|
Very (Martian Crater)
Very is a Impact crater, crater on Mars, located south of the planet's equator in the heavily cratered highlands of Terra Sirenum in the Phaethontis quadrangle at 49.2°S and 177.1°W. It measures approximately in diameter. The crater was named after American astronomer Frank Washington Very. Description On the basis of their form, aspects, positions, and location amongst and apparent interaction with features thought to be rich in water ice, many researchers believed that the processes carving the gullies involve liquid water. However, this remains a topic of active research. As soon as gullies were discovered,Malin, M., Edgett, K. 2000. "Evidence for recent groundwater seepage and surface runoff on Mars". ''Science'' 288, 2330–2335. researchers began to image many gullies over and over, looking for possible changes. By 2006, some changes were found. Later, with further analysis it was determined that the changes could have occurred by dry granular flows rather than being d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmospheric pressure is a few thousandths of Earth's, atmospheric temperature ranges from and cosmic radiation is high. Mars retains some water, in the ground as well as thinly in the atmosphere, forming cirrus clouds, frost, larger polar regions of permafrost and ice caps (with seasonal snow), but no liquid surface water. Its surface gravity is roughly a third of Earth's or double that of the Moon. It is half as wide as Earth or twice the Moon, with a diameter of , and has a surface area the size of all the dry land of Earth. Fine dust is prevalent across the surface and the atmosphere, being picked up and spread at the low Martian gravity even by the weak wind of the tenuous atmosphere. The terrain of Mars roughly follows a north-south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank Washington Very
Frank Washington Very (February 12, 1852 – November 23, 1927) was a U.S. astronomer, astrophysicist, and meteorologist. He was born in Salem, Massachusetts, and educated at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (1873) where he taught physics after his graduation. After several years at MIT, Very was employed at the Allegheny Observatory at the University of Pittsburgh, where he worked from 1878–1895. In 1890, he became a professor and chair of astronomy at the University of Pittsburgh (then known as the Western University of Pennsylvania), concurrent with his post at Allegheny Observatory. He was then made professor and acting director of the Ladd Observatory at Brown University from 1896–1897. After his time at Brown, he worked as an independent researcher for nearly a decade until 1906, when he was appointed director of the Westwood Astrophysical Observatory in Westwood, Massachusetts. Very's most important work was in measuring the temperatures of the surfaces of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Crater
An impact crater is a depression (geology), depression in the surface of a solid astronomical body formed by the hypervelocity impact event, impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact craters typically have raised rims and floors that are lower in elevation than the surrounding terrain. Impact craters are typically circular, though they can be elliptical in shape or even irregular due to events such as landslides. Impact craters range in size from microscopic craters seen on lunar rocks returned by the Apollo Program to simple bowl-shaped depressions and vast, complex, multi-ringed impact basins. Meteor Crater is a well-known example of a small impact crater on Earth. Impact craters are the dominant geographic features on many solid Solar System objects including the Moon, Mercury (planet), Mercury, Callisto (moon), Callisto, Ganymede (moon), Ganymede, and most small moons and asteroids. On other planet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
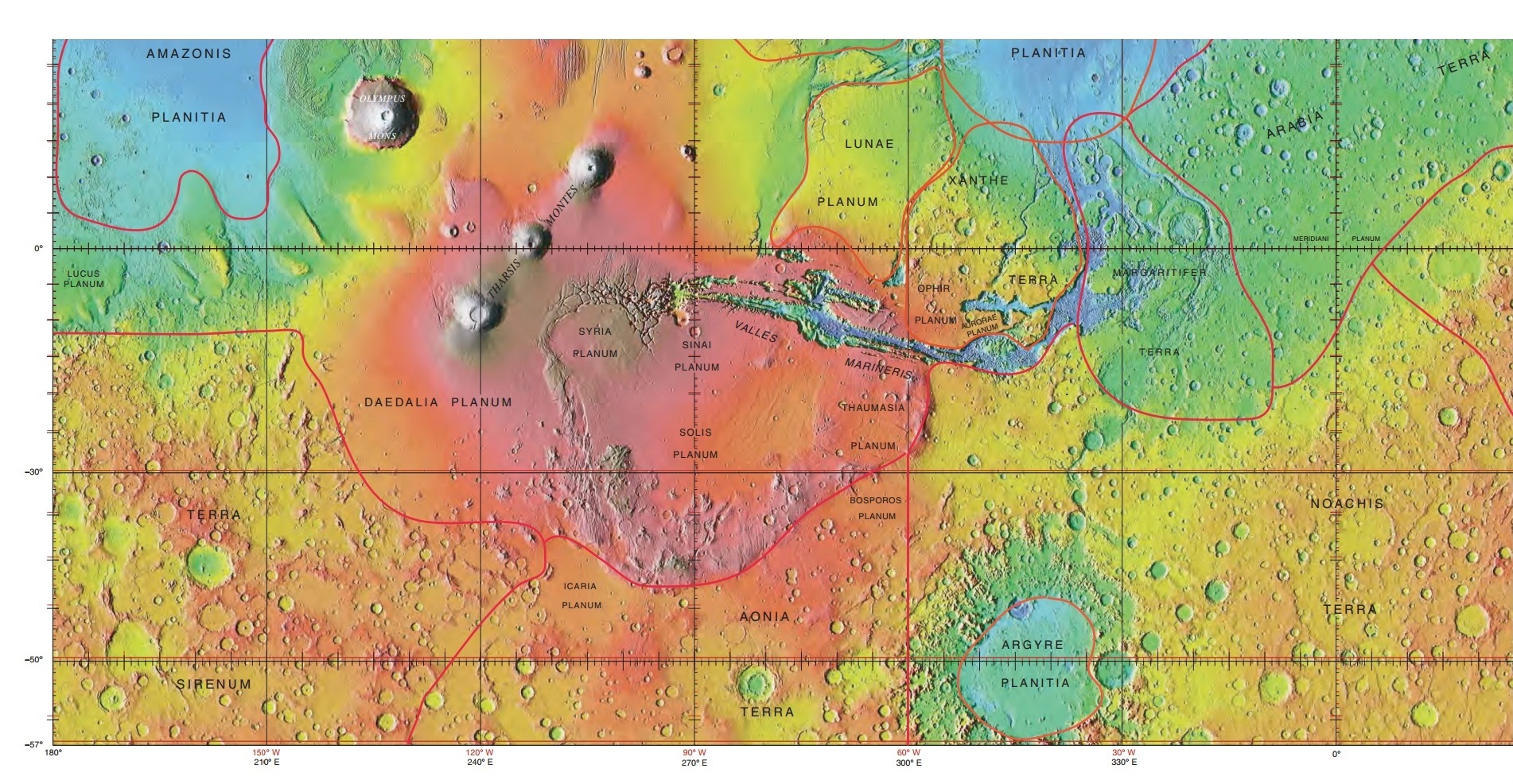
Terra Sirenum
Terra Sirenum is a large region in the southern hemisphere of the planet Mars. It is centered at and covers 3900 km at its broadest extent. It covers latitudes 10 to 70 South and longitudes 110 to 180 W. Terra Sirenum is an upland area notable for massive cratering including the large Newton Crater. Terra Sirenum is in the Phaethontis quadrangle and the Memnonia quadrangle of Mars. A low area in Terra Sirenum is believed to have once held a lake that eventually drained through Ma'adim Vallis. Terra Sirenum is named after the Sirens, who were birds with the heads of girls. In the ''Odyssey'' these girls captured passing seamen and killed them. Chloride deposits Evidence of deposits of chloride based minerals in Terra Sirenum was discovered by the 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter's Thermal Emission Imaging System in March 2008. The deposits are approximately 3.5 to 3.9 billion years old. This suggests that near-surface water was widespread in early Martian history, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaethontis Quadrangle
The Phaethontis quadrangle is one of a series of list of quadrangles on Mars, 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Phaethontis quadrangle (geography), quadrangle is also referred to as MC-24 (Mars Chart-24). The name comes from Phaethon, the son of Helios. The Phaethontis quadrangle lies between 30° and 65° south latitude and 120° and 180° west longitude on Mars. This latitude range is where numerous gullies have been discovered. An old feature in this area, called Terra Sirenum lies in this quadrangle; Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter discovered iron/magnesium smectites there. Part of this quadrangle contains what is called the Electris deposits, a deposit that is thick. It is light-toned and appears to be weak because of few boulders. Among a group of large craters is Mariner Crater, first observed by the Mariner 4, Mariner 4 spacecraft in the summer of 1965. It was named after that spacecraft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; , UAI) is an international non-governmental organization (INGO) with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and development through global cooperation. It was founded on 28 July 1919 in Brussels, Belgium and is based in Paris, France. The IAU is composed of individual members, who include both professional astronomers and junior scientists, and national members, such as professional associations, national societies, or academic institutions. Individual members are organised into divisions, committees, and working groups centered on particular subdisciplines, subjects, or initiatives. the Union had 85 national members and 12,734 individual members, spanning 90 countries and territories. Among the key activities of the IAU is serving as a forum for scientific conferences. It sponsors nine annual symposia and holds a triannual General Assembly that sets policy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gasa (crater)
Gasa is an impact rayed crater in the Eridania quadrangle on Mars at 35.68° S and 230.72° W. and is 6.5 km in diameter. Its name was approved in 2009, and it was named after a place in Bhutan. Gullies are evident in the images. It is now believed that the impact that created Gasa happened in a larger crater whose floor was covered with debris-covered glaciers. The larger crater is known as Cilaos, it is located at 35.71° S and 230.52° W. and is 21.4 km in diameter. Its name was approved on 15 August 2016, and it was named after a place in the island of Réunion. Gullies Gasa Crater contains many gullies. Gullies occur on steep slopes, especially on the walls of craters. Gullies are believed to be relatively young because they have few, if any craters. Moreover, they lie on top of sand dunes which themselves are considered to be quite young. Usually, each gully has an alcove, channel, and apron. Some studies have found that gullies occur on slopes that fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Craters On Mars
__NOTOC__ This is a list of craters on Mars. Impact craters on Mars larger than exist by the hundreds of thousands, but only about one thousand of them have names. Names are assigned by the International Astronomical Union after petitioning by relevant scientists, and in general, only craters that have a significant research interest are given names. Martian craters are named after famous scientists and science fiction authors, or if less than in diameter, after towns on Earth. Craters cannot be named for living people, and names for small craters are rarely intended to commemorate a specific town. Latitude and longitude are given as planetographic coordinates with west longitude. Catalog Martian craters are listed alphabetically on the following partial lists: * List of craters on Mars: A–G * List of craters on Mars: H–N * List of craters on Mars: O–Z Names are grouped into tables for each letter of the alphabet, containing the crater's name (linked if articl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Craters On Mars
__NOTOC__ This is a list of craters on Mars. Impact craters on Mars larger than exist by the hundreds of thousands, but only about one thousand of them have names. Names are assigned by the International Astronomical Union after petitioning by relevant scientists, and in general, only craters that have a significant research interest are given names. Martian craters are named after famous scientists and science fiction authors, or if less than in diameter, after towns on Earth. Craters cannot be named for living people, and names for small craters are rarely intended to commemorate a specific town. Latitude and longitude are given as planetographic coordinates with west longitude. Catalog Martian craters are listed alphabetically on the following partial lists: * List of craters on Mars: A–G * List of craters on Mars: H–N * List of craters on Mars: O–Z Names are grouped into tables for each letter of the alphabet, containing the crater's name (linked if article e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |