|
Victoria Class Battleship
The Royal Navy's ''Victoria'' class (or ''Sans Pareil'' class) of the 1880s was the first class of ironclad warship (sometimes described as a battleship) which used triple expansion steam engines, previous classes having used compound engines. There were only two ships in this class. The lead ship, , was sunk in an accidental collision with another Royal Navy battleship, HMS ''Camperdown'' in the Mediterranean Sea with the loss of half of her crew. Her sister ship, , survived until she was scrapped in April 1907. Design This class was intended to be an improved version of , and it was originally called the ''new Conquerors''. Armament The original intention had been to fit 13.5 inch (343 mm), 67-ton guns in place of the ''Conqueror''s 12 inch (305 mm) guns in the single forward turret but late during the design it was decided to enlarge them to take the 16.25 inch (413 mm), 110-ton gun. Similar guns had been supplied by the manufacturer, Sir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armstrong Whitworth
Sir W G Armstrong Whitworth & Co Ltd was a major British manufacturing company of the early years of the 20th century. With headquarters in Elswick, Tyne and Wear, Elswick, Newcastle upon Tyne, Armstrong Whitworth built armaments, ships, locomotives, automobiles and aircraft. The company was founded by William Armstrong, 1st Baron Armstrong, William Armstrong in 1847, becoming Armstrong Mitchell and then Armstrong Whitworth through mergers. In 1927, it merged with Vickers Limited to form Vickers-Armstrongs, with its automobile and aircraft interests purchased by John Siddeley, 1st Baron Kenilworth, J D Siddeley. History In 1847, the engineer William George Armstrong founded the Elswick, Tyne and Wear, Elswick works at Newcastle, to produce hydraulic machinery, cranes and bridges, soon to be followed by artillery, notably the Armstrong breech-loading gun, with which the British Army was re-equipped after the Crimean War. In 1882, it merged with the shipbuilding firm of Charles Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Ship
The lead ship, name ship, or class leader is the first of a series or class of ships that are all constructed according to the same general design. The term is applicable to naval ships and large civilian vessels. Large ships are very complex and may take five to ten years to build. Improvements based on experience with building and operating the lead ship are likely to be incorporated into the design or construction of later ships in the class, so it is rare to have vessels that are identical. The second and later ships are often started before the first one is completed, launched and tested. Nevertheless, building copies is still more efficient and cost effective than building prototypes, and the lead ship will usually be followed by copies with some improvements rather than radically different versions. The improvements will sometimes be retrofitted to the lead ship. Occasionally, the lead ship will be launched and commissioned for shakedown testing before following ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gunboat
A gunboat is a naval watercraft designed for the express purpose of carrying one or more guns to bombard coastal targets, as opposed to those military craft designed for naval warfare, or for ferrying troops or supplies. History Pre-steam era In the age of sail, a gunboat was usually a small undecked vessel carrying a single smoothbore cannon in the bow, or just two or three such cannons. A gunboat could carry one or two masts or be oar-powered only, but the single-masted version of about length was most typical. Some types of gunboats carried two cannon, or else mounted a number of swivel guns on the railings. The small gunboat had advantages: if it only carried a single cannon, the boat could manoeuvre in shallow or restricted areas – such as rivers or lakes – where larger ships could sail only with difficulty. The gun that such boats carried could be quite heavy; a 32-pounder for instance. As such boats were cheap and quick to build, naval forces favoured swarm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such a device was called an automotive, automobile, locomotive, or fish torpedo; colloquially, a ''fish''. The term ''torpedo'' originally applied to a variety of devices, most of which would today be called mines. From about 1900, ''torpedo'' has been used strictly to designate a self-propelled underwater explosive device. While the 19th-century battleship had evolved primarily with a view to engagements between armored warships with large-caliber guns, the invention and refinement of torpedoes from the 1860s onwards allowed small torpedo boats and other lighter surface vessels, submarines/submersibles, even improvised fishing boats or frogmen, and later light aircraft, to destroy large ships without the need of large guns, though somet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Mediterranean Fleet
The British Mediterranean Fleet, also known as the Mediterranean Station, was a formation of the Royal Navy. The Fleet was one of the most prestigious commands in the navy for the majority of its history, defending the vital sea link between the United Kingdom and the majority of the British Empire in the Eastern Hemisphere. The first Commander-in-Chief for the Mediterranean Fleet was the appointment of General at Sea Robert Blake in September 1654 (styled as Commander of the Mediterranean Fleet). The Fleet was in existence until 1967. Pre-Second World War The Royal Navy gained a foothold in the Mediterranean Sea when Gibraltar was captured by the British in 1704 during the War of Spanish Succession, and formally allocated to Britain in the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht. Though the British had maintained a naval presence in the Mediterranean before, the capture of Gibraltar allowed the British to establish their first naval base there. The British also used Port Mahon, on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The sea was an important rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regia Marina
The , ) (RM) or Royal Italian Navy was the navy of the Kingdom of Italy () from 1861 to 1946. In 1946, with the birth of the Italian Republic (''Repubblica Italiana''), the changed its name to '' Marina Militare'' ("Military Navy"). Origins The was established on 17 March 1861 following the proclamation of the formation of the Kingdom of Italy. Just as the Kingdom was a unification of various states in the Italian peninsula, so the was formed from the navies of those states, though the main constituents were the navies of the former kingdoms of Sardinia and Naples. The new Navy inherited a substantial number of ships, both sail- and steam-powered, and the long naval traditions of its constituents, especially those of Sardinia and Naples, but also suffered from some major handicaps. Firstly, it suffered from a lack of uniformity and cohesion; the was a heterogeneous mix of equipment, standards and practice, and even saw hostility between the officers from the various f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy (, ) was a unitary state that existed from 17 March 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 10 June 1946, when the monarchy was abolished, following civil discontent that led to an 1946 Italian institutional referendum, institutional referendum on 2 June 1946. This resulted in a modern Italian Republic. The kingdom was established through the unification of several states over a decades-long process, called the . That process was influenced by the House of Savoy, Savoy-led Kingdom of Sardinia (1720–1861), Kingdom of Sardinia, which was one of Italy's legal Succession of states, predecessor states. In 1866, Italy Third Italian War of Independence, declared war on Austrian Empire, Austria in Italo-Prussian Alliance, alliance with Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia and, upon its victory, received the region of Veneto. Italian troops Capture of Rome, entered Rome in 1870, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Class Battleship Starboard Elevation And Deck Plan
Victoria most commonly refers to: * Queen Victoria (1819–1901), Queen of the United Kingdom and Empress of India * Victoria (state), a state of Australia * Victoria, British Columbia, Canada, a provincial capital * Victoria, Seychelles, the capital city of the Seychelles * Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of victory Victoria may also refer to: Animals and plants * ''Victoria'' (moth), a moth genus in the family Geometridae * ''Victoria'' (plant), a waterlily genus in the family Nymphaeaceae * Victoria plum, a plum cultivar * Victoria (goose), the first goose to receive a prosthetic 3D printed beak * Victoria (grape), another name for the German/Italian wine grape Trollinger Arts and entertainment Films * ''Victoria'', a Russian 1917 silent film directed by Olga Preobrazhenskaya, based on the Knut Hamsun novel * ''Victoria'' (1935 film), a German film * ''Victoria'' (1972 film), a Mexican film based on Henry James' 1880 novel ''Washington Square'' * ''Victoria'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
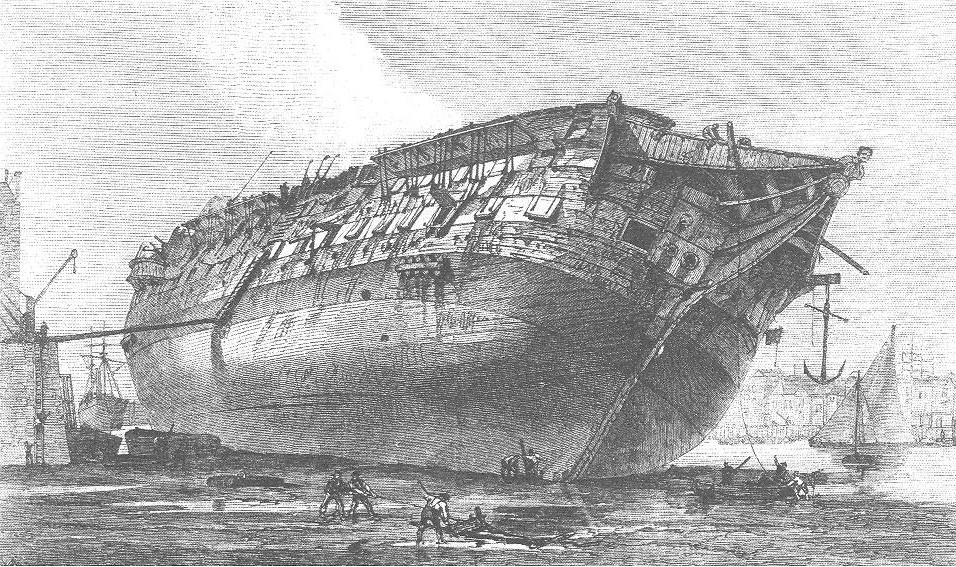
Ship Breaking
Ship breaking (also known as ship recycling, ship demolition, ship scrapping, ship dismantling, or ship cracking) is a type of ship disposal involving the breaking up of ships either as a source of Interchangeable parts, parts, which can be sold for re-use, or for the extraction of raw materials, chiefly scrap. Modern ships have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years before corrosion, Fatigue (material), metal fatigue and a lack of parts render them uneconomical to operate. Ship-breaking allows the materials from the ship, especially steel, to be recycled and made into new products. This lowers the demand for mined iron ore and reduces energy use in the steelmaking process. Fixtures and other equipment on board the vessels can also be reused. While ship-breaking is sustainable, there are concerns about its use by poorer countries without stringent environmental legislation. It is also labour-intensive, and considered one of the world's most dangerous industries. In 2012, roughly 1,250 oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister Ship
A sister ship is a ship of the same Ship class, class or of virtually identical design to another ship. Such vessels share a nearly identical hull and superstructure layout, similar size, and roughly comparable features and equipment. They often share a common naming theme, either being named after the same type of thing or person (places, constellations, heads of state) or with some kind of alliteration. Typically the ship class is named for the first ship of that class. Often, sisters become more differentiated during their service as their equipment (in the case of naval vessels, their armament) are separately altered. For instance, the U.S. warships , , , and are all sister ships, each being an . Perhaps the most famous sister ships were the White Star Line's s trio, consisting of , and . As with some other liners, the sisters worked as running mates. Of the three sister ships, ''Titanic'' and ''Britannic'' would both sink within a year of being launched, while RMS ''O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |