|
Vitelline Layer
The vitelline membrane or vitelline envelope is a structure surrounding the outer surface of the plasma membrane of an ovum (the oolemma) or, in some animals (e.g., birds), the extracellular yolk and the oolemma. It is composed mostly of protein fibers, with protein receptors needed for sperm binding which, in turn, are bound to sperm plasma membrane receptors. The species-specificity between these receptors contributes to prevention of breeding between different species. It is called zona pellucida in mammals. Between the vitelline membrane and the oolemma (ovum cell membrane) is a fluid-filled perivitelline space. As soon as the spermatozoon fuses with the ovum, signal transduction occurs, resulting in an increase of cytoplasmic calcium ions. This itself triggers the cortical reaction, which results in depositing several substances onto the vitelline membrane through exocytosis of the cortical granules, transforming it into a hard layer called the “fertilization membrane”, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell, being selectively permeable to ions and organic molecu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zona Pellucida-like Domain
The zona pellucida-like domain (ZP domain / ZP-like domain / ZP module) is a large protein region of about 260 amino acids. It has been recognised in a variety of receptor-like eukaryotic glycoproteins. All of these molecules are mosaic proteins with a large extracellular region composed of various domains, often followed by either a transmembrane domain and a short cytoplasmic region or by a GPI-anchor. Functional and crystallographic studies revealed that the "ZP domain" region common to all these proteins is a protein polymerization module that consists of two distinct but structurally related immunoglobulin-like domains, ZP-N and ZP-C, separated by an interdomain linker (ITD). The ZP module is located in the C-terminal portion of the extracellular region and – with the exception of non-polymeric family member ENG – contains 8 or 10 conserved Cys residues involved in disulfide bonds. The ZP-C domain contains a EHP/IHP motif that controls polymerization. The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oviduct
The oviduct in vertebrates is the passageway from an ovary. In human females, this is more usually known as the fallopian tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, or will degenerate in the body. Normally, these are paired structures, but in birds and some cartilaginous fishes, one or the other side fails to develop (together with the corresponding ovary), and only one functional oviduct can be found. Except in teleosts, the oviduct is not directly in contact with the ovary. Instead, the most anterior portion ends in a funnel-shaped structure called the infundibulum, which collects eggs as they are released by the ovary into the body cavity. The only female vertebrates to lack oviducts are the jawless fishes. In these species, the single fused ovary releases eggs directly into the body cavity. The fish eventually extrudes the eggs through a small genital pore towards the rear of the body. Fish and amphibia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
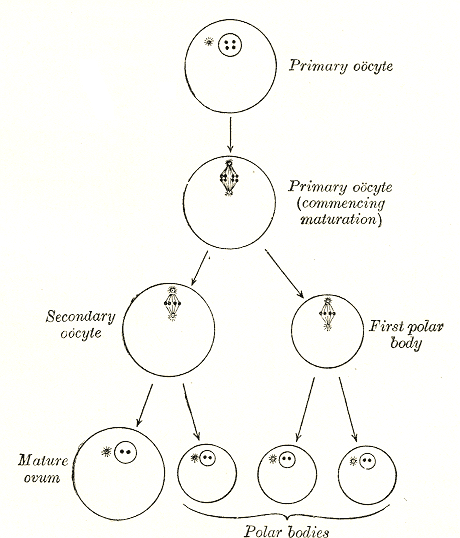
Oocyte
An oocyte (, oöcyte, or ovocyte) is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Formation The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation. Characteristics Cytoplasm Oocytes are rich in cytoplasm, which contains yolk granules to nourish the cell early in development. Nucleus During the primary oocyte stage of oogenesis, the nucleus is called a germinal vesicle. The only normal human type of secondary oocyte has the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulosa Cell
A granulosa cell or follicular cell is a somatic cell of the sex cord that is closely associated with the developing female gamete (called an oocyte or egg) in the ovary of mammals. Structure and function In the Folliculogenesis#Primordial, primordial ovarian follicle, and later in follicle development (folliculogenesis), granulosa cells advance to form a multilayered cumulus oophorus surrounding the oocyte in the preovulatory or antral follicle, antral (or Graafian) follicle. The major functions of granulosa cells include the production of sex steroids, as well as myriad growth factors thought to interact with the oocyte during its development. The sex steroid production begins with follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary, stimulating granulosa cells to convert androgens (coming from the thecal cells) to estradiol by aromatase during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. However, after ovulation the granulosa cells turn into granulosa lutein cells th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovulation
Ovulation is an important part of the menstrual cycle in female vertebrates where the egg cells are released from the ovaries as part of the ovarian cycle. In female humans ovulation typically occurs near the midpoint in the menstrual cycle and after the follicular phase. Ovulation is stimulated by an increase in luteinizing hormone (LH). The ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilized by sperm. If it is not, it will break down in less than a day. Meanwhile, the uterine lining ( endometrium) continues to thicken to be able to receive a fertilized egg. If no conception occurs, the uterine lining will eventually break down and be shed from the body via the vagina during menstruation. Some people choose to track ovulation in order to improve or aid becoming pregnant by timing intercourse with their ovulation. The signs of ovulation may include cervical muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Press
Academic Press (AP) is an academic book publisher founded in 1941. It launched a British division in the 1950s. Academic Press was acquired by Harcourt, Brace & World in 1969. Reed Elsevier said in 2000 it would buy Harcourt, a deal completed the next year, after a regulatory review. Thus, Academic Press is now an imprint of Elsevier. Academic Press publishes reference books, serials and online products in the subject areas of: * Communications engineering * Economics * Environmental science * Finance * Food science and nutrition * Geophysics * Life sciences * Mathematics and statistics * Neuroscience * Physical sciences * Psychology Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Its subject matter includes the behavior of humans and nonhumans, both consciousness, conscious and Unconscious mind, unconscious phenomena, and mental processes such as thoughts, feel ... Well-known products include the '' Methods in Enzymology'' series and encyclopedias such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocrine glands, secreting various hormones that play a role in the menstrual cycle and fertility. The ovary progresses through many stages beginning in the prenatal period through menopause. Structure Each ovary is whitish in color and located alongside the lateral wall of the uterus in a region called the ovarian fossa. The ovarian fossa is the region that is bounded by the external iliac artery and in front of the ureter and the internal iliac artery. This area is about 4 cm x 3 cm x 2 cm in size.Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . The ovaries are surrounded by a capsule, and have an outer cortex and an inner medulla. The capsule is of dense connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sperm Lysin
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, which are known as spermatozoa, while some red algae and fungi produce non-motile sperm cells, known as spermatia. Flowering plants contain non-motile sperm inside pollen, while some more basal plants like ferns and some gymnosperms have motile sperm. Sperm cells form during the process known as spermatogenesis, which in amniotes (reptiles and mammals) takes place in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles. This process involves the production of several successive sperm cell precursors, starting with spermatogonia, which differentiate into spermatocytes. The spermatocytes then undergo meiosis, reducing their chromosome number by half, which produces spermatids. The spermatids then mature and, in animals, construct a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusca
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum after Arthropoda. The number of additional fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000, and the proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine biology, marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat, as numerous groups are freshwater mollusc, freshwater and even terrestrial molluscs, terrestrial species. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomy (biology), taxonomic class (biology), classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurobiology, neurologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teleost
Teleostei (; Ancient Greek, Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts (), is, by far, the largest group of ray-finned fishes (class Actinopterygii), with 96% of all neontology, extant species of fish. The Teleostei, which is variously considered a Division (zoology), division or an infraclass in different taxonomic systems, include over 26,000 species that are arranged in about 40 order (biology), orders and 448 family (biology), families. Teleosts range from giant oarfish measuring or more, and ocean sunfish weighing over , to the minute male anglerfish ''Photocorynus spiniceps'', just long. Including not only torpedo-shaped fish built for speed, teleosts can be flattened vertically or horizontally, be elongated cylinders or take specialised shapes as in anglerfish and seahorses. The difference between teleosts and other bony fish lies mainly in their jaw bones; teleosts have a movable premaxilla and corresponding modifications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |