed into the metal-barreled hand cannon. The technology gradually spread throughout Eurasia during the 14th century. Older firearms typically used black powder as a propellant, but modern firearms use smokeless powder or other explosive propellants. Most modern firearms (with the notable exception of smoothbore shotguns) have rifled barrels to impart spin to the projectile for improved flight stability. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossbow
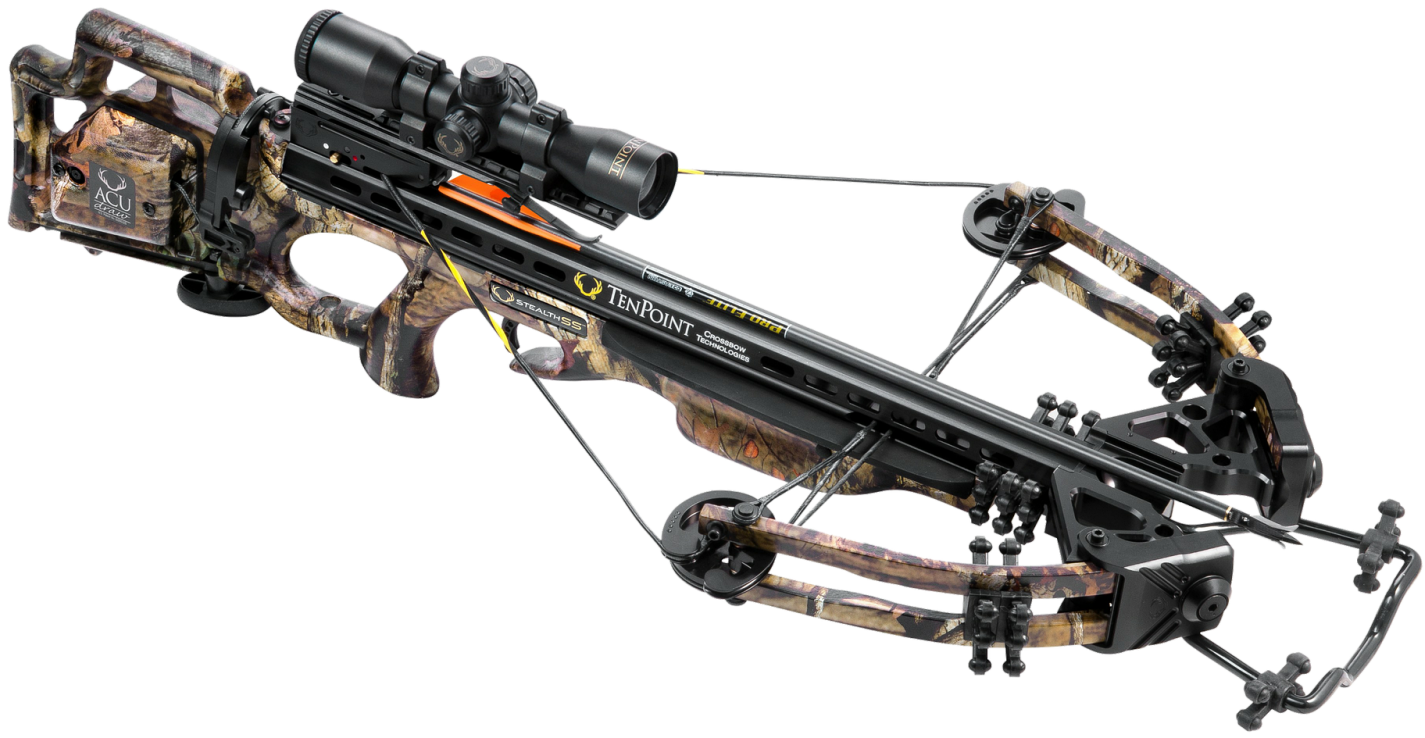
A crossbow is a ranged weapon using an Elasticity (physics), elastic launching device consisting of a Bow and arrow, bow-like assembly called a ''prod'', mounted horizontally on a main frame called a ''tiller'', which is hand-held in a similar fashion to the stock (firearms), stock of a long gun. Crossbows shoot arrow-like projectiles called ''crossbow bolt, bolts'' or ''quarrels''. A person who shoots crossbow is called a ''crossbowman'', an ''arbalister'' or an ''arbalist (crossbowman), arbalist'' (after the arbalest, a European crossbow variant used during the 12th century). Crossbows and bows use the same elastic launch principles, but differ in that an archer using a Bow and arrow, bow must draw-and-shoot in a quick and smooth motion with limited or no time for aiming, while a crossbow's design allows it to be spanned and cocked ready for use at a later time and thus affording them unlimited time to aim. When shooting bows, the archer must fully perform the bow draw, draw, h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picatinny Rail
The 1913 rail (MIL-STD-1913 rail) is an American rail integration system designed by Richard Swan that provides a mounting platform for firearm accessories. It forms part of the NATO standard STANAG 2324 rail. It was originally used for mounting of telescopic sights atop the receivers of larger caliber rifles. Once established as United States Military Standard, its use expanded to also attaching other accessories, such as: iron sights, tactical lights, laser sights, night-vision devices, reflex sights, holographic sights, foregrips, bipods, slings and bayonets. An updated version of the rail is adopted as a NATO standard as the STANAG 4694 NATO Accessory Rail. History Attempts to standardize the Weaver rail mount designs date from work by the A.R.M.S. company and Richard Swanson in the early 1980s. Specifications for the M16A2E4 rifle and the M4E1 carbine received type classification generic in December 1994. These were the M16A2 and the M4 modified wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leupold & Stevens
Leupold & Stevens, Inc. is an American manufacturer of telescopic sights, red dot sights, binoculars, rangefinders, spotting scopes, and eyewear located in Beaverton, Oregon, United States. The company, started in 1907, is on its fifth generation of family ownership.Leeson, Fred (November 17, 1996). "All in the family". ''The Oregonian''. History Leupold & Stevens was founded by the German immigrant Markus Friedrich (Fred) Leupold and his brother-in-law Adam Voelpel in 1907, under the name Leupold & Voelpel. At the time, the company specialized in the repair of survey equipment. In 1911, Leupold & Voelpel was contracted by John Cyprian (J.C.) Stevens to manufacture a water level recorder he had designed and patented. After the initial success of the product, he was made partner in 1914 and the company was renamed Leupold, Voelpel, and Co.Stevens, John Cyprian. ''The Autobiography of a Civil Engineer'', published 1959. Besides the first water level recorder, the company invented ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windage
In aerodynamics, firearms ballistics, and automobiles, windage is the effects of some fluid, usually air (e.g., wind) and sometimes liquids, such as oil. Aerodynamics Windage is a force created on an object by friction when there is relative movement between air and the object. Windage loss is the reduction in efficiency due to windage forces. For example, electric motors are affected by friction between the rotor and air. Large alternators have significant losses due to windage. To reduce losses, hydrogen gas may be used, since it is less dense. Causes of windage are: * The object is moving and being slowed by resistance from the air. * A wind is blowing, producing a force on the object. The term can refer to: * The effect of the force, for example the deflection of a missile or an aircraft by a cross wind. * The area and shape of the object that make it susceptible to friction, for example those parts of a boat that are exposed to the wind. Aerodynamic streamlining can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meade Instruments
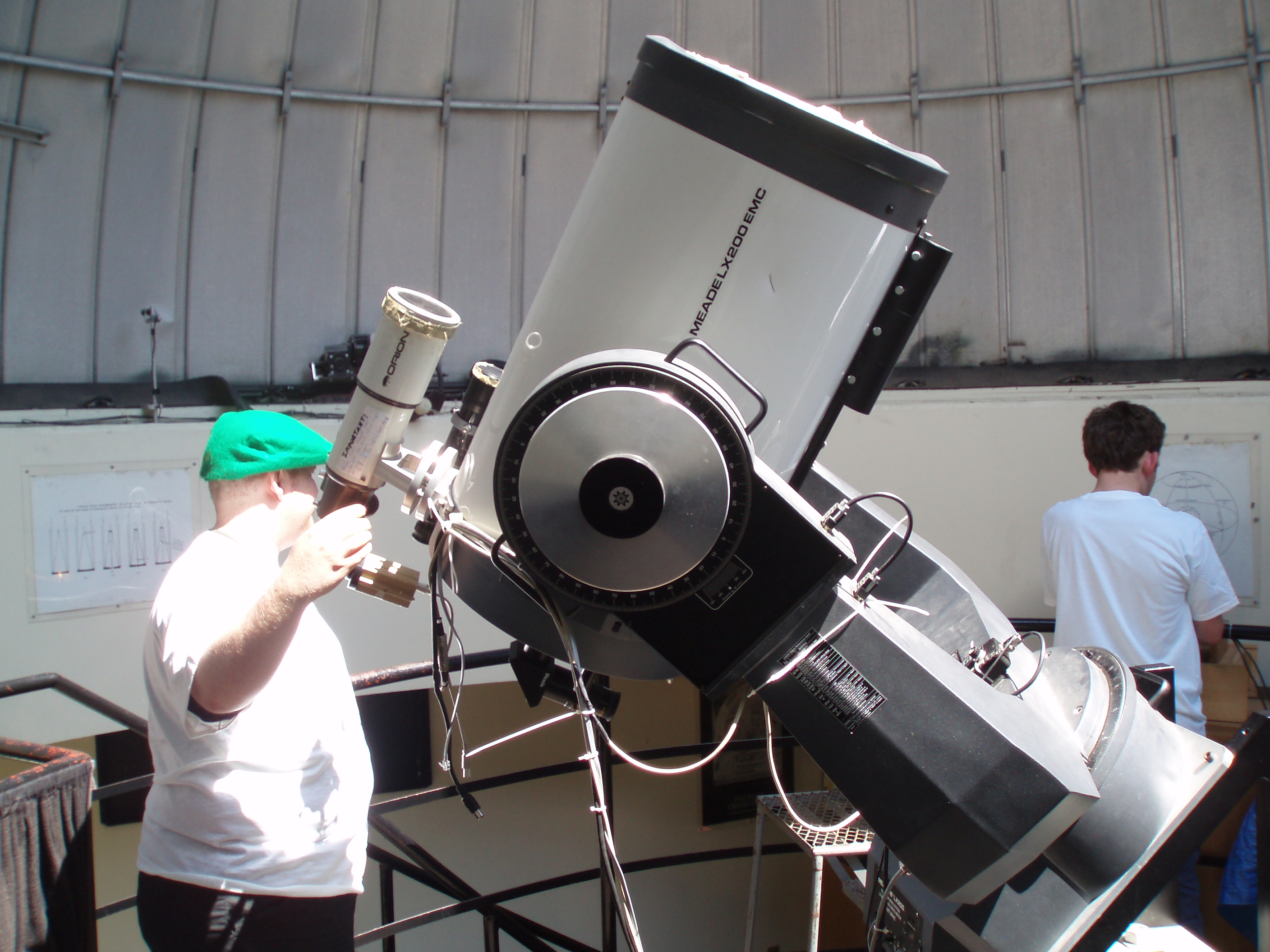
Meade Instruments Corporation (also shortened to Meade) was an American multinational corporation, multinational company (law), company headquartered in Watsonville, California, that manufactured, imported and distributed telescopes, binoculars, spotting scopes, microscopes, charge-coupled device, CCD cameras, and telescope accessories for the consumer market. It was, at one point, the world's largest manufacturer of telescopes. Besides selling under its "Meade" brand name, the company sells solar telescopes under the brand "Coronado". In July 2024, Sky and Telescope magazine reported that Optronic Technologies, the owner of Meade Instruments and Orion Telescopes, had closed their facilities in California and had laid off all of their employees. As of July 15, there had been no official announcement from the company, and S&T said they were trying to get more information from their sources. As of December, 2024, the Sky&Telescope website announced that the assets of Meade, Corona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alliant Techsystems
Alliant Techsystems Inc. (ATK) was an American Aerospace manufacturer, aerospace and arms industry, arms manufacturer headquartered in Arlington County, Virginia. The company operated across 22 states, Puerto Rico, and internationally. ATK revenue in fiscal year 2014 was about US$4.8 billion. On April 29, 2014, ATK announced that it would spin off its Sporting Group and merge its Aerospace and Defense Groups with Orbital Sciences Corporation. The spinoff of the Sporting Group to create Vista Outdoor and the merger leading to the creation of Orbital ATK were completed on February 9, 2015. The companies began operations as separate entities on February 20, 2015. Orbital ATK was bought by Northrop Grumman in 2018. History ATK was launched as an independent company in 1990 after Honeywell spun off its defense businesses to shareholders. The former Honeywell businesses had supplied defense products and systems to the U.S. and its allies for 50 years, including the first electronic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picatinny Rails
The 1913 rail (MIL-STD-1913 rail) is an American rail integration system designed by Richard Swan that provides a mounting platform for firearm accessories. It forms part of the NATO standard STANAG 2324 rail. It was originally used for mounting of telescopic sights atop the receivers of larger caliber rifles. Once established as United States Military Standard, its use expanded to also attaching other accessories, such as: iron sights, tactical lights, laser sights, night-vision devices, reflex sights, holographic sights, foregrips, bipods, slings and bayonets. An updated version of the rail is adopted as a NATO standard as the STANAG 4694 NATO Accessory Rail. History Attempts to standardize the Weaver rail mount designs date from work by the A.R.M.S. company and Richard Swanson in the early 1980s. Specifications for the M16A2E4 rifle and the M4E1 carbine received type classification generic in December 1994. These were the M16A2 and the M4 modified with new upp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Integration System
file:Dovetail.jpg, A dovetail rail on a rifle receiver for scope mount, mounting a Sight (device), sight A rail integration system (RIS; also called a rail accessory system (RAS), rail interface system, rail system, mount, base, gun rail, or simply a rail) is a generic term for any standardization, standardized attachment system for mounting firearm accessories via bar stock, bar-like straight brackets (i.e. "rails") often with regularly spaced slots. Rail systems are usually made of strips of metal or polymer screw-fastened onto the gun's receiver (firearms), receiver, barrel shroud, handguard, or stock (firearms)#Fore-end, fore-end stock to allow variable-position attachments. An advantage of the multiple rail slots is the moveable positions to adjust for optimal placement of each item for a user's preferences, along with the ability to switch different items at different placements due to varying eye reliefs on gun sights. Firearm accessories commonly compatible with or inten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |