|
Wadi Al-Arish
Wadi al-Arish is a dry riverbed in the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt. The river, when it flowed, was 250 kilometers long and flowed intro the Mediterranean Sea near the town of Arish. Wadi al-Arish is considered by some, including geographer Ishtori Haparchi, to be the Brook of Egypt mentioned in the Hebrew Bible that formed the southernmost border of the Land of Israel. The Wadi al-Arish catchment is the largest drainage system in the Sinai Peninsula. The African Humid Period The African humid period (AHP; also known by other names) was a climate period in Africa during the late Pleistocene and Holocene geologic epochs, when northern Africa was wetter than today. The covering of much of the Sahara desert by grass ... was the last time a river consistently flowed through the riverbed. The Wadi al-Arish was an important site in the Battle of Magdhaba. References {{coord, 31.1462, 33.8059, type:river_region:EG, display=title Wadis of Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadi
Wadi ( ; ) is a river valley or a wet (ephemerality, ephemeral) Stream bed, riverbed that contains water only when heavy rain occurs. Wadis are located on gently sloping, nearly flat parts of deserts; commonly they begin on the distal portions of alluvial fans and extend to inland sabkhas or dry lakes. Permanent channels do not exist, due to lack of continual water flow. Water percolates down into the stream bed, causing an abrupt loss of energy and resulting in vast deposition. Wadis may develop dams of sediment that change the stream patterns in the next flash flood. Wadis tend to be associated with centers of human population because sub-surface water is sometimes available in them. Nomadic and pastoral desert peoples will rely on seasonal vegetation found in wadis, even in regions as dry as the Sahara, as they travel in complex transhumance routes. The centrality of wadis to water – and human life – in desert environments gave birth to the distinct sub-field of wadi h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinai Peninsula
The Sinai Peninsula, or simply Sinai ( ; ; ; ), is a peninsula in Egypt, and the only part of the country located in Asia. It is between the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Red Sea to the south, and is a land bridge between Asia and Africa. Sinai has a land area of about (6 percent of Egypt's total area) and a population of approximately 600,000 people. Administratively, the vast majority of the area of the Sinai Peninsula is divided into two Governorates of Egypt, governorates: the South Sinai Governorate and the North Sinai Governorate. Three other governorates span the Suez Canal, crossing into African Egypt: Suez Governorate on the southern end of the Suez Canal, Ismailia Governorate in the center, and Port Said Governorate in the north. In the classical era, the region was known as Arabia Petraea. The peninsula acquired the name ''Sinai'' in modern times due to the assumption that a mountain near Saint Catherine's Monastery is the Biblical Mount Sinai. Mount Sinai i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arish
ʻArish or el-ʻArīsh ( ' ) is the capital and largest city of the North Sinai Governorate of Egypt, as well as the largest city on the Sinai Peninsula, lying on the Mediterranean coast northeast of Cairo and west of the Egypt–Gaza border. The population was 204,391 in 2023. In antiquity and the Early Middle Ages, the city was known as Rinokoroura (, ). ʻArīsh is located at the mouth of Wadi al-Arish, a long ephemeral watercourse. The Azzaraniq Protectorate is on the eastern side of ʻArīsh. Etymology There are several hypothetical possibilities for the origin of the modern name of the city, which is first mentioned under it in the 9th century. One possibility is that the name might be an Arab phonetic transcription of a pre-existing toponym. However, there is no name that fully qualifies as such, apart from the Ariza () of Hierokles, which is difficult to interpret. Another possibility is that the name el-Arish was given to a city that already existed in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishtori Haparchi
Ishtori Haparchi (1280–1355), also Estori Haparchi and Ashtori ha-Parhi () is the pen name of the 14th-century Jewish physician, geographer, and traveller, Isaac HaKohen Ben Moses.''Encyclopedia Judaica'' Keter, Jerusalem, 1972, "Estori Ha-Parchi," vol. 6, p.918. Yeshurun vol. 21 p. 855 Pen name HaParchi is commonly known by the title ''Kaftor va-Ferach'' taken from the name of his work. Another scholarly opinion suggests that the name HaParchi refers to his birthplace, Florence, which translates to "Perach" (Flower) in Hebrew. ''Ish Tori'', as he refers to himself in his book, may mean "Man of Tours", the capital of the medieval French county of Touraine,Ronald L. Eisenberg Essential Figures in Jewish Scholarship p. 72, ''Eshtori (Ishtori) ha-Parchi (France, 1280-1355)''. Accessed 8 October 2018. though according to other opinions "Ishtori" was simply his personal name, a single word. Biography Ishtori Haparchi was born in Jewish Provence in 1280. Haparchi was descended from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
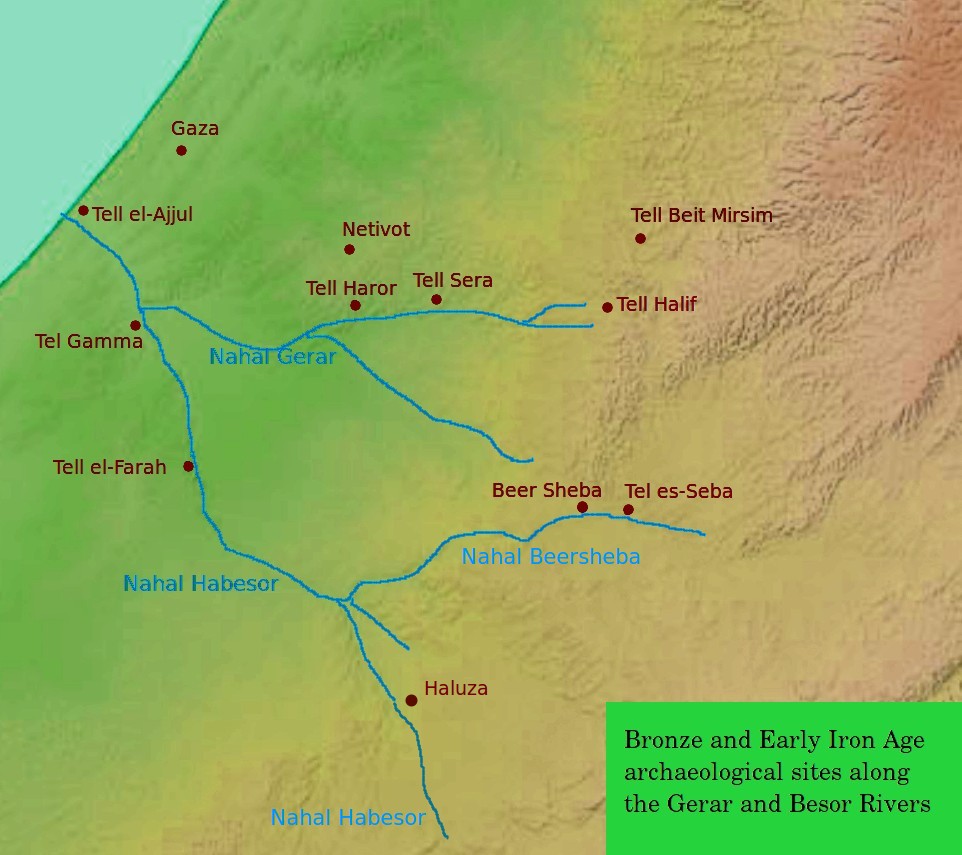
Brook Of Egypt
The Brook of Egypt () is a wadi identified in the Hebrew Bible as forming the southernmost border of the Land of Israel. A number of scholars in the past identified it with Wadi al-Arish, an ephemeral river flowing into the Mediterranean sea near the Egyptian city of Arish, while other scholars, including Israeli archaeologist Nadav Na'aman and the Italian Mario Liverani believe that the Besor stream, just to the south of Gaza, is the landform referenced in the Bible. A related phrase is ('river of Egypt'), used in Genesis . Nahal Besor The Israeli archaeologist Nadav Na'aman and the Italian Mario Liverani have suggested that Wadi Gaza or Nahal Besor, was the Brook of Egypt.Nadav Na'amanThe Brook of Egypt and Assyrian Policy on the Egyptian Border.Tel Aviv 6 (1979), pp. 68–90Mario Liverani (1995). Neo-Assyrian geography, p. 111. Università di Roma, Dipartimento di scienze storiche, archeologiche e antropologiche dell'Antichità. Certainly, it was controlled by Egypt i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach" . '' Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; ; or ), also known in Hebrew as (; ), is the canonical collection of scriptures, comprising the Torah (the five Books of Moses), the Nevi'im (the Books of the Prophets), and the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Of Israel
The Land of Israel () is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine. The definitions of the limits of this territory vary between passages in the Hebrew Bible, with specific mentions in , , and . Nine times elsewhere in the Bible, the settled land is referred as " from Dan to Beersheba", and three times it is referred as "from the entrance of Hamath unto the brook of Egypt" (, and ). These biblical limits for the land differ from the borders of established historical Israelite and later Jewish kingdoms, including the United Kingdom of Israel, the two kingdoms of Israel (Samaria) and Judah, the Hasmonean kingdom, and the Herodian kingdom. At their heights, these realms ruled lands with similar but not identical boundaries. Jewish religious belief defines the land as where Jewish religious law prevailed and ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catchment
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the drainage divide, made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern. Other terms for a drainage basin are catchment area, catchment basin, drainage area, river basin, water basin, and impluvium. In North America, they are commonly called a watershed, though in other English-speaking places, " watershed" is used only in its original sense, that of the drainage divide line. A drainage basin's boundaries are determined by watershed delineation, a common task in environmental engineering and science. In a closed drainage basin, or endorheic basin, rather than flowing to the ocean, water converges toward the interior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Humid Period
The African humid period (AHP; also known by other names) was a climate period in Africa during the late Pleistocene and Holocene geologic epochs, when northern Africa was wetter than today. The covering of much of the Sahara desert by grasses, trees and lakes was caused by changes in the Earth's axial tilt, changes in vegetation and dust in the Sahara which strengthened the African monsoon, and increased greenhouse gases. During the preceding Last Glacial Maximum, the Sahara contained extensive dune fields and was mostly uninhabited. It was much larger than today, and its lakes and rivers such as Lake Victoria and the White Nile were either dry or at low levels. The humid period began about 14,600–14,500 years ago at the end of Heinrich event 1, simultaneously to the Bølling–Allerød warming. Rivers and lakes such as Lake Chad formed or expanded, glaciers grew on Mount Kilimanjaro and the Sahara retreated. Two major dry fluctuations occurred; during the Younger Dryas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Magdhaba
The Battle of Magdhaba took place on 23 December 1916 during the Defence of Egypt section of the Sinai and Palestine Campaign in the First World War.The Battles Nomenclature Committee assigned 'Affair' to those engagements between forces smaller than a division; 'Action' to engagements between divisions and 'Battle' to engagements between corps. attles Nomenclature Committee 1922 p. 7/ref> The attack by the Anzac Mounted Division took place against an entrenched Ottoman Army garrison to the south and east of Bir Lahfan in the Sinai desert, some inland from the Mediterranean coast. This Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) victory against the Ottoman Empire garrison also secured the town of El Arish after the Ottoman garrison withdrew. In August 1916, a combined Ottoman and German Empire army had been forced to retreat to Bir el Abd, after the British victory in the Battle of Romani. During the following three months the defeated force retired further eastwards to El Arish, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |