|
Villain Hitting
Villain hitting, da siu yan (), demon exorcising, or petty person beating, is a folk sorcery popular in the Guangdong area of China and Hong KongÔÇöprimarily associated with Cantonese. Its purpose is to curse one's enemies using magic. Villain hitting is often considered a humble career, and the ceremony is often performed by older ladies, though some shops sell " DIY" kits. Villain hitting has been preliminarily included in the list of "intangible cultural heritage" by the Hong Kong Home Affairs Bureau, and was selected as "Best Way to Get It Off Your Chest" in ''TIME'' magazine's 2009 "Best of Asia" feature. Villain The concept of "villain" is divided into two types, specific and general. Specific Specific villains are individuals cursed by the villain hitter due to the hatred of their enemies who employ the hitter. A villain could be a famous person hated by the public such as a politician or could be personally known to their enemy, such as when the request is to curse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canal Road Flyover
Canal Road East (), Canal Road West () and the Canal Road Flyover () are important roads in the Wan Chai District of Hong Kong Island, between the areas of East Point near Causeway Bay, and Morrison Hill near Wan Chai. History Before urban development, the area was the estuary of the Wong Nai Chung river, which flowed through Happy Valley. The 4th Governor of Hong Kong, John Bowring, developed the estuary area and named it (or Bowring City). was built during the mid to late 1850s, fed by Wong Nai Chung. Because the long and narrow canal resembled the neck of a goose it was known as ''Ngo Keng Kan'' (). It was used by small vessels that could pass under various bridges along the route. The landmark across the canal, built in 1861, was known as ''Ngo Keng Kiu'' () and carried the Hong Kong Tramways line across the waterway. The surrounding area, Bowrington, is also known as ''Ngo Keng''. The original wooden bridge was replaced by an iron one that opened in March 1892. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
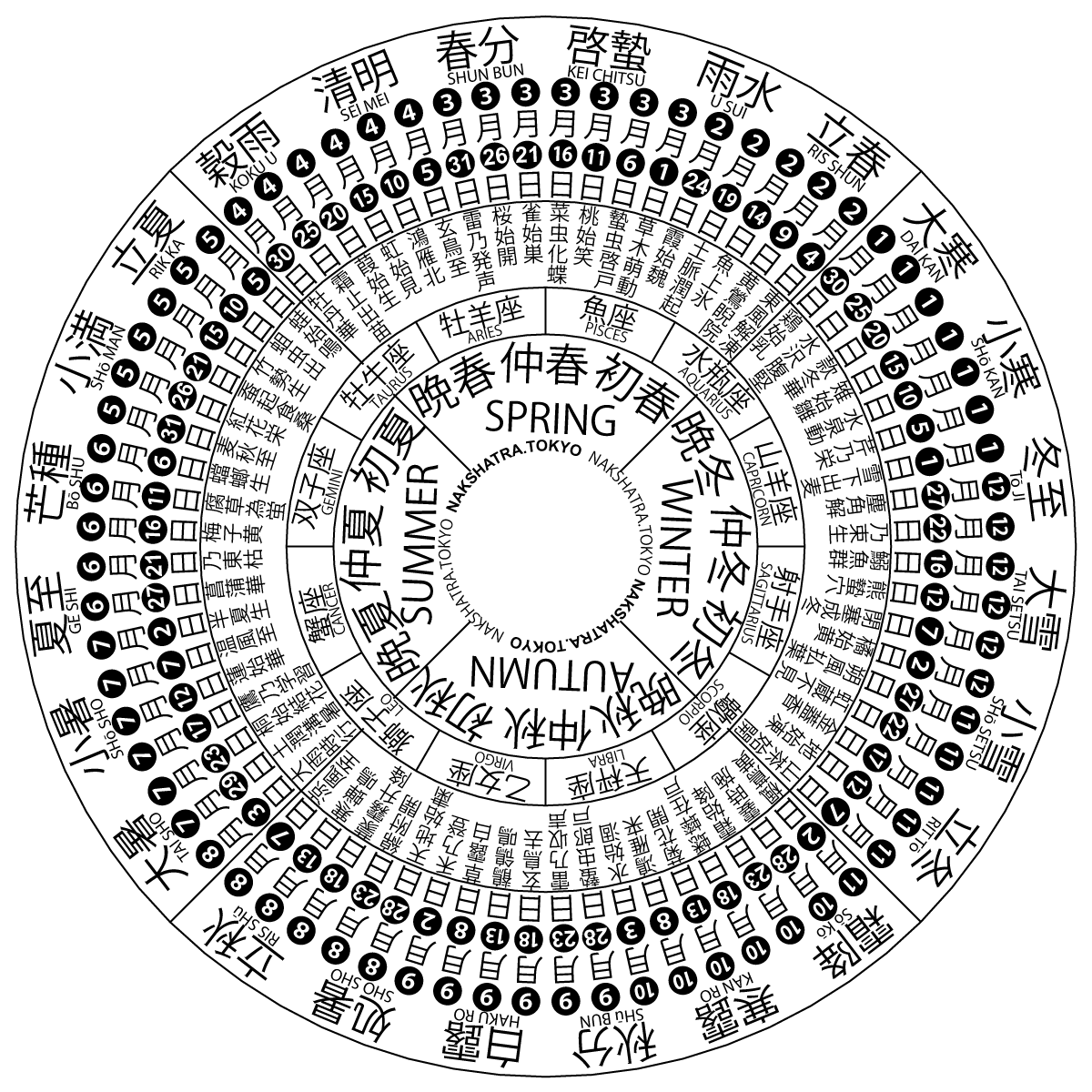
Solar Term
A solar term (or ''ji├ęq├Č'', zh, t=š»ÇŠ░ú, s=ŔŐéŠ░ö) is any of twenty-four periods in traditional Chinese lunisolar calendars that matches a particular astronomical event or signifies some natural phenomenon. The points are spaced 15┬░ apart along the ecliptic and are used by lunisolar calendars to stay synchronized with the seasons, which is crucial for agrarian societies. The solar terms are also used to calculate intercalary months; which month is repeated depends on the position of the sun at the time. According to the '' Book of Documents'', the first determined term was Dongzhi (Winter Solstice) by Dan, the Duke of Zhou, while he was trying to locate the geological center of the Western Zhou dynasty, by measuring the length of the sun's shadow on an ancient type of sundial called ┬á(). Then four terms of seasons were set, which were soon evolved as eight terms; not until the Taichu Calendar of 104 BC were all twenty-four solar terms officially included in the Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhi Jiao
Poe divination (, from the Hokkien , Min Dong BUC: ''bu─âk-bu┼Ći'', 'cast moon blocks', also written ''bwa bwei'', Mandarin ) is a traditional Chinese divination method, in which the diviner throws or drops two small wooden pieces (or occasionally, coins of similar face value and design) on the floor, and interprets the divine answer using the positions of the pieces. This method can be used to tell whether the future course of action the diviner is considering is recommended or not. The pieces, called (''bwei'') in Taiwanese or jiaobei in Mandarin, look somewhat like two shells of a clam or bivalve mollusk. (in Japanese) Upon throwing the wooden pieces, divination often results in three answering positions. The first is , when one of the blocks has its flat side facing up and the other has its flat side facing down; this shows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gui Ren Paper
Gui or GUI may refer to: People Surname * Gui (surname), an ancient Chinese surname, ''xing'' * Bernard Gui (1261 or 1262ÔÇô1331), inquisitor of the Dominican Order * Luigi Gui (1914ÔÇô2010), Italian politician * Gui Minhai (born 1964), ChineseÔÇôborn Swedish scholar and publisher * Vittorio Gui (1885ÔÇô1975), Italian composer Given name * Gui Bonsiepe (born 1934), German designer and academic * Gui Boratto (born 1974), Brazilian musician * Gui Carvalho (born 2002), Brazilian basketball player * Gui de Cambrai (), French writer * Gui de Cavalhon (), Proven├žal nobleman * Gui Guerrejat (died 1178), Occitan noble * Gui de Maillesec (died 1412), French bishop and cardinal * Gui Mallon (born 1953), Brazilian composer * Gui Rochat (born 1933), American art dealer * Gui d'Ussel (), French troubadour Places * Guangxi, abbreviated in Chinese as Gu├Č (Šíé), a province of China * Guizhou, abbreviated in Chinese as Gu├Č (Ŕ┤Á), a province of China * Gui, Burkina Faso * Gui Prefecture ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Tiger (mythology)
The White Tiger (), is one of the Four Symbols of the Chinese constellations. It is sometimes called the White Tiger of the West (). It represents the west in terms of direction and the autumn season. It is known as ''Byakko'' in Japanese, Baekho in Korean, and in Vietnamese. Seven Mansions As with the other three Symbols, there are seven astrological " Mansions" (positions of the Moon The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...) within the White Tiger. The names and determinative stars are: See also * Byakkotai References {{Chinese constellations Chinese constellations Chinese gods Chinese legendary creatures Mythological tigers Tigers in popular culture Four Symbols Onmy┼Źd┼Ź deities Animals in Chinese mythology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
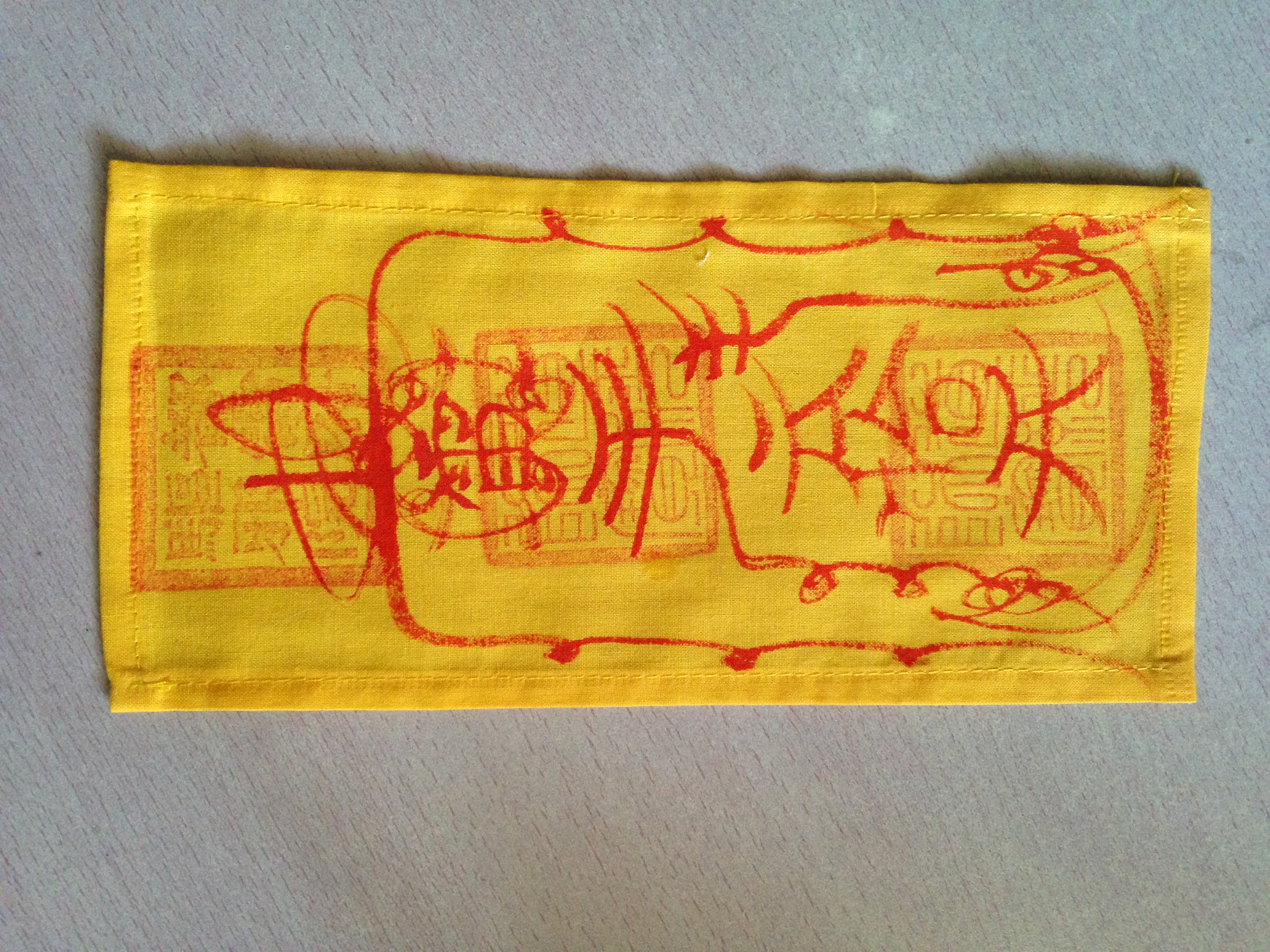
Fulu
() are Asemic writing, asemic Daoist, Taoist magic symbols and incantations, translatable into English as 'talismanic script', which are written or painted on talismans by Taoist practitioners. These practitioners are called , an informal group made up of priests from different schools of Taoism. Like most aspects of Taoist practice, use of these objects is not confined to Taoism: they have been incorporated into several forms of Chinese Buddhism, and have inspired the used in Buddhism in Japan, Japanese Buddhism and Shinto and the used in Korean shamanism. Etymology are instructions for deities and spirits, symbols for exorcism, and recipes for potions or charms used to treat ailments. A is a registry for the memberships of priests, which additionally lists the skills they are trained in. History Scholarly research into the history of Taoist symbolism has always been a particular challenge, because historically, Taoist priests have often used abstruse, obscure imag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candle
A candle is an ignitable candle wick, wick embedded in wax, or another flammable solid substance such as tallow, that provides light, and in some cases, a Aroma compound, fragrance. A candle can also provide heat or a method of keeping time. Candles have been used for over two millennia around the world, and were a significant form of indoor lighting until the invention of other types of light sources. Although electric light has largely made candle use nonessential for illumination, candles are still commonly used for functional, symbolic and aesthetic purposes and in specific cultural and religious settings. Early candles may be made of beeswax, but these candles were expensive and their use was limited to the elite and the churches. Tallow was a cheaper but a less aesthetically pleasing alternative. A variety of different materials have been developed in the modern era for making candles, including paraffin wax, which together with efficient production techniques, made can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
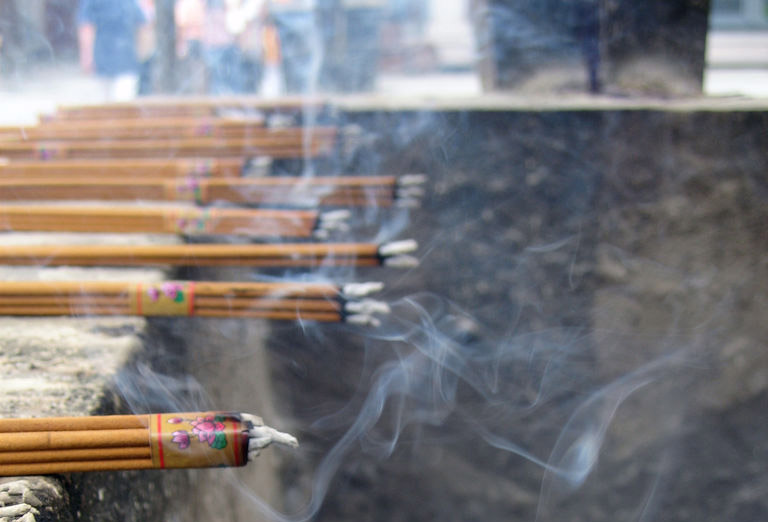
Incense
Incense is an aromatic biotic material that releases fragrant smoke when burnt. The term is used for either the material or the aroma. Incense is used for aesthetic reasons, religious worship, aromatherapy, meditation, and ceremonial reasons. It may also be used as a simple deodorant or insect repellent. Incense is composed of aromatic plant materials, often combined with essential oils. The forms taken by incense differ with the underlying culture, and have changed with advances in technology and increasing number of uses. Incense can generally be separated into two main types: "indirect-burning" and "direct-burning." Indirect-burning incense (or "non-combustible incense") is not capable of burning on its own, and requires a separate heat source. Direct-burning incense (or "combustible incense") is lit directly by a flame and then fanned or blown out, leaving a glowing ember that smoulders and releases a smoky fragrance. Direct-burning incense is either a paste formed around a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |