|
Volcanism On Mars
Volcanic activity, or volcanism, has played a significant role in the geologic evolution of Mars. Scientists have known since the Mariner 9 mission in 1972 that volcanic features cover large portions of the Martian surface. These features include extensive lava flows, vast lava plains, and the largest known volcanoes in the Solar System. Martian volcanic features range in age from Noachian (>3.7 billion years) to late Amazonian (< 500 million years), indicating that the planet has been volcanically active throughout its history, and some speculate it probably still is so today. Both and Mars are large, differentiated |
Olympus Mons M9 PIA02999
Olympus or Olympos ( grc, Ὄλυμπος, link=no) may refer to: Mountains In antiquity Greece * Mount Olympus in Thessaly, northern Greece, the home of the twelve gods of Olympus in Greek mythology * Mount Olympus (Lesvos), located in Lesbos * Mount Olympus (Euboea), located in Euboea * Mount Olympus (Attica), located in East Attica * Mount Olympus (Skyros), located in Skyros * Mount Lykaion, located in Arcadia Turkey * Mysian Olympus (present-day Uludağ), in northwest Turkey * Paphlagonian Olympus (present-day Arıt Dağı near Bartın) * Mount Nif (present-day Nif Dağı in Aegean Turkey) * Lycian Olympus (present-day Tahtalı Dağı near Kemer) Cyprus * Mount Olympus (Cyprus), the highest point (1952 m) on the island of Cyprus In modern times United States * Mount Olympus (Washington), on the Olympic Peninsula * Mount Olympus (Utah), on the Wasatch Front * Mount Olympus (San Francisco), in the Ashbury Heights neighborhood New Zealand * Mount Olympus, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural satellites. Besides molten rock, magma may also contain suspended crystals and gas bubbles. Magma is produced by melting of the mantle or the crust in various tectonic settings, which on Earth include subduction zones, continental rift zones, mid-ocean ridges and hotspots. Mantle and crustal melts migrate upwards through the crust where they are thought to be stored in magma chambers or trans-crustal crystal-rich mush zones. During magma's storage in the crust, its composition may be modified by fractional crystallization, contamination with crustal melts, magma mixing, and degassing. Following its ascent through the crust, magma may feed a volcano and be extruded as lava, or it may solidify underground to form an intrusion, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
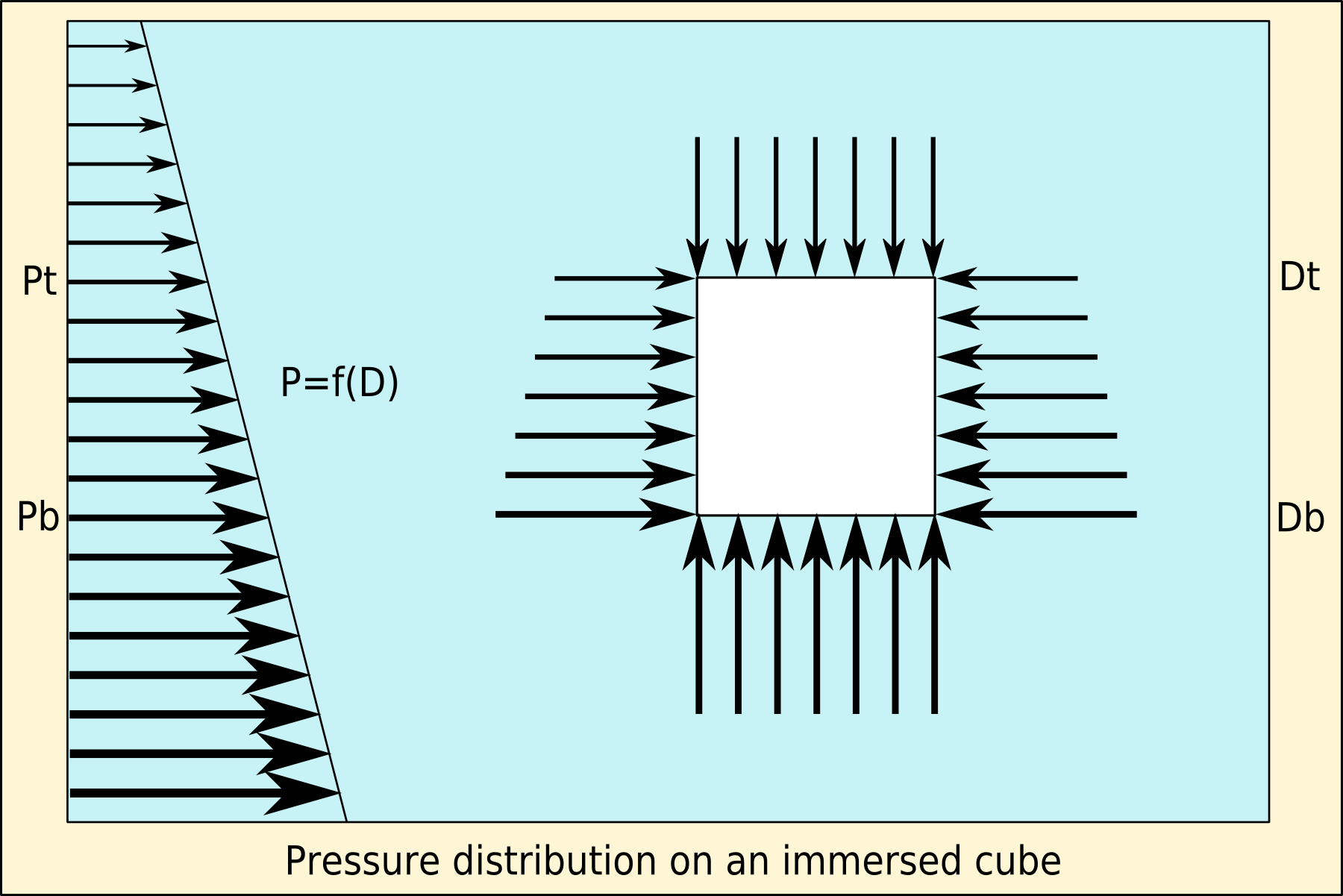
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diapir
A diapir (; , ) is a type of igneous intrusion in which a more mobile and ductily deformable material is forced into brittle overlying rocks. Depending on the tectonic environment, diapirs can range from idealized mushroom-shaped Rayleigh–Taylor-instability-type structures in regions with low tectonic stress such as in the Gulf of Mexico to narrow dikes of material that move along tectonically induced fractures in surrounding rock. The term was introduced by the Romanian geologist Ludovic Mrazek, who was the first to understand the principle of salt tectonics and plasticity. The term ''diapir'' may be applied to igneous structures, but it is more commonly applied to non-igneous, relatively cold materials, such as salt domes and mud diapirs. Occurrence Differential loading causes salt deposits covered by overburden (sediment) to rise upward toward the surface and pierce the overburden, forming diapirs (including salt domes), pillars, sheets, or other geologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both " ice" and " rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicate Minerals Silicate minerals are rock-forming minerals made up of silicate groups. They are the largest and most important class o |