|
Vomer Bone
The vomer (; ) is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones. The vomer forms the inferior part of the nasal septum in humans, with the superior part formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone. The name is derived from the Latin word for a ploughshare and the shape of the bone. In humans The vomer is situated in the median plane, but its anterior portion is frequently bent to one side. It is thin, somewhat quadrilateral in shape, and forms the hinder and lower part of the nasal septum; it has two surfaces and four borders. The surfaces are marked by small furrows for blood vessels, and on each is the nasopalatine groove, which runs obliquely downward and forward, and lodges the nasopalatine nerve and vessels. Borders The ''superior border'', the thickest, presents a deep furrow, bounded on either s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facial Skeleton
The facial skeleton comprises the ''facial bones'' that may attach to build a portion of the skull. The remainder of the skull is the neurocranium. In human anatomy and development, the facial skeleton is sometimes called the ''membranous viscerocranium'', which comprises the mandible and dermatocranial elements that are not part of the braincase. Structure In the human skull, the facial skeleton consists of fourteen bones in the face: * Inferior turbinal (2) * Lacrimal bones (2) * Mandible * Maxilla (2) * Nasal bones (2) * Palatine bones (2) * Vomer * Zygomatic bones (2) Variations Elements of the ''cartilaginous viscerocranium'' (i.e., splanchnocranial elements), such as the hyoid bone, are sometimes considered part of the facial skeleton. The ethmoid bone (or a part of it) and also the sphenoid bone are sometimes included, but otherwise considered part of the neurocranium. Because the maxillary bones are fused, they are often collectively listed as only one bone. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Anatomy Structure The maxilla is a paired bone - the two maxillae unite with each other at the intermaxillary suture. The maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla: pyramid-shaped; has an orbital, a nasal, an infratemporal, and a facial surface; contains the maxillary sinus. * Four processes: ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process It has three surfaces: * the anterior, posterior, medial Features of the maxilla include: * t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
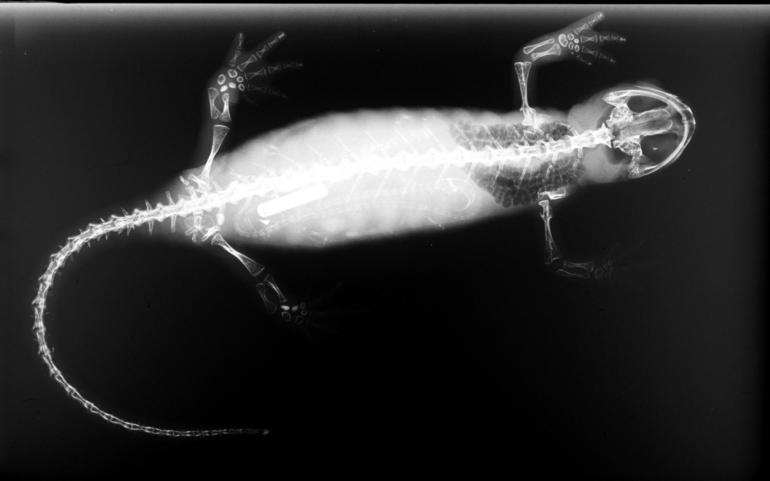
Necturus
''Necturus'' is a genus of aquatic salamanders in the family Proteidae. Species of the genus are native to the eastern United States and Canada. They are commonly known as waterdogs and mudpuppies. The common mudpuppy ''(N. maculosus)'' is probably the best-known species – as an amphibian with gill slits, it is often dissected in comparative anatomy classes. The common mudpuppy has the largest distribution of any fully aquatic salamander in North America. Taxonomy The genus ''Necturus'' is under scrutiny by herpetologists. The relationship between the species is still being studied. In 1991, Collins recommended ''N. maculosus louisianensis'' be elevated to full species status as ''N. louisianensis''. Originally described by Viosca as a species, it is usually considered a subspecies of the common mudpuppy (''N. maculosus''). However, the interpretation of Collins was not largely followed. Petranka, J.W. (1998). ''Salamanders of the United States and Canada''. Washington, D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela, the sole surviving order from the group Caudata. ''Urodela'' is a scientific Latin term based on the Ancient Greek : ourà dēlē "conspicuous tail". ''Caudata'' is the Latin for "tailed ones", from : "tail". Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains; most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm. Salamanders never have more than four toes on their front legs and five on their rear legs, but some species have fewer digits and others lack hind limbs. Their permeable skin usually makes them reliant on habitats in or near water or other cool, damp places. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight Bird skeleton, skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 Order (biology), orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have Bird wing, wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the Flightless bird, loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemism, endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting Taxonomy, taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern Cladistics, cladistic taxonomy regards that group as Paraphyly, paraphyletic, since Genetics, genetic and Paleontology, paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excluding the amniotes (tetrapods with an amniotic membrane, such as modern reptiles, birds and mammals). All extant taxon, extant (living) amphibians belong to the monophyletic subclass (biology), subclass Lissamphibia, with three living order (biology), orders: Anura (frogs and toads), Urodela (salamanders), and Gymnophiona (caecilians). Evolved to be mostly semiaquatic, amphibians have adapted to inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living in freshwater ecosystem, freshwater, wetland or terrestrial ecosystems (such as riparian woodland, fossorial and even arboreal habitats). Their biological life cycle, life cycle typically starts out as aquatic animal, aquatic larvae with gills known as tadpoles, but some species have devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labyrinthodont
"Labyrinthodontia" (Greek, 'maze-toothed') is an informal grouping of extinct predatory amphibians which were major components of ecosystems in the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras (about 390 to 150 million years ago). Traditionally considered a subclass of the class Amphibia, modern classification systems recognize that labyrinthodonts are not a formal natural group (clade) exclusive of other tetrapods. Instead, they consistute an evolutionary grade (a paraphyletic group), ancestral to living tetrapods such as lissamphibians (modern amphibians) and amniotes (reptiles, mammals, and kin). "Labyrinthodont"-grade vertebrates evolved from lobe-finned fishes in the Devonian, though a formal boundary between fish and amphibian is difficult to define at this point in time. "Labyrinthodont" generally refers to extinct four-limbed tetrapods with a large body size and a crocodile-like lifestyle. The name describes the pattern of infolding of the dentin and enamel of the teeth, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammals has been usually termed as the incisive bone. Other terms used for this structure include premaxillary bone or ''os premaxillare'', intermaxillary bone or ''os intermaxillare'', and Goethe's bone. Human anatomy In human anatomy, the premaxilla is referred to as the incisive bone (') and is the part of the maxilla which bears the incisor teeth, and encompasses the anterior nasal spine and alar region. In the nasal cavity, the premaxillary element projects higher than the maxillary element behind. The palatal portion of the premaxilla is a bony plate with a generally transverse orientation. The incisive foramen is bound anteriorly and laterally by the premaxilla and posteriorly by the palatine process of the maxilla. It is formed from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteichthyes
Osteichthyes ( ; ), also known as osteichthyans or commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a Biodiversity, diverse clade of vertebrate animals that have endoskeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish) and the extinct placoderms and acanthodians, which have endoskeletons primarily composed of cartilage. The vast majority of extant taxon, extant fish are members of Osteichthyes, being an extremely diverse and abundant group consisting of 45 order (biology), orders, over 435 family (biology), families and 28,000 species. The group is divided into two main clades, the ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii, which makes up the vast majority of extant fish) and the lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii, which gave rise to all land vertebrates, i.e. tetrapods). The oldest known fossils of bony fish are about 425 million years old from the late Silurian, which are also transitional fossils showing a dentition, tooth pattern th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavior of the receiving individuals. There are ''alarm signal, alarm pheromones'', ''food trail pheromones'', ''sex pheromones'', and many others that affect behavior or physiology. Pheromones are used by many organisms, from basic unicellular prokaryotes to complex multicellular eukaryotes. Their use among insects has been particularly well documented. In addition, some vertebrates, plants and ciliates communicate by using pheromones. The ecological functions and evolution of pheromones are a major topic of research in the field of chemical ecology. Background The portmanteau word "pheromone" was coined by Peter Karlson and Martin Lüscher in 1959, based on the Greek language, Greek () and (). Pheromones are also sometimes classified as ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flehmen Reaction
The flehmen response (; from German , and Upper Saxon German ), also called the flehmen position, flehmen reaction, flehmen grimace, flehming, or flehmening, is a behavior in which an animal curls back its upper lip exposing its front teeth, inhales with the nostrils usually closed, and then often holds this position for several seconds. It may be performed over a site or substance of particular interest to the animal, or may be performed with the neck stretched and the head held high in the air. Flehmen is performed by a wide range of mammals, including ungulates and felids. The behavior facilitates the transfer of pheromones and other scents into the vomeronasal organ (VNO, or Jacobson's organ) located above the roof of the mouth via a duct which exits just behind the front teeth of the animal. Etymology The word originates from the German verb . It comes from the Upper Saxon German . The word was introduced in 1930 by Karl Max Schneider, director of the Leipzig zoo and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |