|
WITI Hall Of Fame
The Women in Technology International Hall of Fame was established in 1996 by Women in Technology International (WITI) to honor women who contribute to the fields of science and technology. Women in Technology International Hall of Fame inductees 1996 * Ruth Leach Amonette (1916–2004), IBM's first woman vice president (1943–1953) * Dr. Eleanor K. Baum (born 1940), American electrical engineer and educator. First female dean of (Cooper Union) School of Engineering.Hatch, Sybil E. (2006). ''Changing Our World: True Stories of Women Engineers.'' ASCE Publications, Proffitt, Pamela (1999). ''Notable Women Scientists.'' Gale Group, First female president of the American Society for Engineering Education * Dr. Jaleh Daie (born 1948), managing partner, Aurora Equity, a Palo Alto-based investment company financing technology start ups. Treasurer of Space Foundation, US Space Foundation (first woman appointed to its board of directors). Member of Band of Angels (Investors), Band of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women In Technology International
Women in Technology International (WITI) is an organization promoting the achievements of women in technology and extending support, opportunities, and inspiration. It was founded by Carolyn Leighton in 1989 as the International Network of Women in Technology. It was renamed to the WITI Professional Association in 2001 when it acted as a trade association for women in technology. It is known for producing the List of Women in Technology International Hall of Fame inductees, Women in Technology International Hall of Fame, which inducts women who have made a significant contribution to technology. Started from an email group in 1989, by 2012 the group had grown to 2 million people and became the leading organization for women in technology. The 2014 WITI 25-year conference Powering Up! included speakers such as Gwynne Shotwell, President (corporate title), President and Chief Operating Officer at SpaceX. In 2022, Randstad Technologies announced a partnership with WITI to address gend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Commerce Department
The United States Department of Commerce (DOC) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government. It is responsible for gathering data for business and governmental decision making, establishing industrial standards, catalyzing economic development, promoting foreign direct investment, and safeguarding national economic security. The Department of Commerce is one of four federal agencies authorized to appoint personnel in the United States Foreign Service, and its NOAA Corps — formerly the Coast and Geodetic Survey Corps — is one of the eight branches of the uniformed services of the United States. During a large-scale disaster or catastrophe, it assumes the coordinating responsibilities for the economic recovery support function under the national disaster recovery framework. Since 2023, it has led U.S. government activities related to safe artificial intelligence development and, from 1913 to 1939, it managed the National Aquarium. The department is headed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Scientist
A computer scientist is a scientist who specializes in the academic study of computer science. Computer scientists typically work on the theoretical side of computation. Although computer scientists can also focus their work and research on specific areas (such as algorithm and data structure development and design, software engineering, information theory, database theory, theoretical computer science, numerical analysis, programming language theory, compiler, computer graphics, computer vision, robotics, computer architecture, operating system), their foundation is the theoretical study of computing from which these other fields derive. A primary goal of computer scientists is to develop or validate models, often mathematical, to describe the properties of computational systems (Processor (computing), processors, programs, computers interacting with people, computers interacting with other computers, etc.) with an overall objective of discovering designs that yield useful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frances Allen
Frances Elizabeth Allen (August 4, 1932August 4, 2020) was an American computer scientist and pioneer in the field of optimizing compilers. Allen was the first woman to become an IBM Fellow, and in 2006 became the first woman to win the Turing Award. Her achievements include seminal work in compilers, program optimization, and parallelization. She worked for IBM from 1957 to 2002 and subsequently was a Fellow Emerita. Early life and education Allen grew up on a farm in Peru, New York, near Lake Champlain, as the oldest of six children. Her father was a farmer, and her mother an elementary schoolteacher. Her early elementary education took place in a one-room school house a mile away from her home, and she later attended a local high school. She graduated from The New York State College for Teachers (now part of the University at Albany, SUNY) with a Bachelor of Science degree in mathematics in 1954 and began teaching school in Peru, New York. After two years, she enrolled at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
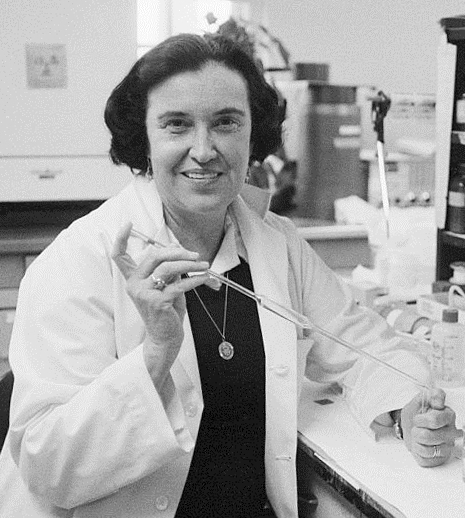
Rosalyn Yalow
Rosalyn Sussman Yalow (July 19, 1921 – May 30, 2011) was an American medical physicist, and a co-winner of the 1977 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (together with Roger Guillemin and Andrew Schally) for development of the radioimmunoassay technique. She was the second woman (after Gerty Cori), and the first American-born woman, to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Biography Childhood Rosalyn Sussman Yalow was born in the Bronx, New York, the daughter of Clara (née Zipper) and Simon Sussman, and was raised in a Jewish household. She went to Walton High School (Bronx), New York City. After high school, she attended the all-female, tuition-free Hunter College, where her mother hoped she would learn to become a teacher. Instead, Yalow decided to study physics. College Yalow knew how to type, and was able to get a part-time position as a secretary to Dr. Rudolf Schoenheimer, a leading biochemist at Columbia University's College of Physicians and Surgeo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project was directed by Major General Leslie Groves of the United States Army Corps of Engineers, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Nuclear physicist J. Robert Oppenheimer was the director of the Los Alamos Laboratory that designed the bombs. The Army program was designated the Manhattan District, as its first headquarters were in Manhattan; the name gradually superseded the official codename, Development of Substitute Materials, for the entire project. The project absorbed its earlier British counterpart, Tube Alloys, and subsumed the program from the American civilian Office of Scientific Research and Development. The Manhattan Project employed nearly 130,000 people at its peak and cost nearly US$2 billion (equivalent to about $ b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate causes of Phenomenon, phenomena, and usually frame their understanding in mathematical terms. They work across a wide range of Physics#Research fields, research fields, spanning all length scales: from atom, sub-atomic and particle physics, through biological physics, to physical cosmology, cosmological length scales encompassing the universe as a whole. The field generally includes two types of physicists: Experimental physics, experimental physicists who specialize in the observation of natural phenomena and the development and analysis of experiments, and Theoretical physics, theoretical physicists who specialize in mathematical modeling of physical systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena. Physicists can apply their k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chien-Shiung Wu
Chien-Shiung Wu ( zh, t=吳健雄, p=Wú Jiànxióng, w=Wu2 Chien4-Hsiung2; May 31, 1912 – February 16, 1997) was a Chinese-American particle physics, particle and experimental physicist who made significant contributions in the fields of nuclear physics, nuclear and particle physics. Wu worked on the Manhattan Project, where she helped develop the process for separating uranium into uranium-235 and uranium-238 isotopes by gaseous diffusion. She is best known for conducting the Wu experiment, which proved that Parity (physics), parity is not conservation law, conserved. This discovery resulted in her colleagues Tsung-Dao Lee and Chen-Ning Yang winning the 1957 Nobel Prize in Physics, while Wu herself was awarded the inaugural Wolf Prize in Physics in 1978. Her expertise in experimental physics evoked comparisons to Marie Curie. Her nicknames include the "First Lady of Physics", the "Chinese Marie Curie" and the "Queen of Nuclear Research". Early life Chien-Shiung Wu was born i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
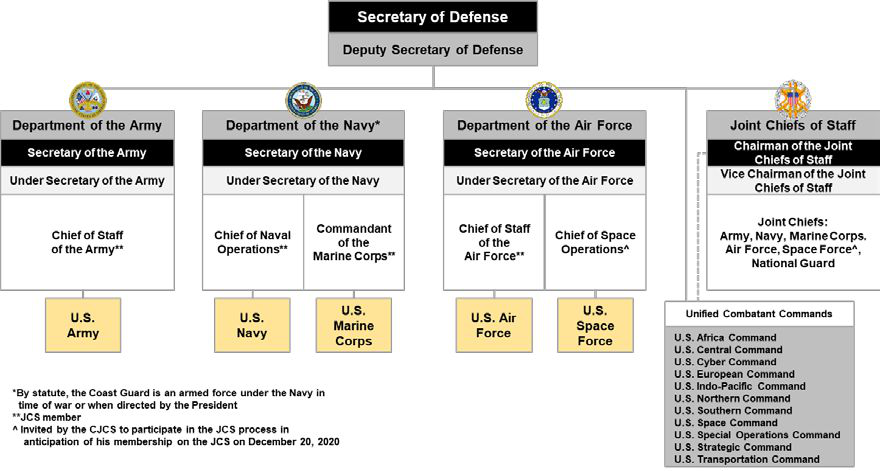
United States Department Of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the United States Army, Army, United States Navy, Navy, United States Marine Corps, Marines, United States Air Force, Air Force, United States Space Force, Space Force, the United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard for some purposes, and related functions and agencies. As of November 2022, the department has over 1.4 million active-duty uniformed personnel in the six armed services. It also supervises over 778,000 National Guard (United States), National Guard and reservist personnel, and over 747,000 civilians, bringing the total to over 2.91 million employees. Headquartered at the Pentagon in Arlington County, Virginia, just outside Washington, D.C., the Department of Defense's stated mission is "to provid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Of The United States
The United States Armed Forces are the Military, military forces of the United States. U.S. United States Code, federal law names six armed forces: the United States Army, Army, United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps, United States Navy, Navy, United States Air Force, Air Force, United States Space Force, Space Force, and the United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard. Since 1949, all of the armed forces, except the Coast Guard, have been permanently part of the United States Department of Defense. They form six of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Each of the different military services is assigned a role and domain. The Army conducts land operations. The Navy and Marine Corps conduct maritime operations, the Marine Corps specializing in amphibious and maritime littoral operations primarily for supporting the Navy. The Air Force conducts air operations. The Space Force conducts space operations. The Coast Guard is unique in that it specializes in maritime opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Secretary Of The Air Force
The secretary of the Air Force, sometimes referred to as the secretary of the Department of the Air Force, (SecAF, or SAF/OS) is the head of the United States Department of the Air Force, Department of the Air Force and the service secretary for the United States Air Force and United States Space Force. The secretary of the Air Force is a civilian appointed by the President of the United States, president, by and with the advice and consent of the United States Senate, Senate. The secretary reports to the United States Secretary of Defense, secretary of defense and/or the United States Deputy Secretary of Defense, deputy secretary of defense, and is by statute responsible for and has the authority to conduct all the affairs of the Department of the Air Force. The secretary works closely with their civilian deputy, the United States Under Secretary of the Air Force, under secretary of the Air Force; and their military deputies, the Chief of Staff of the United States Air Force, ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a Private university, private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of modern technology and science. In response to the increasing Technological and industrial history of the United States, industrialization of the United States, William Barton Rogers organized a school in Boston to create "useful knowledge." Initially funded by a land-grant universities, federal land grant, the institute adopted a Polytechnic, polytechnic model that stressed laboratory instruction in applied science and engineering. MIT moved from Boston to Cambridge in 1916 and grew rapidly through collaboration with private industry, military branches, and new federal basic research agencies, the formation of which was influenced by MIT faculty like Vannevar Bush. In the late twentieth century, MIT became a leading center for research in compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |