|
Voiceless Bilabial Stop
The voiceless bilabial plosive or stop is a type of consonantal sound used in most spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is p. Features Features of the voiceless bilabial plosive: Varieties Occurrence Research has shown that incidental learning positively impacts the acquisition of the /p/ sound for Arabic speakers and other EFL learners. This is particularly interesting given that the stop is missing from about 10% of languages that have a . (See voiced velar stop for another such gap.) This is an areal feature of the circum-Saharan zone (Africa north of the equator plus the Arabian Peninsula). It is not known how old this areal feature is, and whether it might be a recent phenomenon due to Arabic as a prestige language, or whether Arabic was itself affected by a more ancient areal pattern. It is found in other areas as well; for example, Fijian, Onge, and many Papuan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract, except for the h sound, which is pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Examples are and [b], pronounced with the lips; and [d], pronounced with the front of the tongue; and [g], pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced throughout the vocal tract; , [v], , and [z] pronounced by forcing air through a narrow channel (fricatives); and and , which have air flowing through the nose (nasal consonant, nasals). Most consonants are Pulmonic consonant, pulmonic, using air pressure from the lungs to generate a sound. Very few natural languages are non-pulmonic, making use of Ejective consonant, ejectives, Implosive consonant, implosives, and Click consonant, clicks. Contrasting with consonants are vowels. Since the number of speech sounds in the world's languages is much greater than the number of letters in any one alphabet, Linguis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fijian Language
Fijian (') or iTaukei is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language of the Malayo-Polynesian languages, Malayo-Polynesian family spoken by some 350,000–450,000 ethnic Fijians as a native language. The 1997 Constitution of Fiji#New Constitution for 2013, 2013 Constitution established Fijian as an official languages of Fiji, language of Fiji, along with English and Fiji Hindi and there is discussion about establishing it as the "national language". Fijian is a verb–object–subject, VOS language. Standard Fijian is based on the Bau (island)#Language, Bau dialect, which is an East Fijian language. Pidgin Fijian, A pidginized form is used by many Indo-Fijians and Chinese in Fiji, Chinese on the islands, while Pidgin Hindustani is used by many rural ethnic Fijians and Chinese in areas dominated by Indo-Fijians. History History of the language The Fijian language was introduced to Fiji 3500 years ago by the islands' first settlers. For millennia, it was the only spoke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algerian Arabic
Algerian Arabic (, romanized: ), natively known as , or , is a variety of Arabic spoken in Algeria. It belongs to the Maghrebi Arabic dialect continuum and is mostly intelligible with the Tunisian and Moroccan dialects. Darja () means "everyday/colloquial dialect". Like other varieties of Maghrebi Arabic, Algerian Arabic has a mostly Semitic vocabulary. It contains Berber, Punic, and African Romance influences and has some loanwords from French, Andalusi Arabic, Ottoman Turkish and Spanish. Berber loanwords represent 8% to 9% of its vocabulary. Use Algerian Arabic is the native dialect of 75% to 80% of Algerians and is mastered by 85% to 100% of them. It is a spoken language used in daily communication and entertainment, while Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) is generally reserved for official use and education. As in the rest of the Arab world, this linguistic situation has been described as diglossia: MSA is nobody's first acquired language; it is learned through f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns language codes to 32 varieties of Arabic, including its standard form of Literary Arabic, known as Modern Standard Arabic, which is derived from Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as ( "the eloquent Arabic") or simply ' (). Arabic is the List of languages by the number of countries in which they are recognized as an official language, third most widespread official language after English and French, one of six official languages of the United Nations, and the Sacred language, liturgical language of Islam. Arabic is widely taught in schools and universities around the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrillic Script
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic languages, Slavic, Turkic languages, Turkic, Mongolic languages, Mongolic, Uralic languages, Uralic, Caucasian languages, Caucasian and Iranian languages, Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia, and used by many other minority languages. , around 250 million people in Eurasia use Cyrillic as the official script for their national languages, with Russia accounting for about half of them. With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the Languages of the European Union#Writing systems, European Union, following the Latin script, Latin and Greek alphabet, Greek alphabets. The Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in the First Bulga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
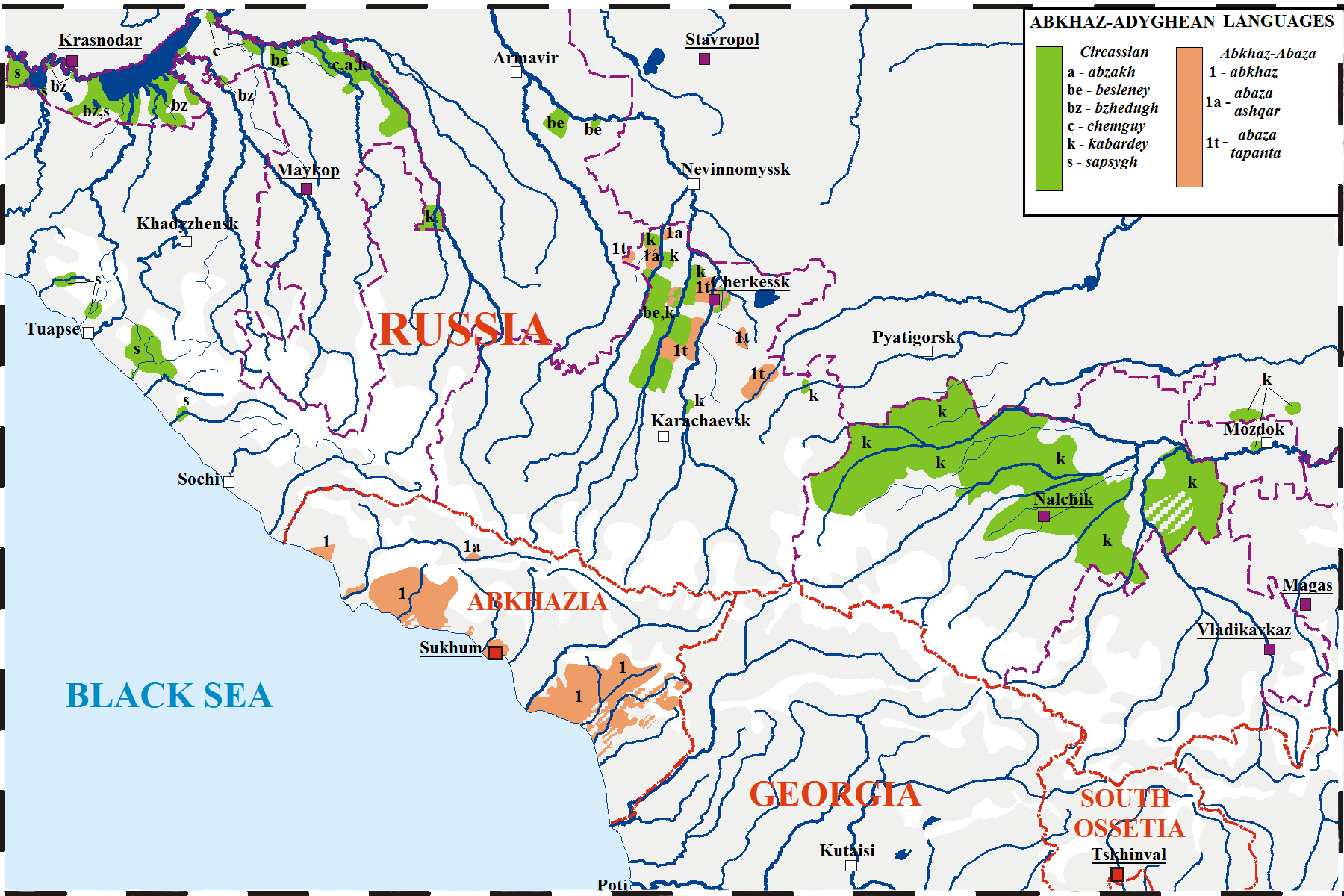
Adyghe Language
Adyghe ( or ; also known as West Circassian) is a Northwest Caucasian language spoken by the western subgroups of Circassians. It is spoken mainly in Russia, as well as in Turkey, Jordan, Syria, Iraq and Israel, where Circassians settled after the Circassian genocide (–1870) by the Russian Empire. It is closely related to the Kabardian language, Kabardian (East Circassian) language, though some reject the distinction between the two languages in favor of both being dialects of a unitary Circassian languages, Circassian language. The literary standard of Adyghe is based on its Temirgoy dialect. Adyghe and Russian language, Russian are the two official languages of the Adygea, Republic of Adygea in the Russian Federation. In Russia, there are around 128,000 speakers of Adyghe, almost all of them native speakers. In total, some 300,000 speak it worldwide. The largest Adyghe-speaking community is in Turkey, spoken by the diaspora from the Russo-Circassian War, Russian–Circassi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abkhazia
Abkhazia, officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a List of states with limited recognition, partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, at the intersection of Eastern Europe and West Asia. It covers and has a population of around 245,000. Its capital and largest city is Sukhumi. The political status of Abkhazia is a central issue of the Abkhazia conflict and Georgia–Russia relations. Abkhazia has been International recognition of Abkhazia and South Ossetia, recognised as an independent state only by 5 states: Russia, Venezuela, Nicaragua, Nauru, and Syria. Georgia (country), Georgia and other countries consider Abkhazia as a Georgia's sovereign territory.Olga Oliker, Thomas S. Szayna. Faultlines of Conflict in Central Asia and the South Caucasus: Implications for the U.S. Army. Rand Corporation, 2003, .Emmanuel Karagiannis. Energy and Security in the Caucasus. Routledge, 2002. . Lacking effective control over the Abkhazian territ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abkhaz Alphabet
The Abkhaz alphabet is a Cyrillic alphabet used for the Abkhaz language. Abkhaz did not become a written language until the 19th century. Up until then, Abkhazians, especially princes, had been using Greek (up to c. 9th century), Georgian (9–19th centuries), and partially Turkish (18th century) languages. The Abkhaz word for alphabet is анбан (anban), which was borrowed from Georgian ანბანი (anbani). History The first Abkhaz alphabet was created in 1862 by Peter von Uslar. It had 55 letters and was based on the Cyrillic script. Another version, having 51 letters, was used in 1892 by Dimitry Gulia and K. Machavariani. In 1909, the alphabet was again expanded to 55 letters by Andria Tchotchua to adjust to the extensive consonantal inventory of Abkhaz. In 1926, during the ''korenizatsiya'' policy in the Soviet Union, the Cyrillic alphabet was replaced by a Latin alphabet devised by Nikolay Marr. It featured 76 letters and was called the "Abkhaz ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abkhaz Language
Abkhaz, also known as Abkhazian, is a Northwest Caucasian languages, Northwest Caucasian language most closely related to Abaza language, Abaza. It is spoken mostly by the Abkhazians, Abkhaz people. It is one of the official languages of Abkhazia, where around 190,000 people speak it. Furthermore, it is spoken by thousands of members of the Abkhazian diaspora in Turkey, Georgia (country), Georgia's autonomous republic of Adjara, Syria, Jordan, and several Western countries. 27 October is the day of the Abkhazian language in Georgia (country), Georgia. Classification Abkhaz is a Northwest Caucasian languages, Northwest Caucasian language and is thus related to Adyghe language, Adyghe. The language of Abkhaz is especially close to Abaza language, Abaza, and they are sometimes considered dialects of the same language,''B. G. Hewitt Abkhaz 1979;'' page 1. Abazgi, of which the literary dialects of Abkhaz and Abaza are simply two ends of a dialect continuum. Grammatically, the two ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensions To The IPA
The Extensions to the International Phonetic Alphabet for Disordered Speech, commonly abbreviated extIPA , are a set of letters and diacritics devised by the International Clinical Phonetics and Linguistics Association to augment the International Phonetic Alphabet for the phonetic transcription of disordered speech. Some of the symbols are used for transcribing features of normal speech in IPA transcription, and are accepted as such by the International Phonetic Association. Many sounds found only in disordered speech are indicated with diacritics, though an increasing number of dedicated letters are used as well. Special letters are included to transcribe the speech of people with lisps and cleft palates. The extIPA repeats several standard-IPA diacritics that are unfamiliar to most people but transcribe features that are common in disordered speech. These include preaspiration , linguolabial , laminal fricatives , and for a sound (segment or feature) with no available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspiration (phonetics)
In phonetics, aspiration is a strong burst of breath that accompanies either the release or, in the case of preaspiration, the closure of some obstruents. In English, aspirated consonants are allophones in complementary distribution with their unaspirated counterparts, but in some other languages, notably most South Asian languages and East Asian languages, the difference is contrastive. Transcription In the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), aspirated consonants are written using the symbols for voiceless consonants followed by the aspiration modifier letter , a superscript form of the symbol for the voiceless glottal fricative . For instance, represents the voiceless bilabial stop, and represents the aspirated bilabial stop. Voiced consonants are seldom actually aspirated. Symbols for voiced consonants followed by , such as , typically represent consonants with murmured voiced release (see below). In the grammatical tradition of Sanskrit, aspirated co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindustani Language
Hindustani is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in North India and Pakistan as the lingua franca of the region. It is also spoken by the Deccani people, Deccani-speaking community in the Deccan plateau. Hindustani is a pluricentric language with two Standard language, standard Register (sociolinguistics), registers, known as Hindi (Sanskritisation (linguistics), Sanskritised register written in the Devanagari script) and Urdu (Persianization, Persianized and Arabization, Arabized register written in the Perso-Arabic script) which serve as official languages of India and Pakistan, respectively. Thus, it is also called Hindi–Urdu. Colloquial registers of the language fall on a spectrum between these standards. In modern times, a third variety of Hindustani with significant English influences has also appeared, which is sometimes called Hinglish or Urdish.Salwathura, A. N.Evolutionary development of ‘hinglish’language within the Indian sub-continent. ''International Journal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |