|
Virginia Secession Convention Of 1861
The Virginia Secession Convention of 1861 was called in the state capital of Richmond to determine whether Virginia would secede from the United States, govern the state during a state of emergency, and write a new Constitution for Virginia, which was subsequently voted down in a referendum under the Confederate Government. Background and composition Abraham Lincoln's presidential election reflected the nation's sectional divide. Before his inauguration, Secessionist assembly majorities in the Deep South states resolved to secede from the United States and form the Confederate States of America if Lincoln won the election. Virginia was deeply divided over whether to join them, as were the eight states in the Upper South. In January 1861, the Virginia Assembly called a special convention for the sole purpose of considering secession from the United States. Following an election on February 4, 1861, the counties and cities returned a convention of delegates amounting to about one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janney
Janney may refer to: People * Allison Janney (born 1959), American actress * Christopher Janney (born 1950), American interactive sound and light artist * Craig Janney (born 1967), American retired hockey player * Edward Janney an American musician, producer and artist * Ernest Lloyd Janney (1893–1941), Provisional Commander of the Canadian Aviation Corps from 1914 to 1915 * Eli H. Janney (1831–1912), American inventor * Eli Janney (musician), American record producer and musician * Frederick Wistar Morris Janney (1919–1979), Central Intelligence Agency officer * Jack R. Janney (1924–2006), American structural engineer and innovator in the understanding of structural collapses * John Janney (1798–1872), Virginia politician, president of the American Virginia Secession Convention * Leon Janney (1917–1980), American actor and radio personality * Russell Janney (1884–1963), American theatrical producer and novelist * William Janney (1908–1992), American actor * Janney Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia In The American Civil War
Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia was one of the original seven Slave states and free states, slave states that formed the Confederate States of America in February 1861, triggering the American Civil War, U.S. Civil War. The state governor, Democrat Joseph E. Brown, wanted locally raised troops to be used only for the defense of Georgia, in defiance of Confederate president Jefferson Davis, who wanted to deploy them on other battlefronts. When the Union blockade prevented Georgia from exporting its plentiful cotton in exchange for key imports, Brown ordered farmers to grow food instead, but the breakdown of transport systems led to desperate shortages. There was not much fighting in Georgia until September 1863, when Confederates under Braxton Bragg defeated William S. Rosecrans at Battle of Chickamauga, Chickamauga Creek. In May 1864, William T. Sherman started pursuing the Confederates towards Atlanta, which he captured in September, in advance of his Sherman's March to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Janney
John Janney (November 8, 1798 – January 5, 1872) was a member of the Whig Party in Virginia prior to its demise, delegate to the Virginia General Assembly from Loudoun County and served as President of the Virginia Secession Convention in 1861. Early life John Janney was born November 8, 1798, in Alexandria, Virginia, to devout Quaker parents. When Janney was still a boy his parents moved to Goose Creek (present day Lincoln) in Loudoun County where there was a thriving Quaker community. Janney attended school at the local meeting house until he was teenager. He then left to study law at the county court in Leesburg under Richard Henderson. At 18, Janney was admitted to the bar of that court, where he quickly gained the respect of his peers as well as rose through the ranks of the local Whig Party. Early career In 1831, he helped to draft a bill to abolish slavery in Virginia for the General Assembly. Two years later Janney was elected to that body's lower chamber as a dele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott (June 13, 1786May 29, 1866) was an American military commander and political candidate. He served as Commanding General of the United States Army from 1841 to 1861, and was a veteran of the War of 1812, American Indian Wars, Mexican–American War, and the early stages of the American Civil War. Scott was the Whig Party's presidential nominee in the 1852 election but was defeated by Democrat Franklin Pierce. He was known as Old Fuss and Feathers for his insistence on proper military etiquette and the Grand Old Man of the Army for his many years of service. Scott was born near Petersburg, Virginia, in 1786. After training as a lawyer and brief militia service, he joined the army in 1808 as a captain of the light artillery. In the War of 1812, Scott served on the Canadian front, taking part in the Battle of Queenston Heights and the Battle of Fort George, and was promoted to brigadier general in early 1814. He served with distinction in the Battle of Chippawa bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen A
Stephen Anthony Smith (born October 14, 1967), also known as Stephen A., is an American actor, sports television personality, sports radio host, and sports journalist. He makes frequent appearances as an National Basketball Association, NBA analyst for ESPN on ''SportsCenter'', ''NBA Countdown'', and the network's NBA broadcasts. He has also hosted ''The Stephen A. Smith Show'' on ESPN Radio and is a commentator on ESPN's First Take (talk show), ''First Take'', where he appears with Molly Qerim. Smith is a featured columnist for ESPN and ''The Philadelphia Inquirer''. Early life and education Stephen Anthony Smith was born in the Bronx, a borough of New York City. He was raised in the Hollis, Queens, Hollis section of Queens. Smith is the youngest of six children. He has four older sisters and had an older brother, Basil, who died in a car accident in 1992. He also has a half-brother on his father's side. Smith's parents were originally from Saint Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands. Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peace Convention Of 1861
The Peace Conference of 1861 was a meeting of 131 leading American politicians in February 1861, at the Willard Hotel in Washington, D.C., on the eve of the American Civil War. The conference's purpose was to avoid, if possible, the secession of the eight slave states from the upper and border South that had not done so as of that date. The seven states that had already seceded did not attend. Background Before the 1860 election, Republicans were excitedly predicting the end of slavery even in the South. Republican President Abraham Lincoln's election in 1860 led many in the South to conclude that now was the time for their long-discussed secession. Many pro-slavery Southerners, especially in the Lower South, were convinced that the new Republican government was determined to abolish slavery where it already existed. In much of the South, elections were held to select delegates to special conventions to consider secession from the Union. In Congress, efforts were made in both the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Clay
Henry Clay (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the United States Senate, U.S. Senate and United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives. He was the seventh Speaker of the United States House of Representatives, House speaker as well as the ninth United States Secretary of State, secretary of state. He unsuccessfully ran for president in the 1824 United States presidential election, 1824, 1832 United States presidential election, 1832, and 1844 United States presidential election, 1844 elections. He helped found both the National Republican Party and the Whig Party (United States), Whig Party. For his role in defusing sectional crises, he earned the appellation of the "Great Compromiser" and was part of the "Great Triumvirate" of Congressmen, alongside fellow Whig Daniel Webster and Democratic Party (United States), Democrat John C. Calhoun. Clay was born in Hanover County, Virginia, Virginia, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Bell (Tennessee Politician)
John Bell (February 18, 1796September 10, 1869) was an American politician, attorney, and planter who was a candidate for President of the United States in the election of 1860. One of Tennessee's most prominent antebellum politicians,Jonathan Atkins,John Bell" ''Tennessee Encyclopedia of History and Culture'', 2009. Retrieved: October 10, 2012. Bell served in the House of Representatives from 1827 to 1841, and in the Senate from 1847 to 1859. He was Speaker of the House for the 23rd Congress (1834–1835), and briefly served as Secretary of War during the administration of William Henry Harrison (1841). In 1860, he ran for president as the candidate of the Constitutional Union Party, a third party which took a neutral stance on the issue of slavery. He won the electoral votes of three states by a slim margin. Initially an ally of Andrew Jackson, Bell turned against Jackson in the mid-1830s and aligned himself with the National Republican Party and then the Whig P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mason–Dixon Line
The Mason–Dixon line, sometimes referred to as Mason and Dixon's Line, is a demarcation line separating four U.S. states: Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware and West Virginia. It was Surveying, surveyed between 1763 and 1767 by Charles Mason and Jeremiah Dixon as part of the resolution of a border dispute involving Maryland, Pennsylvania, and Delaware in the colonial United States. The largest portion of the Mason–Dixon line, along the southern Pennsylvania border, later became informally known as the boundary between the Slave states and free states, Southern slave states and Northern free states. This usage came to prominence during the debate around the Missouri Compromise of 1820, when drawing boundaries between slave and free territory, and resurfaced during the American Civil War, with border states (American Civil War), border states also coming into play. The Confederate States of America claimed the Virginia (now West Virginia) portion of the line as part of its n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antebellum South
The ''Antebellum'' South era (from ) was a period in the history of the Southern United States that extended from the conclusion of the War of 1812 to the start of the American Civil War in 1861. This era was marked by the prevalent practice of slavery and the associated societal norms it cultivated. Over the course of this period, Southern leaders underwent a transformation in their perspective on slavery. Initially regarded as an awkward and temporary institution, it gradually evolved into a defended concept, with proponents arguing for its positive merits, while simultaneously vehemently opposing the burgeoning abolitionist movement. Society was stratified, inegalitarian, and perceived by immigrants as lacking in opportunities. Consequently, the manufacturing base lagged behind that of the non-slave states. Wealth inequality grew as the larger landholders took the greater share of the profits generated by enslaved persons, which also helped to entrench their power as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas In The American Civil War
Texas declared its secession from the Union on February 1, 1861, and joined the Confederate States on March 2, 1861, after it had replaced its governor, Sam Houston, who had refused to take an oath of allegiance to the Confederacy. As with those of other states, the Declaration of Secession was not recognized by the US government at Washington, DC. Some Texan military units fought in the Civil War east of the Mississippi River, but Texas was more useful for supplying soldiers and horses for the Confederate Army. Texas' supply role lasted until mid-1863, when Union gunboats started to control the Mississippi River, which prevented large transfers of men, horses, or cattle. Some cotton was sold in Mexico, but most of the crop became useless because of the Union's naval blockade of Galveston, Houston, and other ports. Secession In the early winter of 1860, Texan counties sent delegates to a special convention to debate the merits of secession. The convention adopted an " Ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
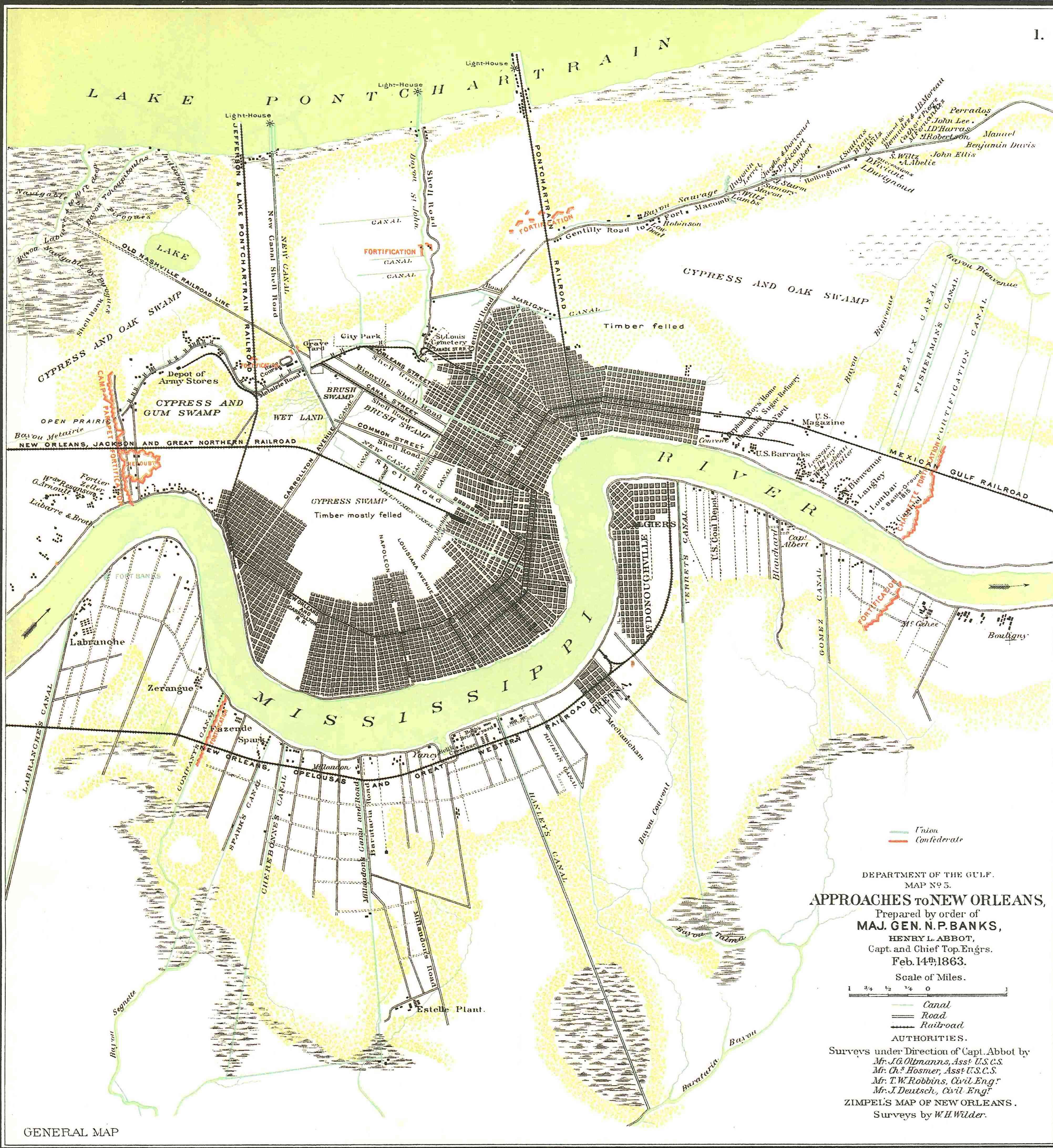
Louisiana In The American Civil War
Louisiana was a dominant population center in the southwest of the Confederate States of America, controlling the wealthy trade center of New Orleans, and contributing the Louisiana Creole people, French Creole and Cajun populations to the demographic composition of a predominantly Anglo-American country. In the Antebellum era, antebellum period, Louisiana was a slave state, where enslaved African Americans had comprised the majority of the population during the eighteenth-century French Louisiana, French and Spanish Louisiana, Spanish dominations. By the time the Louisiana Purchase, United States acquired the territory (1803) and Louisiana became a U.S. state, state (1812), the institution of Slavery in the United States, slavery was entrenched. By 1860, 47% of the state's population were enslaved, though the state also had one of the largest free black populations in the United States. Much of the White American, white population, particularly in the cities, supported slave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |