|
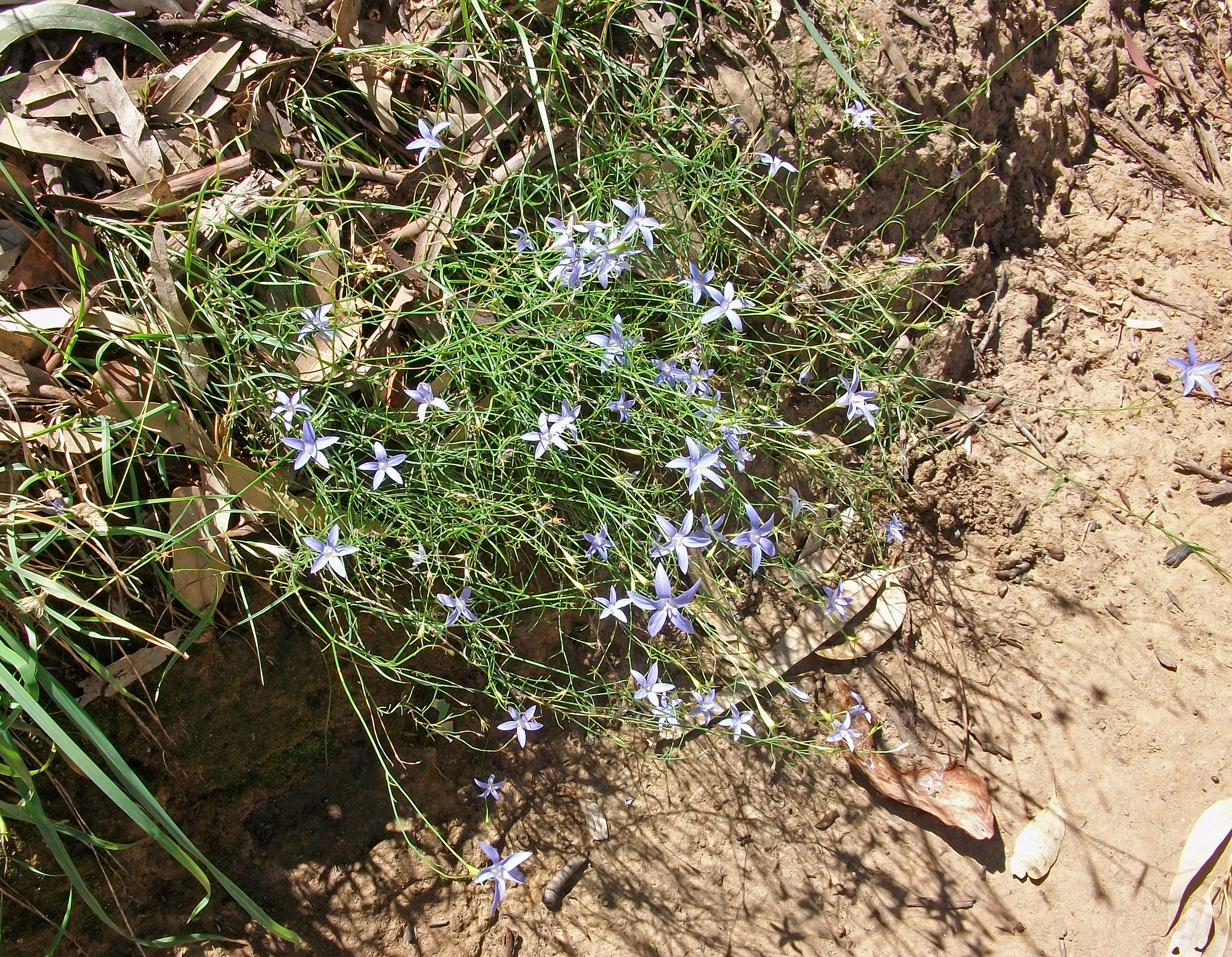
Wahlenbergia Marginata
''Wahlenbergia'' is a genus of around 260 species of flowering plants in the family Campanulaceae. Plants in this genus are perennial or annual herbs with simple leaves and blue to purple bell-shaped flowers, usually with five petals lobes. Species of ''Wahlenbergia'' are native to environments on all continents except North America, and on some isolated islands, but the greatest diversity occurs in the Southern Hemisphere. Description Plants in the genus ''Wahlenbergia'' are annual or perennial herbs, rarely shrubs, and sometimes have rhizomes. The stems are erect, circular in cross section and have simple leaves. The leaves decrease in size up the stem and usually have small scattered teeth on their edges. The flowers are borne on the end of the stems, either singly or arranged in a cyme. There are five sepals that remain until the fruiting stage. The petals are blue to purple and are joined at their base to form a bell-shaped or funnel-shaped tube with five lobes. There are u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Style (botany)
In botany, the style of an angiosperm flower is an organ of variable length that connects the ovary to the stigma. The style does not contain ovules; these are limited to the region of the gynoecium (female organs of the flower) called the "ovary". Structure The style is a narrow extension of the ovary, usually pointing upwards, connecting the ovary to the stigmatic papillae. It may be absent in some plants; in this case, it is referred to as a sessile stigma. Styles generally resemble more or less long tubes. The style can be open (with few cells occupying the central part, or even none), featuring a central canal that may be filled with mucilage. Alternatively, the style can be closed (completely filled with cells). Most plants with syncarpous pistils ( monocotyledons and some eudicotys) have open styles, whereas many eudicots and grasses have closed (solid) styles containing specialized secretory tissues, which connect the stigma to the center of the ovary. These tissu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wahlenbergia
''Wahlenbergia'' is a genus of around 260 species of flowering plants in the Family (biology), family Campanulaceae. Plants in this genus are Perennial plant, perennial or Annual plant, annual Herbaceous plant, herbs with simple leaves and blue to purple bell-shaped flowers, usually with five petals lobes. Species of ''Wahlenbergia'' are native to environments on all continents except North America, and on some isolated islands, but the greatest diversity occurs in the Southern Hemisphere. Description Plants in the genus ''Wahlenbergia'' are annual or perennial herbs, rarely shrubs, and sometimes have rhizomes. The stems are erect, circular in cross section and have simple leaves. The leaves decrease in size up the stem and usually have small scattered teeth on their edges. The flowers are borne on the end of the stems, either singly or arranged in a Inflorescence#Determinate or cymose, cyme. There are five sepals that remain until the fruiting stage. The petals are blue to purple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wahlenbergia Capensis
''Wahlenbergia capensis'', commonly known as the Cape bluebell, is a plant in the family ''Campanulaceae'' and is native to the Cape Province but has been introduced to Australia. It is an annual herb with up to four greenish blue, bell-shaped flowers with spreading petal lobes. Description ''Wahlenbergia capensis'' is an annual herb with a one to a few stems and grows to a height of . The lower leaves are egg-shaped to elliptic but become lance-shaped higher up. They are long and wide, sometimes with wavy edges and small teeth or lobes. Each plant has up to four bluish-green long stalked flowers that are dark blue near the centre and often have black spots. The five sepals are triangular, long and hairy. The petals form a tube, bell-shaped near the base with five spreading, egg-shaped to broadly elliptic lobes, long and wide. The five stamens have a filament long and an anther long. The style is dark blue with five branches on its tip. Flowering occurs from September to D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wahlenbergia Violacea
''Wahlenbergia'' is a genus of around 260 species of flowering plants in the family Campanulaceae. Plants in this genus are perennial or annual herbs with simple leaves and blue to purple bell-shaped flowers, usually with five petals lobes. Species of ''Wahlenbergia'' are native to environments on all continents except North America, and on some isolated islands, but the greatest diversity occurs in the Southern Hemisphere. Description Plants in the genus ''Wahlenbergia'' are annual or perennial herbs, rarely shrubs, and sometimes have rhizomes. The stems are erect, circular in cross section and have simple leaves. The leaves decrease in size up the stem and usually have small scattered teeth on their edges. The flowers are borne on the end of the stems, either singly or arranged in a cyme. There are five sepals that remain until the fruiting stage. The petals are blue to purple and are joined at their base to form a bell-shaped or funnel-shaped tube with five lobes. There are u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wahlenbergia Stricta
''Wahlenbergia stricta'', the Australian bluebell, tall bluebell or austral bluebell, is an Australian wildflower from the Campanulaceae family. It is considered the most commonly encountered of the Wahlenbergias. It is found in all Australian states but not the Northern Territory. It is often seen growing by the side of the road, enjoying the extra runoff. ''Wahlenbergia stricta'' is a perennial herb flowering mainly in spring or summer with pale blue bell-like flowers. The leaves are long and linear, long. The five-petalled flowers are erect on long, slender stems and about in diameter. It forms thin, carrot shaped tubers. Cultivation Australian bluebells are generally easily propagated by division or root cutting. The seed is a very fine, black powder. It germinates readily in a few weeks and is best directly sown into tubes or cells as the seed and plant are very small and hard to separate and prick out. There are a number of common cultivars, including various shade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wahlenbergia Roxburghii
''Wahlenbergia roxburghii'', the Roxburgh bellflower or dwarf cabbage tree, is an extinct member of a group of four species of ''Wahlenbergia'' once known from the island of Saint Helena, in the South Atlantic Ocean. It was last seen by naturalist John Charles Melliss in 1872. William Roxburgh recorded it in the thick forests on the south face of Diana's Peak. De Candolle notes it in dense woods around Diana's Peak and Halley's Mount. Burchell notes it 'On Sandy Bay ridge near Taylor's. Flowering: probably August to March. It was exceedingly rare in Meliss's time, it is not in his book as he had not found it. It was probably the increase of Phormium tenax planting on the ridge that pushed ''Wahlenbergia roxburghii'' into final extinction. It is an example of one of the early extinctions of Saint Helena plants as a result of human activity, with a history similar to that of the stringwood (''Acalypha rubrinervis''), (see List of extinct plants). See also *Flora of St Helena The fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Helena
Saint Helena (, ) is one of the three constituent parts of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, a remote British overseas territory. Saint Helena is a volcanic and tropical island, located in the South Atlantic Ocean, some 1,874 km (1,165 miles) west of the mainland of the continent of Africa, with the Southern African nations of Angola and Namibia on its southeastern coast being the closest nations geographically. The island is around west of the coast of southwestern South Africa, and east of the major seaport city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil in South America. Saint Helena measures about and had a population of 4,439 in the 2021 census. It was named after Helena, mother of Constantine I, Saint Helena (AD c.246/248–330), influential mother of the famous Roman Emperor Constantine the Great, Saint Constantine I the Great. (A.D 272–337, reigned 306–337), of the ancient Roman Empire. It is one of the most remote major islands in the world and was uninhabited unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australasia
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand (overlapping with Polynesia), and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands (overlapping with Melanesia). The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologically, where the term covers several slightly different but related regions. Derivation and definitions Charles de Brosses coined the term (as French ''Australasie'') in ''Histoire des navigations aux terres australes'' (1756). He derived it from the Latin for "south of Asia" and differentiated the area from Polynesia (to the east) and the southeast Pacific ( Magellanica). In the late 19th century, the term Australasia was used in reference to the "Australasian colonies". In this sense it related specifically to the British colonies south of Asia: New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Western Australia, Victoria (i.e., the Australian colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surface area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With nearly billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population. Demographics of Africa, Africa's population is the youngest among all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Based on 2024 projections, Africa's population will exceed 3.8 billion people by 2100. Africa is the least wealthy inhabited continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, ahead of Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including Geography of Africa, geography, Climate of Africa, climate, corruption, Scramble for Africa, colonialism, the Cold War, and neocolonialism. Despite this lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uppsala University
Uppsala University (UU) () is a public university, public research university in Uppsala, Sweden. Founded in 1477, it is the List of universities in Sweden, oldest university in Sweden and the Nordic countries still in operation. Initially founded in the 15th century, the university rose to significance during the rise of Swedish Empire, Sweden as a great power at the end of the 16th century and was then given relative financial stability with a large donation from Monarchy of Sweden, King Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden, Gustavus Adolphus in the early 17th century. Uppsala also has an important historical place in Swedish national culture, and national identity, identity for the Swedish establishment: in historiography, religion, literature, politics, and music. Many aspects of Swedish academic culture in general, such as the white student cap, originated in Uppsala. It shares some peculiarities, such as the student nation system, with Lund University and the University of Helsink ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Göran Wahlenberg
Georg (Göran) Wahlenberg (1 October 1780 – 22 March 1851) was a Swedish naturalist. He was born in Kroppa, Värmland County. Wahlenberg matriculated at Uppsala University in 1792, received his doctorate in Medicine in 1806, was appointed ''botanices demonstrator'' in 1814, and professor of medicine and botany in 1829, succeeding Carl Peter Thunberg. He was the last holder of the undivided chair that in the previous century had been held by Linnaeus. After his death in 1851, the chair was divided into more delimited professorships, and botany became the main duty of the borgströmian professorship, at the time held by Elias Fries. Wahlenberg made his main work in the field of plant geography and published, among other things the ''Flora lapponica'' (1812) and other works on the plant world of northernmost Sweden. He was among the first major scholars to contribute to the plant taxonomy and geography of the High Tatras in the Habsburg monarchy where he carried out re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |