|
VOR-DME
In radio navigation, a VOR/DME is a radio beacon that combines a VHF omnidirectional range (VOR) with a distance-measuring equipment (DME). The VOR allows the receiver to measure its Bearing (navigation), bearing to or from the beacon, while the DME provides the slant distance between the receiver and the station. Together, the two measurements allow the receiver to compute a position fix. The VOR system was first introduced in the 1930s, but did not enter significant commercial use until the early 1950s. It became much more practical with the introduction of low-cost Solid state (electronics), solid state receivers in the 1960s. DME was a modification of World War II-era navigation systems like Gee-H (navigation), Gee-H, and began development in 1946. Like VOR, it only became practical with the introduction of solid state receivers during the 1960s. In 1948, the United States Congress directed civilian and military aviation to standardize on VOR/DME equipment. However, the milita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VHF Omnidirectional Range
Very High Frequency Omnidirectional Range Station (VOR) is a type of short-range VHF radio navigation system for aircraft, enabling aircraft with a VOR receiver to determine the azimuth (also radial), referenced to magnetic north, between the aircraft to/from fixed VOR ground transmitter, radio beacons. VOR and the first DME(1950) system (referenced to 1950 since different from today's DME/N) to provide the slant range distance, were developed in the United States as part of a U.S. civil/military program for Aeronautical Navigation Aids in 1945. Deployment of VOR and DME(1950) began in 1949 by the U.S. CAA (Civil Aeronautics Administration). ICAO standardized VOR and DME(1950) in 1950 in ICAO Annex ed.1. Frequencies for the use of VOR are standardized in the very high frequency (VHF) band between 108.00 and 117.95 MHz Chapter 3, Table A. To improve azimuth accuracy of VOR even under difficult siting conditions, Doppler VOR (DVOR) was developed in the 1960s. VOR is accordi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VOR-DME
In radio navigation, a VOR/DME is a radio beacon that combines a VHF omnidirectional range (VOR) with a distance-measuring equipment (DME). The VOR allows the receiver to measure its Bearing (navigation), bearing to or from the beacon, while the DME provides the slant distance between the receiver and the station. Together, the two measurements allow the receiver to compute a position fix. The VOR system was first introduced in the 1930s, but did not enter significant commercial use until the early 1950s. It became much more practical with the introduction of low-cost Solid state (electronics), solid state receivers in the 1960s. DME was a modification of World War II-era navigation systems like Gee-H (navigation), Gee-H, and began development in 1946. Like VOR, it only became practical with the introduction of solid state receivers during the 1960s. In 1948, the United States Congress directed civilian and military aviation to standardize on VOR/DME equipment. However, the milita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warburg - 2018-04-19 - Drehfunkfeuer DVOR-DME WRB (04)
Warburg (; Westphalian: ''Warberich'' or ''Warborg'') is a town in eastern North Rhine-Westphalia, central Germany on the river Diemel near the three-state point shared by Hessen, Lower Saxony and North Rhine-Westphalia. It is in Höxter district and Detmold region. Warburg is the midpoint in the ''Warburger Börde''. Since March 2012 the city is allowed to call itself 'Hanseatic City of Warburg'. Geography The main town, consisting of the Old Town (''Altstadt'') and the New Town (''Neustadt'') and bearing the same name as the whole town, is a hill town. While the Old Town lies in the Diemel Valley, the New Town rises on the heights above the Diemel. The Warburg municipal area borders in the west on the Sauerland and in the northwest on the Eggegebirge foothills, while in the north and northeast the ''Warburger Börde'' abuts the town and in the south stretches the Diemel Valley. Constituent communities Warburg consists of the following 16 centres: * Bonenburg (1,107 inhabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TACAN
A tactical air navigation system, commonly referred to by the acronym TACAN, is a navigation system initially designed for naval aircraft to acquire moving landing platforms (i.e., ships) and later expanded for use by other military aircraft. It provides the user with bearing and distance (slant-range or hypotenuse) to a ground or ship-borne station. It is, from an end-user perspective, a more accurate version of the VOR/ DME system that provides bearing and range information for civil aviation. The DME portion of the TACAN system is available for civil use; at VORTAC facilities where a VOR is combined with a TACAN, civil aircraft can receive VOR/DME readings. Aircraft equipped with TACAN avionics can use this system for enroute navigation as well as non-precision approaches to landing fields. However, a TACAN-only equipped aircraft cannot receive bearing information from a VOR-only station. History The TACAN navigation system is an evolution of radio transponder navigation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Navigation
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geopositioning. A satellite navigation system with global coverage is termed global navigation satellite system (GNSS). , four global systems are operational: the United States's Global Positioning System (GPS), Russia's Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS), China's BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS), and the European Union's Galileo. Two regional systems are operational: India's NavIC and Japan's QZSS. ''Satellite-based augmentation systems'' (SBAS), designed to enhance the accuracy of GNSS, include Japan's Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS), India's GAGAN and the European EGNOS, all of them based on GPS. Previous iterations of the BeiDou navigation system and the present Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), operationally known as NavIC, are examples of stand-alone operating regional navigation satellite systems (RNSS). Satellite navigation devices d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decca Navigator
The Decca Navigator System was a hyperbolic navigation, hyperbolic radio navigation system that allowed ships and aircraft to determine their position by using radio signals from a dedicated system of static radio transmitters. The system used phase comparison between pairs of low frequency signals between 70 and 129 kilohertz, kHz, as opposed to pulse timing systems like Gee (navigation), Gee and LORAN. This made it much easier to design receivers using 1940s electronics, and operation was simplified by giving a direct readout of Decca coordinates without the complexity of a cathode-ray tube and highly skilled operator. The system was developed by Decca Radar, Decca in the UK. It was first deployed by the Royal Navy during World War II for the vital task of clearing the minefields to enable the D-Day landings. The Allied forces needed an accurate system not known to the Germans and thus free of jamming. After the war, it came off the secret list and was commercially deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
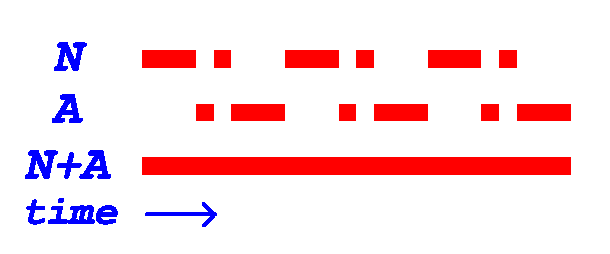
Low-frequency Radio Range
The low-frequency radio range, also known as the four-course radio range, LF/MF four-course radio range, A-N radio range, Adcock radio range, or commonly "the range", was the main Radio navigation, navigation system used by aircraft for instrument flight rules, instrument flying in the 1930s and 1940s, until the advent of the VHF omnidirectional range (VOR), beginning in the late 1940s. It was used for en route navigation as well as instrument approaches and Holding (aviation), holds. Based on a network of radio towers which transmitted Radiation pattern, directional radio signals, the radio range defined specific Airway (aviation), airways in the sky. Pilots navigated using low-frequency radio by listening to a stream of automated "A" and "N" Morse codes. For example, they would turn or slip the aircraft to the right when hearing an "N" stream ("dah-dit, dah-dit, ..."), to the left when hearing an "A" stream ("di-dah, di-dah, ..."), and fly straight ahead when these sounds merged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ICAO
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO ) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that coordinates the principles and techniques of international air navigation, and fosters the planning and development of international scheduled air transport, air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth. The ICAO headquarters are located in the Quartier international de Montréal of Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The ICAO Council adopts standards and recommended practices concerning air navigation, its infrastructure, flight inspection, prevention of unlawful interference, and facilitation of border-crossing procedures for international civil aviation. ICAO defines the protocols for Aviation accidents and incidents, air accident investigation that are followed by :Organizations investigating aviation accidents and incidents, transport safety authorities in countries signatory to the Convention on International Civil Aviation. The Air Navigation Commission (ANC) is the techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |