|
WRN Helicase
Werner syndrome ATP-dependent helicase, also known as DNA helicase, RecQ-like type 3, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''WRN'' gene. WRN is a member of the RecQ Helicase family. Helicase enzymes generally unwind and separate double-stranded DNA. These activities are necessary before DNA can be copied in preparation for cell division (DNA replication). Helicase enzymes are also critical for making a blueprint of a gene for protein production, a process called transcription. Further evidence suggests that Werner protein plays a critical role in repairing DNA. Overall, this protein helps maintain the structure and integrity of a person's DNA. The ''WRN'' gene is located on the short (p) arm of chromosome 8 between positions 12 and 11.2, from base pair 31,010,319 to base pair 31,150,818. Structure and function WRN is a member of the RecQ Helicase family. It is the only RecQ Helicase that contains 3' to 5' exonuclease activity. These exonuclease activities include de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicase
Helicases are a class of enzymes that are vital to all organisms. Their main function is to unpack an organism's genetic material. Helicases are motor proteins that move directionally along a nucleic double helix, separating the two hybridized nucleic acid strands (hence '' helic- + -ase''), via the energy gained from ATP hydrolysis. There are many helicases, representing the great variety of processes in which strand separation must be catalyzed. Approximately 1% of eukaryotic genes code for helicases. The human genome codes for 95 non-redundant helicases: 64 RNA helicases and 31 DNA helicases. Many cellular processes, such as DNA replication, transcription, translation, recombination, DNA repair and ribosome biogenesis involve the separation of nucleic acid strands that necessitates the use of helicases. Some specialized helicases are also involved in sensing viral nucleic acids during infection and fulfill an immunological function. Genetic mutations that affect helicase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune Checkpoint
Immune checkpoints are regulators of the immune system. These pathways are crucial for self-tolerance, which prevents the immune system from attacking cells indiscriminately. However, some cancers can protect themselves from attack by stimulating immune checkpoint targets. Inhibitory checkpoint molecules are targets for cancer immunotherapy due to their potential for use in multiple types of cancers. Currently approved checkpoint inhibitors block CTLA4, PD-1 and PD-L1. For the related basic science discoveries, James P. Allison and Tasuku Honjo won the Tang Prize, Tang Prize in Biopharmaceutical Science and the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2018. Stimulatory checkpoint molecules Four stimulatory checkpoint molecules are members of the TNF receptor superfamily, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily—CD27, CD40, OX40, GITR and CD137. Another two stimulatory checkpoint molecules belong to the B7-CD28 superfamily—CD28 itself and ICOS. * CD27: This molec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G-quadruplex
In molecular biology, G-quadruplex secondary structures (G4) are formed in nucleic acids by sequences that are rich in guanine. They are helical in shape and contain guanine tetrads that can form from one, two or four strands. The unimolecular forms often occur naturally near the ends of the chromosomes, better known as the telomeric regions, and in transcriptional regulatory regions of multiple genes, both in microbes and across vertebrates including oncogenes in humans. Four guanine bases can associate through Hoogsteen hydrogen bonding to form a square planar structure called a guanine tetrad (G-tetrad or G-quartet), and two or more guanine tetrads (from G-tracts, continuous runs of guanine) can stack on top of each other to form a G-quadruplex. The placement and bonding to form G-quadruplexes is not random and serve very unusual functional purposes. The quadruplex structure is further stabilized by the presence of a cation, especially potassium, which sits in a centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
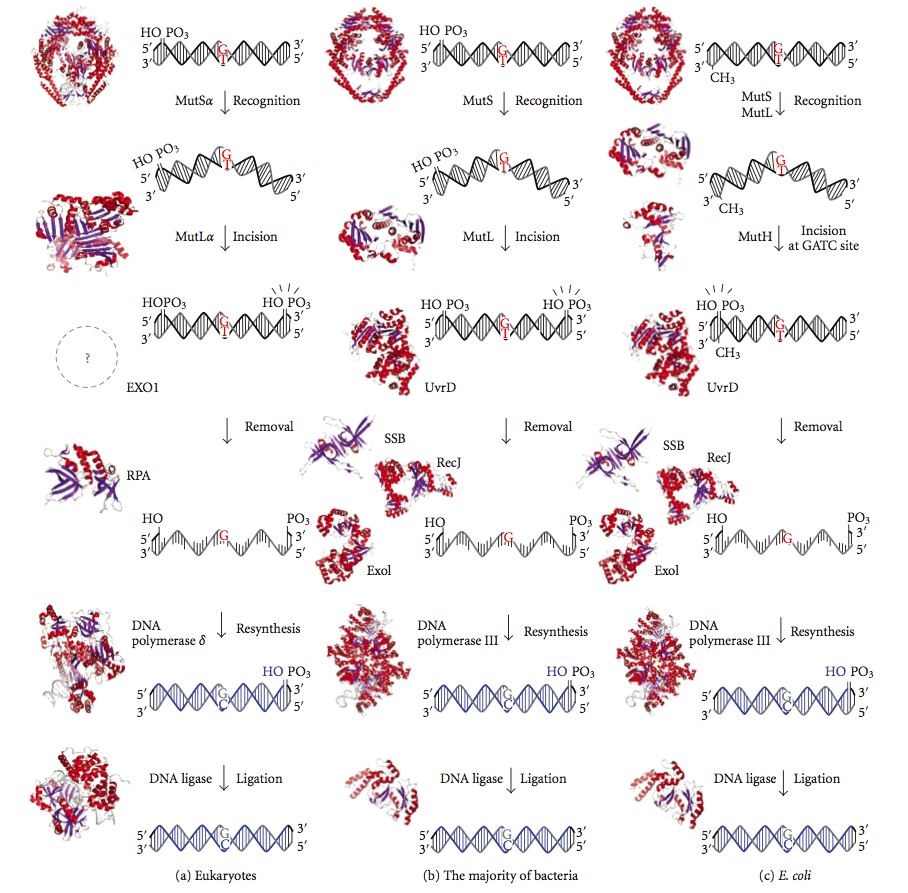
Mismatch Repair
DNA mismatch repair (MMR) is a system for recognizing and repairing erroneous insertion, deletion, and mis-incorporation of nucleobase, bases that can arise during DNA replication and Genetic recombination, recombination, as well as DNA repair, repairing some forms of DNA damage. Mismatch repair is strand-specific. During DNA synthesis the newly synthesised (daughter) strand will commonly include errors. In order to begin repair, the mismatch repair machinery distinguishes the newly synthesised strand from the template (parental). In gram-negative bacteria, transient methylase, hemimethylation distinguishes the strands (the parental is methylated and daughter is not). However, in other prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the exact mechanism is not clear. It is suspected that, in eukaryotes, newly synthesized lagging-strand DNA transiently contains Nick (DNA), nicks (before being sealed by DNA ligase) and provides a signal that directs mismatch proofreading systems to the appropriate st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsatellites
A microsatellite is a tract of repetitive DNA in which certain DNA motifs (ranging in length from one to six or more base pairs) are repeated, typically 5–50 times. Microsatellites occur at thousands of locations within an organism's genome. They have a higher mutation rate than other areas of DNA leading to high genetic diversity. Microsatellites are often referred to as short tandem repeats (STRs) by forensic geneticists and in genetic genealogy, or as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) by plant geneticists. Microsatellites and their longer cousins, the minisatellites, together are classified as VNTR (variable number of tandem repeats) DNA. The name "satellite" DNA refers to the early observation that centrifugation of genomic DNA in a test tube separates a prominent layer of bulk DNA from accompanying "satellite" layers of repetitive DNA. They are widely used for DNA profiling in cancer diagnosis, in kinship analysis (especially paternity testing) and in forensic identific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
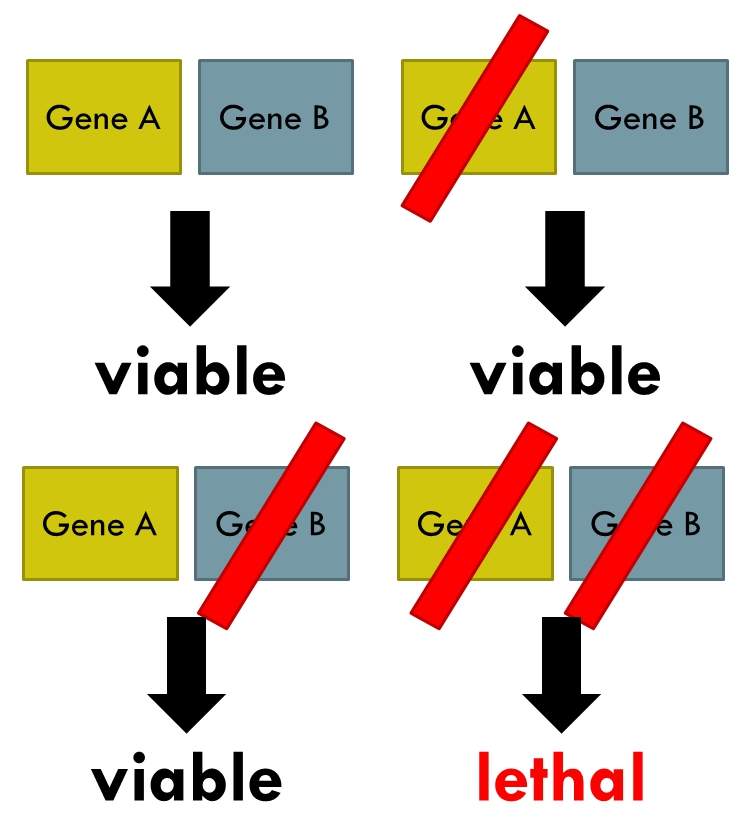
Synthetic Lethality
Synthetic lethality is defined as a type of genetic interaction where the combination of two genetic events results in cell death or death of an organism. Although the foregoing explanation is wider than this, it is common when referring to synthetic lethality to mean the situation arising by virtue of a combination of deficiencies of two or more genes leading to cell death (whether by means of apoptosis or otherwise), whereas a deficiency of only one of these genes does not. In a synthetic lethal genetic screen, it is necessary to begin with a mutation that does not result in cell death, although the effect of that mutation could result in a differing phenotype (slow growth for example), and then systematically test other mutations at additional loci to determine which, in combination with the first mutation, causes cell death arising by way of deficiency or abolition of expression. Synthetic lethality has utility for purposes of molecular targeted cancer therapy. The first exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aging
Ageing (or aging in American English) is the process of becoming Old age, older until death. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi; whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentially biologically immortal. In a broader sense, ageing can refer to single cells within an organism which have Cellular senescence, ceased dividing, or to the Population ageing, population of a species. In humans, ageing represents the accumulation of changes in a human being over time and can encompass physical, psychological, and social changes. Reaction time, for example, may slow with age, while memories and general knowledge typically increase. Of the roughly 150,000 people who die each day across the globe, about two-thirds die from age-related causes. Current Theory of aging, ageing theories are assigned to the damage concept, whereby the accumulation of damage (such as DNA oxidation) may cause biological systems to fail, or to the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (; : nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have #Anucleated_cells, no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have Multinucleate, many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long strands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are Nuclear organization, structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from substitution, insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics ( phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Werner Syndrome
Werner syndrome (WS) or Werner's syndrome, also known as "adult progeria",James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ''Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology''. (10th ed.). Saunders. . is a rare autosomal recessive disorder which is characterized by the appearance of premature aging. Werner syndrome is named after the German scientist Otto Werner. He identified the syndrome in four siblings observed with premature aging, which he explored as the subject of his dissertation of 1904. It has a global incidence rate of less than 1 in 100,000 live births (although incidence in Japan and Sardinia is higher, affecting 1 in 20,000–40,000 and 1 in 50,000, respectively). 1,300 cases had been reported as of 2006. Affected individuals typically grow and develop normally until puberty; the mean age of diagnosis is twenty-four, often realized when the adolescent growth spurt is not observed. The youngest person diagnosed was six years old. The median and mean ages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |