|
Vilnius Offensive
The Vilnius offensive (; ) occurred as part of the third phase of Operation Bagration, the Soviet Red Army's strategic summer offensive against the German ''Wehrmacht'' in June and July 1944. It lasted from 5 July to 13 July 1944 and ended with a Soviet victory. During the offensive, Soviet forces encircled and captured the city of Vilnius; this phase is sometimes referred to as the Battle of Vilnius. However, 3,000 German soldiers of the encircled garrison managed to break out with their commander, Reiner Stahel. Prelude During the interwar, the Vilnius Region was disputed between the Second Polish Republic and Lithuania. During the invasion of Poland, the city was seized by the Soviet Union and later transferred to Lithuania under the terms of the Soviet–Lithuanian Mutual Assistance Treaty. It was captured by the Germans in June 1941. From 23 June 1944, the Red Army conducted a strategic offensive operation under the code-name Operation Bagration, expelling the ''Wehrmac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
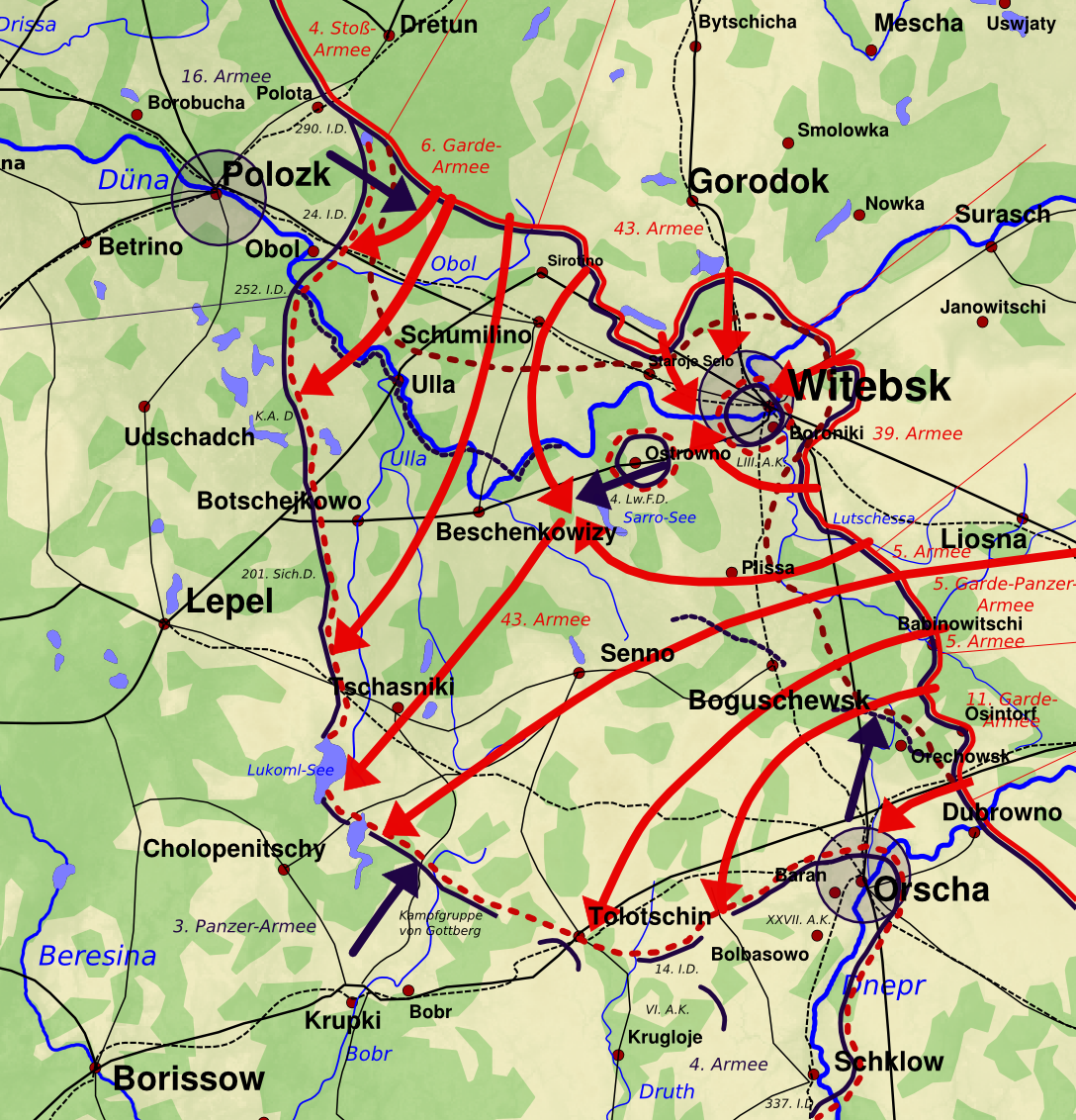
Operation Bagration
Operation Bagration () was the codename for the 1944 Soviet Byelorussian strategic offensive operation (), a military campaign fought between 22 June and 19 August 1944 in Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet Byelorussia in the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II, just over two weeks after the start of Operation Overlord in the west. It was during this operation that Nazi Germany was forced to fight simultaneously on two major fronts for the first time since the war began. The Soviet Union destroyed 28 of the divisions of Army Group Centre and completely shattered the German front line. The overall engagement is the largest defeat in German military history, with around 450,000 German casualties, while setting the stage for the subsequent isolation of 300,000 German soldiers in the Courland Pocket. On 22 June 1944, the Red Army attacked Army Group Centre in Byelorussia, with the objective of encircling and destroying its main component armies. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
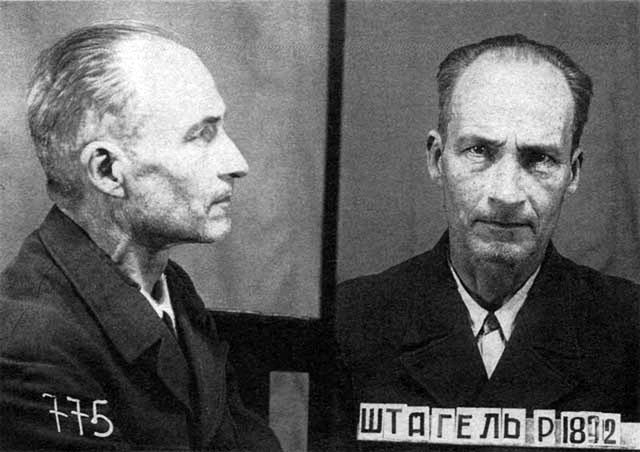
Reiner Stahel
Rainer Joseph Karl August Stahel (sometimes wrongly written as ''Reiner''; 15 January 1892 – 30 November 1955) was a German military officer and war criminal. He is best known for his retreat from Vilna and the command of the garrison of Warsaw during the Warsaw Uprising of 1944. Arrested by the NKVD in Romania, he spent the rest of his life in Soviet captivity. Early life Stahel was born in Bielefeld. On 1 April 1911, he joined the 1. Lothringisches Infanterie-Regiment Nr. 130 of the Prussian Army. World War I He fought with the German Army during World War I. By the end of the war, he had moved to Finland and joined the Finnish Army participating in the Finnish Civil War. Interwar In 1933 he went to Nazi Germany where he worked at the Ministry of Aviation. World War II Stahel participated in the German invasion of the Soviet Union as commander of Flakregiments 34 (June 1941), Flakregiment 99 (April 1942) and 4th Luftwaffe Field Division (September 1942). During t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stavka
The ''Stavka'' ( Russian and Ukrainian: Ставка, ) is a name of the high command of the armed forces used formerly in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union and currently in Ukraine. In Imperial Russia ''Stavka'' referred to the administrative staff, and to the General Headquarters in the late 19th-century Imperial Russian armed forces and subsequently in the Soviet Union. In Western literature it is sometimes written in uppercase (''STAVKA''), although it is not an acronym. ''Stavka'' may refer to its members, as well as to the headquarters location (its original meaning from the old Russian word '' ставка'', 'tent'). Stavka of the Supreme Commander during World War I The commander-in-chief of the Russian army at the beginning of World War I was Grand Duke Nicholas Nicholaievitch, a grandson of Tsar Nicholas I. Appointed at the last minute in August 1914, he played no part in formulating the military plans in use at the beginning of the war. Nikolai Yanushke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minsk Offensive
The Minsk offensive () was part of the second phase of the Belorussian strategic offensive of the Red Army in summer 1944, commonly known as Operation Bagration. The Red Army encircled the German 4th Army (Wehrmacht), Fourth Army in the city of Minsk. Hitler ordered the Fourth Army to hold fast, declaring the city to be a fortified place () and defended even if encircled. The Soviet Fifth Guards Tank Army (Soviet Union), 5th Guards Tank Army attacked from the north-east, while the 2nd Guards Tank Corps moved in from the east, and the 65th Army advanced from the south. About 100,000 Axis soldiers from the Fourth and Ninth Armies were encircled, of whom some 40,000 were killed and most of the rest captured. The result was a complete victory for the Red Army, the liberation of Minsk, and the rapid destruction of much of the German Army Group Centre. Role in the conflict The capturing of Minsk played an important role in Operation Bagration and in World War II, WWII itself. With the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minsk
Minsk (, ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach (Berezina), Svislach and the now subterranean Nyamiha, Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the administrative centre of Minsk region and Minsk district. it has a population of about two million, making Minsk the Largest cities in Europe, 11th-most populous city in Europe. Minsk is one of the administrative capitals of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU). First mentioned in 1067, Minsk became the capital of the Principality of Minsk, an appanage of the Principality of Polotsk, before being annexed by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1242. It received town privileges in 1499. From 1569, it was the capital of Minsk Voivodeship, an administrative division of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was part of the territories annexed by the Russian Empire in 1793, as a consequence of the Second Part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitebsk
Vitebsk or Vitsyebsk (, ; , ; ) is a city in northern Belarus. It serves as the administrative center of Vitebsk Region and Vitebsk District, though it is administratively separated from the district. As of 2025, it has 358,927 inhabitants, making it the country's fourth-largest city. It is served by Vitebsk Vostochny Airport and Vitebsk Air Base. History Middle Ages Vitebsk developed from a river harbor where the Vićba River (Віцьба, from which it derives its name) flows into the larger Western Dvina, which is spanned in the city by the Kirov Bridge. Archaeological research indicates that Baltic tribes had settlements at the mouth of Vitba. In the 9th century, Slavic settlements of the tribal union of the Krivichs replaced them. According to the '' Chronicle of Michael Brigandine'' (1760), Princess Olga of Kiev founded Vitebsk (also recorded as Dbesk, Vidbesk, Videbsk, Vitepesk, or Vicibesk) in 974. Other versions give 947 or 914. Academician Boris Rybakov an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group North
Army Group North () was the name of three separate army groups of the Wehrmacht during World War II. Its rear area operations were organized by the Army Group North Rear Area. The first Army Group North was deployed during the invasion of Poland and subsequently renamed Army Group B. The second Army Group North was created on 22 June 1941 from the former Army Group C and used in the northern sector of the Eastern Front from 1941 to January 1945. By then, this second Army Group North had gotten trapped in the Courland Pocket and was accordingly redesignated Army Group Courland. On the same day, the former Army Group Center, which was now defending the northernmost sector of the contiguous Eastern Front, was renamed Army Group North, assuming the status of the third and final iteration of the army group. First deployment of Army Group North: September – October 1939 The staff of Army Group North was formally assembled on 2 September 1939 from the headquarters of 2nd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the world's largest brackish water basin. The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. It is a Continental shelf#Shelf seas, shelf sea and marginal sea of the Atlantic with limited water exchange between the two, making it an inland sea. The Baltic Sea drains through the Danish straits into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, Great Belt and Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia (divided into the Bothnian Bay and the Bothnian Sea), the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga and the Bay of Gdańsk. The "Baltic Proper" is bordered on its northern edge, at latitude 60°N, by Åland and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group Centre
Army Group Centre () was the name of two distinct strategic German Army Groups that fought on the Eastern Front in World War II. The first Army Group Centre was created during the planning of Operation Barbarossa, Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union, as one of the three German Army formations assigned to the invasion. After Army Group North was trapped in the Courland Pocket in mid-1944, it was renamed to Army Group Courland and the first Army Group Centre was renamed "Army Group North". The second iteration of Army Group Centre was formed by the redesignation of Army Group A as the replacement for the first Army Group Centre. Formation and Command The army group was officially created by Adolf Hitler when he issued Führer Directive 21 on 18 December 1940, ordering German forces to prepare for an attack on Soviet Russia in 1941. The first commanding officer of Army Group Centre was Field Marshal Fedor von Bock, who would lead it until he was relieved on 18 December 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and several of its European Axis allies starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during World War II. More than 3.8 million Axis troops invaded the western Soviet Union along a front, with the main goal of capturing territory up to a line between Arkhangelsk and Astrakhan, known as the A-A line. The attack became the largest and costliest military offensive in history, with around 10 million combatants taking part in the opening phase and over 8 million casualties by the end of the operation on 5 December 1941. It marked a major escalation of World War II, opened the Eastern Front—the largest and deadliest land war in history—and brought the Soviet Union into the Allied powers. The operation, code-named after the Holy Roman Emperor Frederick Barbarossa ("red beard"), put into action Nazi Germany's ideological goals of eradicating communism and conquering the western Soviet Union to repopulate it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet–Lithuanian Mutual Assistance Treaty
The Soviet–Lithuanian Mutual Assistance Treaty (, ) was a bilateral treaty signed between the Soviet Union and Lithuania on October 10, 1939. According to provisions outlined in the treaty, Lithuania would acquire about one fifth of the Vilnius Region, including Lithuania's historical capital, Vilnius, and in exchange would allow five List of Soviet Union military bases abroad, Soviet military bases with 20,000 troops to be established across Lithuania. In essence the treaty with Lithuania was very similar to the treaties that the Soviet Union signed Soviet–Estonian Mutual Assistance Treaty, with Estonia on September 28, and Soviet–Latvian Mutual Assistance Treaty, with Latvia on October 5. According to Soviet propaganda, official Soviet sources, the Soviet military was strengthening the defenses of a weak nation against possible attacks by Nazi Germany. The treaty provided that Lithuania's sovereignty would not be affected. However, in reality the treaty opened the door for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |