|
Warburg Effect (oncology)
In oncology, the Warburg effect () is the observation that most cancers use aerobic glycolysis and lactic acid fermentation for energy generation rather than the mechanisms used by non-cancerous cells. This observation was first published by Otto Heinrich Warburg, who was awarded the 1931 Nobel Prize in Physiology for his "discovery of the nature and mode of action of the respiratory enzyme". The existence of the Warburg effect has fuelled popular misconceptions that cancer can be treated by dietary reductions in sugar and carbohydrate. In fermentation, the last product of glycolysis, pyruvate, is converted into lactate (lactic acid fermentation) or ethanol ( alcoholic fermentation). While fermentation produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP) only in low yield compared to the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation of aerobic respiration, it allows proliferating cells to convert nutrients such as glucose and glutamine more efficiently into biomass by avoiding unnecessary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crabtree Effect
The Crabtree effect, named after the English biochemist Herbert Grace Crabtree, describes the phenomenon whereby the yeast, ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'', produces ethanol (alcohol) in aerobic conditions at high external glucose concentrations rather than producing biomass via the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, the usual process occurring aerobically in most yeasts e.g. ''Kluyveromyces'' spp. This phenomenon is observed in most species of the ''Saccharomyces'', '' Schizosaccharomyces, Debaryomyces, Brettanomyces, Torulopsis, Nematospora,'' and ''Nadsonia'' genera. Increasing concentrations of glucose accelerates glycolysis (the breakdown of glucose) which results in the production of appreciable amounts of ATP through substrate-level phosphorylation. This reduces the need of oxidative phosphorylation done by the TCA cycle via the electron transport chain and therefore decreases oxygen consumption. The phenomenon is believed to have evolved as a competition mechanism (due to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerobic Fermentation
Aerobic fermentation or aerobic glycolysis is a metabolic process by which cells metabolize sugars via fermentation in the presence of oxygen and occurs through the repression of normal respiratory metabolism. Preference of aerobic fermentation over aerobic respiration is referred to as the Crabtree effect in yeast, and is part of the Warburg effect in tumor cells. While aerobic fermentation does not produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in high yield, it allows proliferating cells to convert nutrients such as glucose and glutamine more efficiently into biomass by avoiding unnecessary catabolic oxidation of such nutrients into carbon dioxide, preserving carbon-carbon bonds and promoting anabolism. Aerobic fermentation in yeast Aerobic fermentation evolved independently in at least three yeast lineages (''Saccharomyces'', '' Dekkera'', '' Schizosaccharomyces''). It has also been observed in plant pollen, trypanosomatids, mutated ''E. coli'', and tumor cells. Crabtree-positive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-deoxy-D-glucose
2-Deoxy--glucose is a glucose molecule which has the 2-hydroxyl group replaced by hydrogen, so that it cannot undergo further glycolysis. As such; it acts to competitively inhibit the production of glucose-6-phosphate from glucose at the phosphoglucoisomerase level (step 2 of glycolysis). 2-Deoxyglucose labeled with tritium or carbon-14 has been a popular ligand for laboratory research in animal models, where distribution is assessed by tissue-slicing followed by autoradiography, sometimes in tandem with either conventional or electron microscopy. 2-DG is up taken by the glucose transporters of the cell. Therefore, cells with higher glucose uptake, for example tumor cells, have also a higher uptake of 2-DG. Since 2-DG hampers cell growth, its use as a tumor therapeutic has been suggested, and in fact, 2-DG is in clinical trials. It is not completely clear how 2-DG inhibits cell growth. The fact that glycolysis is inhibited by 2-DG, seems not to be sufficient to explain why 2-DG tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
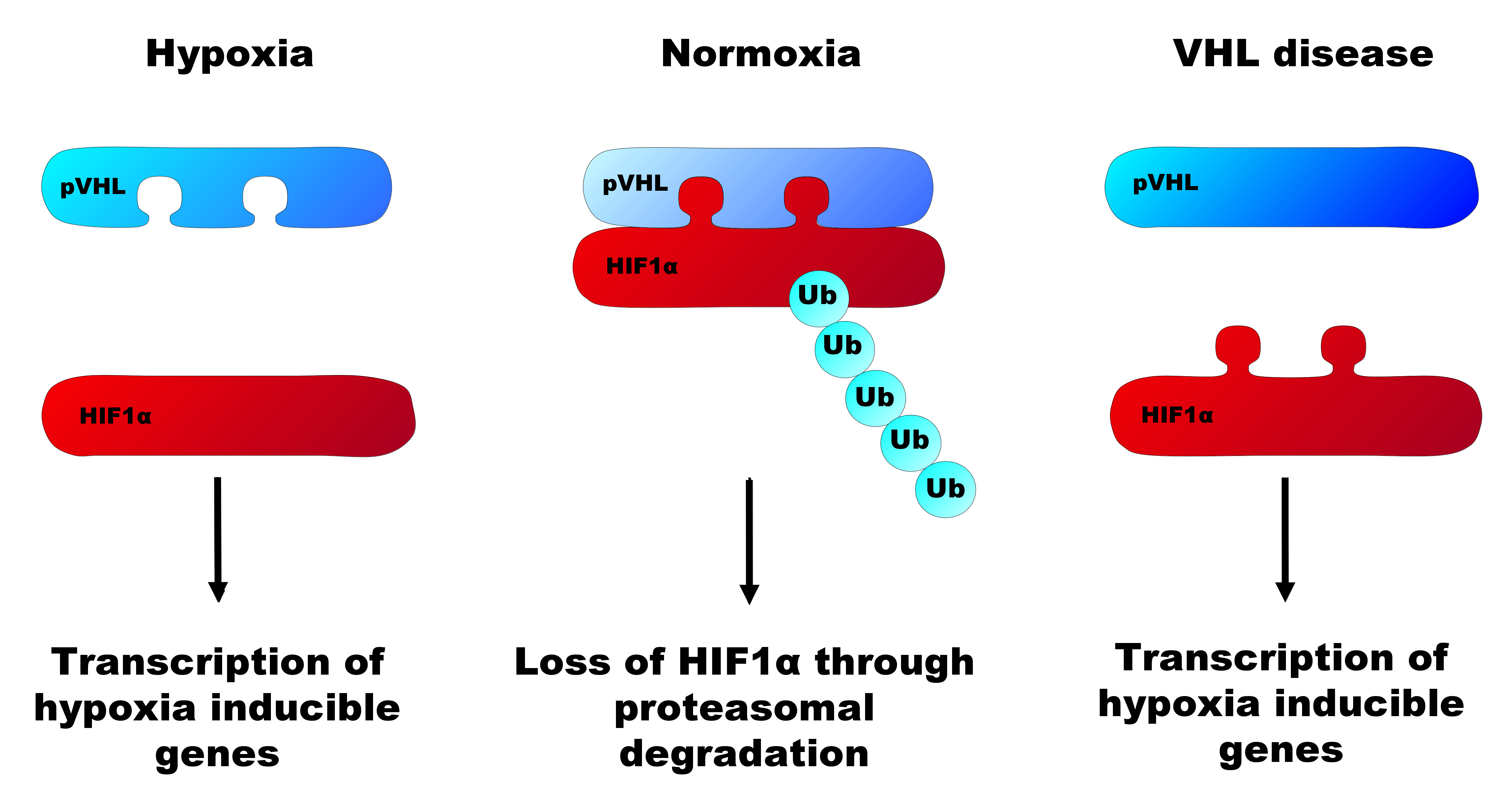
Von Hippel–Lindau Tumor Suppressor
The Von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor also known as pVHL is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''VHL'' gene. Mutations of the VHL gene are associated with Von Hippel–Lindau disease, which is characterized by hemangioblastomas of the brain, spinal cord and retina. It is also associated with kidney and pancreatic lesions. Function The protein encoded by the VHL gene is the substrate recognition component of a protein complex that includes elongin B, elongin C, and cullin-2, and possesses E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. This complex is involved in the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), which are transcription factors that play a central role regulating gene expression in response to changing oxygen levels. RNA polymerase II subunit POLR2G/RPB7 is also reported to be a target of this protein. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been observed. The resultant protein is produced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Cancer
Kidney cancer, also known as renal cancer, is a group of cancers that starts in the kidney. Symptoms may include blood in the urine, a lump in the abdomen, or back pain. Fever, weight loss, and tiredness may also occur. Complications can include metastasis, spread to the lungs or brain. The main types of kidney cancer are renal cell cancer (RCC), transitional cell cancer (TCC), and Wilms' tumor. RCC makes up approximately 80% of kidney cancers, and TCC accounts for most of the rest. Risk factors for RCC and TCC include smoking, certain pain medications, previous bladder cancer, being overweight, high blood pressure, certain chemicals, and a family history. Risk factors for Wilms' tumor include a family history and certain genetic disorders such as WAGR syndrome. Diagnosis may be suspected based on symptoms, urine testing, and medical imaging. It is confirmed by tissue biopsy. Treatment may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy. Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
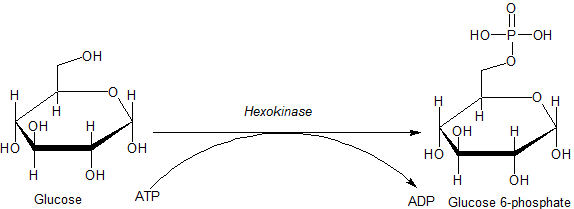
Hexokinase
A hexokinase is an enzyme that irreversibly phosphorylates hexoses (six-carbon sugars), forming hexose phosphate. In most organisms, glucose is the most important substrate for hexokinases, and glucose-6-phosphate is the most important product. Hexokinase possesses the ability to transfer an inorganic phosphate group from ATP to a substrate. Hexokinases should not be confused with glucokinase, which is a specific hexokinase found in the liver. All hexokinases are capable of phosphorylating several hexoses but hexokinase IV(D) is often misleadingly called glucokinase, though it is no more specific for glucose than the other mammalian isoenzymes. Variation Genes that encode hexokinase have been discovered in every domain of life, and exist among a variety of species that range from bacteria, yeast, and plants to humans and other vertebrates. The enzymes from yeast, plants and vertebrates all show clear sequence evidence of homology, but those of bacteria may not be relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giffen Good
In microeconomics and consumer theory, a Giffen good is a product that people consume more of as the price rises and vice versa, violating the law of demand. For ordinary goods, as the price of the good rises, the substitution effect makes consumers purchase less of it, and more of substitute goods; the income effect can either reinforce or weaken this decline in demand, but for an ordinary good never outweighs it. By contrast, a Giffen good is so strongly an inferior good (in higher demand at lower incomes) that the contrary income effect more than offsets the substitution effect, and the net effect of the good's price rise is to increase demand for it. This phenomenon is known as the Giffen paradox. Background Giffen goods are named after Scottish economist Sir Robert Giffen, to whom Alfred Marshall attributed this idea in his book '' Principles of Economics'', first published in 1890. Giffen first proposed the paradox from his observations of the purchasing habits o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biology), morphology) and death. These changes include Bleb (cell biology), blebbing, Plasmolysis, cell shrinkage, Karyorrhexis, nuclear fragmentation, Pyknosis, chromatin condensation, Apoptotic DNA fragmentation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses 50 to 70 1,000,000,000, billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For the average human child between 8 and 14 years old, each day the approximate loss is 20 to 30 billion cells. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malignant Transformation
Malignant transformation is the process by which cells acquire the properties of cancer. This may occur as a primary process in normal tissue, or secondarily as ''malignant degeneration'' of a previously existing benign tumor. Causes There are many causes of primary malignant transformation, or tumorigenesis. Most human cancers in the United States are caused by external factors, and these factors are largely avoidable. These factors were summarized by Doll and Peto in 1981, and were still considered to be valid in 2015. These factors are listed in the table. a Reproductive and sexual behaviors include: number of partners; age at first menstruation; zero versus one or more live births Examples of diet-related malignant transformation Diet and colon cancer Colon cancer provides one example of the mechanisms by which diet, the top factor listed in the table, is an external factor in cancer. The Western diet of African Americans in the United States is associated with a ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor Suppressor Gene
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell (biology), cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or reduction in its function. In combination with other genetic mutations, this could allow the cell to grow abnormally. The Loss-of-function mutation, loss of function for these genes may be even more significant in the development of human cancers, compared to the activation of oncogenes. TSGs can be grouped into the following categories: caretaker genes, gatekeeper genes, and more recently landscaper genes. Caretaker genes ensure stability of the genome via DNA repair and subsequently when mutated allow mutations to accumulate. Meanwhile, gatekeeper genes directly regulate cell growth by either inhibiting cell cycle progression or inducing apoptosis. Lastly, landscaper genes regulate growth by contributing to the surrounding e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.Kimball's Biology Pages. "Oncogenes" Free full text Most normal cells undergo a preprogrammed rapid cell death () if critical functions are altered and then malfunction. Activated oncogenes can cause those cells designated for apoptosis to survive and proliferate instead. Most oncogenes began as proto-oncogenes: normal genes involved in cell growth and proliferation or inhibition of apoptosis. If, through mutation, normal genes promoting cellular growth are up-regulated (gain-of-function mutation), they predispose the cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from substitution, insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics ( phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |