|
Volatiles
Volatility or volatile may refer to: Chemistry * Volatility (chemistry), a measuring tendency of a substance or liquid to vaporize easily ** Volatile organic compounds, organic or carbon compounds that can evaporate at normal temperature and pressure *** Volatile anaesthetics, a class of anaesthetics which evaporate or vaporize easily *** Volatile substance abuse, the abuse of household inhalants containing volatile compounds *** Volatile oil, also known as essential oil, an oil derived from plants with aromatic compounds used in cosmetic and flavoring industries * Relative volatility, a measure of vapor pressures of the components in a liquid mixture * Volatile acid/Volatile acidity, a term used inconsisitenly across the fields of winemaking, wastewater treatment, physiology, and other fields * Volatile (astrogeology), a group of compounds with low boiling points that are associated with a planet's or moon's crust and atmosphere Computer science * Volatile variables, variab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volatile (astrogeology)
Volatiles are the group of chemical elements and chemical compounds that can be readily vaporized. In contrast with volatiles, elements and compounds that are not readily vaporized are known as refractory substances. On planet Earth, the term 'volatiles' often refers to the volatile components of magma. In astrogeology volatiles are investigated in the crust or atmosphere of a planet or moon. Volatiles include nitrogen, carbon dioxide, ammonia, hydrogen, methane, sulfur dioxide, water and others. Planetary science Planetary scientists often classify volatiles with exceptionally low melting points, such as hydrogen and helium, as gases, whereas those volatiles with melting points above about 100 K (–173 °C, –280 °F) are referred to as ices. The terms "gas" and "ice" in this context can apply to compounds that may be solids, liquids or gases. Thus, Jupiter and Saturn are gas giants, and Uranus and Neptune are ice giants, even though the vast majority of the "gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volatile Variable
In computer programming, a variable is said to be ''volatile'' if its value can be read or modified asynchronously by something other than the current thread of execution. The value of a volatile variable may spontaneously change for reasons such as: sharing values with other threads; sharing values with asynchronous signal handlers; accessing hardware devices via memory-mapped I/O (where you can send and receive messages from peripheral devices by reading from and writing to memory). Support for these use cases varies considerably among the programming languages that have the volatile keyword. Volatility can have implications regarding function calling conventions and how variables are stored, accessed and cached. In C and C++ In C and C++, volatile is a type qualifier, like const, and is a part of a type (e.g. the type of a variable or field). The behavior of the volatile keyword in C and C++ is sometimes given in terms of suppressing optimizations of an optimizing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volatile Substance Abuse
Inhalants are a broad range of household and industrial chemicals whose volatile vapors or pressurized gases can be concentrated and breathed in via the nose or mouth to produce Substance intoxication, intoxication, in a manner not intended by the manufacturer. They are inhaled at room temperature through volatilization (in the case of gasoline or acetone) or from a pressurized container (e.g., nitrous oxide or butane), and do not include drugs that are sniffed after burning or heating. While a few inhalants are prescribed by medical professionals and used for List of medical inhalants, medical purposes, as in the case of inhaled anesthetics and nitrous oxide (an anxiolytic and pain relief agent prescribed by dentists), this article focuses on inhalant use of household and industrial propellants, glues, fuels, and other products in a manner not intended by the manufacturer, to produce Substance intoxication, intoxication or other psychoactive effects. These products are used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volatility (memory Forensics)
Volatility is an open-source memory forensics framework for incident response and malware analysis. It is written in Python and supports Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ... (as of version 2.5). Volatility was created by Aaron Walters, drawing on academic research he did in memory forensics. Operating system support Volatility supports investigations of the following memory images: Windows: * 32-bit Windows XP (Service Pack 2 and 3) * 32-bit Windows 2003 Server (Service Pack 0, 1, 2) * 32-bit Windows Vista (Service Pack 0, 1, 2) * 32-bit Windows 2008 Server (Service Pack 1, 2) * 32-bit Windows 7 (Service Pack 0, 1) * 32-bit Windows 8, 8.1, and 8.1 Update 1 * 32-bit Windows 10 (initial support) * 64-bit Windows XP (Service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volatile Games
Blitz Games Studios Limited was a British video game developer based in Leamington Spa. Founded in 1990 by the Oliver Twins, who ran the company until its closure in 2013, it is best known for producing games such as ''The Fairly OddParents'', ''Bratz'', ''SpongeBob SquarePants'', ''The Biggest Loser'', and '' Karaoke Revolution''. Divisions Blitz Games Blitz Games created the games that the company first became well known for: family titles, often licensed on popular characters and existing intellectual property. Blitz Arcade ''Blitz Arcade'' was founded in 2006 with a team of 35 people. It was focused on developing downloadable titles of a small scope. Its first release was an advergame series created for the US Burger King chain. After that, Blitz Arcade turned its focus to downloadable titles and had success with its first game of this type: '' SpongeBob SquarePants: Underpants Slam''. They also developed shooter ''PowerUp Forever'', puzzler '' Droplitz'' and the 3DTV-comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volatility, Uncertainty, Complexity And Ambiguity
VUCA is an acronym based on the leadership theories of Warren Bennis and Burt Nanus, to describe or to reflect on the volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity of general conditions and situations. The U.S. Army War College introduced the concept of VUCA in 1987, to describe a more complex multilateral world perceived as resulting from the end of the Cold War. More frequent use and discussion of the term began from 2002. It has subsequently spread to strategic leadership in organizations, from for-profit corporations to education. Meaning The VUCA framework provides a lens through which organizations can interpret their challenges and opportunities. It emphasizes strategic foresight, insight, and the behavior of entities within organizations. Furthermore, it highlights both systemic and behavioral failures often associated with organizational missteps. V = ''Volatility'': Characterizes the rapid and unpredictable nature of change. U = ''Uncertainty'': Denotes the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedersen Index
The Pedersen index is a measure of political volatility in party systems. It was described by Mogens Pedersen in a paper published in 1979 entitled ''The Dynamics of European Party Systems: Changing Patterns of Electoral Volatility''. Pedersen index can be used as an indicator of a change in the party system and to evaluate a change in voter preferences. What the index means "The net change within the electoral party system resulting from individual vote transfers" Construction of the Index The Pedersen index is calculated as : \mathrm = \frac \sum_^n , p_-p_ , , where p_ is the percentage of votes for political party i at election t and p_ is the value for the next election. To calculate the index, the percentage gains of the winning parties must be determined. The resulting index will be between 0 (no parties gained, and thus no parties lost either) and 100 (all the parties from the last election were reduced to zero votes), because for every gain there i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Volatility
In statistics, stochastic volatility models are those in which the variance of a stochastic process is itself randomly distributed. They are used in the field of mathematical finance to evaluate derivative securities, such as options. The name derives from the models' treatment of the underlying security's volatility as a random process, governed by state variables such as the price level of the underlying security, the tendency of volatility to revert to some long-run mean value, and the variance of the volatility process itself, among others. Stochastic volatility models are one approach to resolve a shortcoming of the Black–Scholes model. In particular, models based on Black-Scholes assume that the underlying volatility is constant over the life of the derivative, and unaffected by the changes in the price level of the underlying security. However, these models cannot explain long-observed features of the implied volatility surface such as volatility smile and skew, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
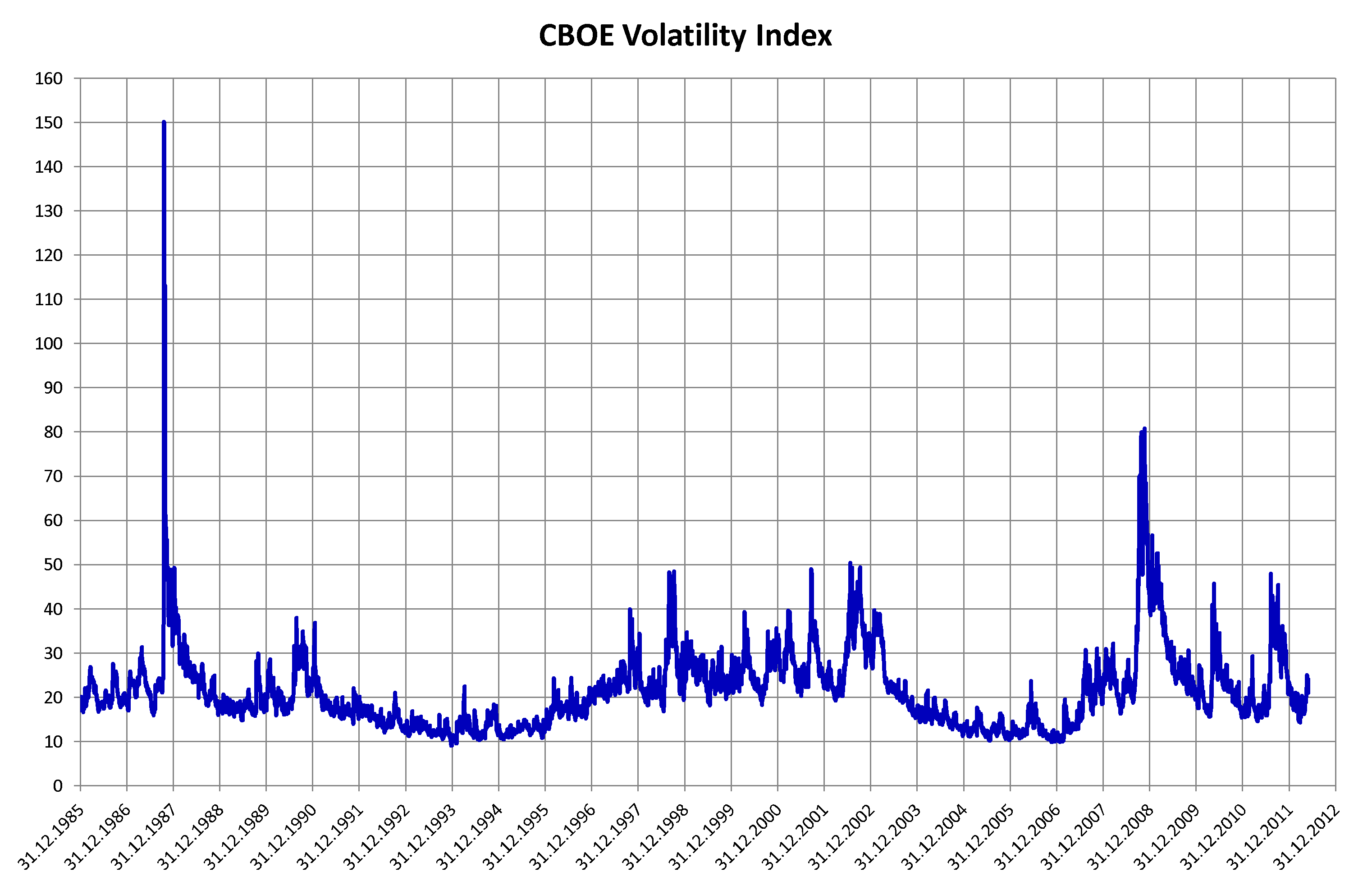
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility (usually denoted by "sigma, σ") is the Variability (statistics), degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a time series of past market prices. Implied volatility looks forward in time, being derived from the market price of a market-traded derivative (in particular, an option). Volatility terminology Volatility as described here refers to the actual volatility, more specifically: * actual current volatility of a financial instrument for a specified period (for example 30 days or 90 days), based on historical prices over the specified period with the last observation the most recent price. * actual historical volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period but with the last observation on a date in the past **near synonymous is realized volatility, the square root of the realized variance, in turn c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volatility (chemistry)
In chemistry, volatility is a material quality which describes how readily a substance vaporizes. At a given temperature and pressure, a substance with high volatility is more likely to exist as a vapour, while a substance with low volatility is more likely to be a liquid or solid. Volatility can also describe the tendency of a vapor to condense into a liquid or solid; less volatile substances will more readily condense from a vapor than highly volatile ones. Differences in volatility can be observed by comparing how fast substances within a group evaporate (or sublimate in the case of solids) when exposed to the atmosphere. A highly volatile substance such as rubbing alcohol (isopropyl alcohol) will quickly evaporate, while a substance with low volatility such as vegetable oil will remain condensed. In general, solids are much less volatile than liquids, but there are some exceptions. Solids that sublimate (change directly from solid to vapor) such as dry ice (solid carbon di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volatile Memory
Volatile memory, in contrast to non-volatile memory, is computer memory that requires power to maintain the stored information; it retains its contents while powered on but when the power is interrupted, the stored data is quickly lost. Volatile memory has several uses including as primary storage. In addition to usually being faster than forms of mass storage such as a hard disk drive, volatility can protect sensitive information, as it becomes unavailable on power-down. Most general-purpose random-access memory (RAM) is volatile. Types There are two kinds of volatile RAM: dynamic and static. Even though both types need continuous electrical current to retain data, there are some important differences between them. Dynamic RAM (DRAM) is very popular due to its cost-effectiveness. DRAM stores each bit of information in a different capacitor within the integrated circuit. DRAM chips need just one single capacitor and one transistor to store each bit of information. This makes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volatile Organic Compound
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic compounds that have a high vapor pressure at room temperature. They are common and exist in a variety of settings and products, not limited to Indoor mold, house mold, Upholstery, upholstered furniture, Handicraft, arts and crafts supplies, Dry cleaning, dry cleaned clothing, and Cleaning agent, cleaning supplies. VOCs are responsible for the odor of scents and perfumes as well as pollutants. They play an important role in communication between animals and plants, such as attractants for pollinators, protection from predation, and even inter-plant interactions. Some VOCs are dangerous to human health or cause harm to the natural environment, environment, often despite the odor being perceived as pleasant, such as "new car smell". Human impact on the environment, Anthropogenic VOCs are regulated by law, especially indoors, where concentrations are the highest. Most VOCs are not acutely toxic, but may have long-term chronic health effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |