|
Water Supply And Sanitation In Bolivia
Bolivia's drinking water and sanitation coverage has greatly improved since 1990 due to a considerable increase in sectoral investment. However, the country continues to suffer from what happens to be the continent's lowest coverage levels and from low quality of services. Political and institutional instability have contributed to the weakening of the sector's institutions at the national and local levels. Two concessions to foreign private companies in two of the three largest cities—Cochabamba and La Paz/El Alto—were prematurely ended in 2000 and 2006 respectively. The country's second largest city, Santa Cruz de la Sierra, relatively successfully manages its own water and sanitation system by way of cooperatives. The government of Evo Morales intends to strengthen citizen participation within the sector. Increasing coverage requires a substantial increase of investment financing. According to the government the main problems in the sector are low access to sanitat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suez (company, 1997–2008)
Suez S.A., known from 1997 to 2001 as Suez-Lyonnaise des eaux, was a leading French multinational corporation headquartered in the 8th arrondissement of Paris, with operations primarily in water, electricity and natural gas supply, and waste management. Suez was the result of a 1997 merger between the '' Compagnie de Suez'' and , a leading French water company. In the early 2000s Suez also owned some media and telecommunications assets, but later divested them. According to the ''Masons Water Yearbook'' 2004/5, Suez served 117.4 million people around the world. The company conducted a merger of equals with fellow utility company Gaz de France on 22 July 2008 to form GDF Suez (called Engie since 2015). The water and waste assets of Suez were spun off into a separate publicly traded company, Suez Environnement. History Suez was (and remains, through GDF Suez) one of the oldest continuously existing multinational corporations in the world, with one line of corporate history datin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-supply Of Water And Sanitation
Self-supply of water and sanitation (also called household-led water supply or individual supply) refers to an approach of incremental improvements to Water supply, water and sanitation services, which are mainly financed by the user. People around the world have been using this approach over centuries to incrementally upgrade their water and sanitation services.Olschewski, A. (2016)A business case for supported Self-supply as service delivery approach to achieve SDGs Skat Foundation, Switzerland, 7 th RWSN Forum “Water for Everyone” 7 ème Forum RWSN « L’eau pour tous » 29 Nov - 02 Dec 2016, Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire The approach does not refer to a specific technology or type of water source or sanitation service although it does have to be feasible to use and construct at a low cost and mostly using tools locally available. The approach is rather about an incremental improvement of these services. It is a Market economy, market-based approach and commonly does not involv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and Grant (money), grants to the governments of Least developed countries, low- and Developing country, middle-income countries for the purposes of economic development. The World Bank is the collective name for the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) and International Development Association (IDA), two of five international organizations owned by the World Bank Group. It was established along with the International Monetary Fund at the 1944 Bretton Woods Conference. After a slow start, its first loan was to France in 1947. In its early years, it primarily focused on rebuilding Europe. Over time, it focused on providing loans to developing world countries. In the 1970s, the World Bank re-conceptualized its mission of facilitating development as being oriented around poverty reduction. For the last 30 years, it has included NGOs and environmental groups in its loan portfolio. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooperative
A cooperative (also known as co-operative, coöperative, co-op, or coop) is "an autonomy, autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned and democratically-controlled wikt:Enterprise, enterprise". Cooperatives are democratically controlled by their members, with each member having one vote in electing the board of directors. They differ from Collective farming, collectives in that they are generally built from the bottom-up, rather than the top-down. Cooperatives may include: * Worker cooperatives: businesses owned and managed by the people who work there * Consumer cooperatives: businesses owned and managed by the people who consume goods and/or services provided by the cooperative * Producer cooperatives: businesses where producers pool their output for their common benefit ** e.g. Agricultural cooperatives * Purchasing cooperatives where members pool their purchasing power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
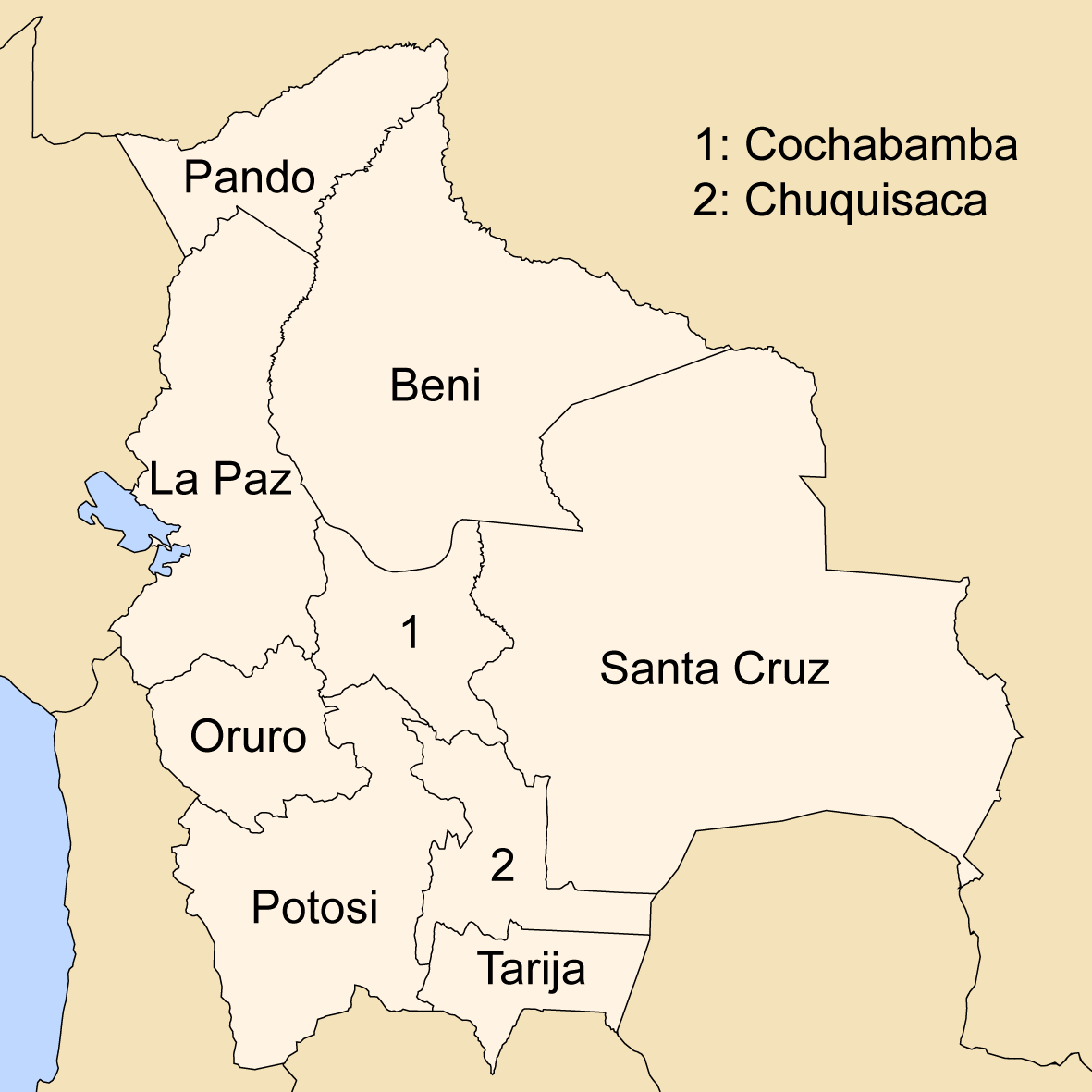
Departments Of Bolivia
Bolivia is a unitary state consisting of nine department (administrative division), departments (). Departments are the primary subdivisions of Bolivia, and possess certain rights under the Constitution of Bolivia. Each department is represented in the Plurinational Legislative Assembly—a bicameralism, bicameral legislature consisting of the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies. Each department is represented by four Senators, while Deputies are awarded to each department in proportion to their total population. Out of the nine departments, La Paz Department (Bolivia), La Paz was originally the most populous, with 2,706,351 inhabitants as of 2012 but the far eastern department of Santa Cruz Department (Bolivia), Santa Cruz has since surpassed it by 2020; Santa Cruz also claims the title as the largest, encompassing . Pando Department, Pando is the least populated, with a population of 110,436. The smallest in area is Tarija Department, Tarija, encompassing . Departments Forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potosi Air
Potosí or Potosi may refer to the following topics, whose names generally originate from the name of Potosí, a city in modern-day Bolivia that was the center of world silver production during the reign of the Spanish Empire: Places United States * Potosi, Missouri, in Washington County * Potosi, Nevada, a ghost town in Clark County, Nevada * Potosi, Texas, in Taylor County * Potosi (town), Wisconsin, in Grant County ** Potosi, Wisconsin, a village within the Town of Potosi Elsewhere * Potosí, the capital of Potosí Department, Bolivia, a silver mining center and UNESCO World Heritage Site * Potosí Department, a department in southwestern Bolivia * Potosí, Nicaragua, a town in Rivas Department * Potosi, Venezuela, a disestablished town in Táchira * San Luis Potosí City, capital and most populous city of San Luis Potosí, Mexico Mountains * Potosi Mountain (Nevada), U.S. * Potosí mountain range or ''Cordillera de Potosí'', to the southeast of the city of Potosí, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Movement Toward Socialism (Bolivia)
Movement for Socialism – Political Instrument for the Sovereignty of the Peoples (; MAS or MAS-IPSP), is a socialist political party in Bolivia. Its followers are known as ''Masistas''. In the December 2005 election, MAS-IPSP won the first ever majority victory by a single Bolivian party. The party continued to rule until 10 November 2019, and was victorious again in the 2020 elections. MAS-IPSP evolved out of the movement to defend the interests of coca growers. Evo Morales has articulated the goals of his party and popular organizations as the need to achieve plurinational unity, and to develop a new hydrocarbon law which guarantees 50% of revenue to Bolivia, although political leaders of MAS-IPSP recently interviewed showed interest in complete nationalization of the fossil fuel industries, as well as the country's lithium deposits. MAS-IPSP is the dominant force in municipal politics in Bolivia. In the most recent municipal elections in 2015, it was the only party to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condominial Sewerage
Condominial sewerage is the application of simplified sewerage coupled with consultations and ongoing interactions between users and agencies during planning and implementation. 2014 (retrieval date), World Health OrganizationSanitation challenge: Turning commitment into reality Accessed June 9, 2014, "...condominial sewers in Latin America... In Brazil, an alternative approach was developed more than 20 years ago and is now adopted as standard in many cities and towns. Condominial approaches are cheaper to build and operate than conventional systems..." Anurodh Lalit Jain, April 29, 2012, The HinduBreaking the sanitation taboo Accessed June 9, 2014, "...Brazil developed a condominial approach or simplified sewerage to construct water and sewerage networks ... Condominial sewerage is a low-cost sewer system that emphasises on community participation in planning and the maintenance of sewer system at the block level. Brazil quickly operationalised a 1,200-km network of condominial sewe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivian Gas Conflict
The Bolivian Gas War (Spanish: ''Guerra del Gas'') or Bolivian gas conflict was a social confrontation in Bolivia reaching its peak in 2003, centering on the exploitation of the country's vast natural gas reserves. The expression can be extended to refer to the general conflict in Bolivia over the exploitation of gas resources, thus including the 2005 protests and the election of Evo Morales as president. Before these protests, Bolivia had seen a series of similar earlier protests during the Cochabamba protests of 2000, which were against the privatization of the municipal water supply. The conflict had its roots in grievances over the government's economic policies concerning natural gas, as well as coca eradication policies, corruption and violent military responses against strikes. The "Bolivian gas war" thus came to a head in October 2003, leading to the resignation of President Gonzalo Sánchez de Lozada (aka "Goni"). Strikes and road blocks mounted by indigenous an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochabamba Protests Of 2000
The Cochabamba Water War, also known as the Bolivian Water War, was a series of protests that took place in Cochabamba, Bolivia's fourth largest city, between December 1999 and April 2000 in response to the privatization of the city's municipal water supply company SEMAPA. The wave of demonstrations and police violence was described as a public uprising against water prices. The tensions erupted when a new firm, Aguas del Tunari (a joint venture involving Bechtel), was required to invest in construction of a long-envisioned dam (a priority of mayor Manfred Reyes Villa), so they had drastically raised water rates. Protests, largely organized through the Coordinadora (Coalition in Defense of Water and Life), a community coalition, erupted in January, February, and April 2000, culminating in tens of thousands marching downtown and battling police. One civilian was killed. On 10 April 2000, the national government reached an agreement with the Coordinadora to reverse the privatizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |