|
Vernolic Acid
Vernolic acid (leukotoxin B or isoleukotoxin) is a long chain fatty acid that is monounsaturated and contains an epoxide. It is a ''cis'' epoxide derived from the C12–C13 alkene of linoleic acid. Vernolic acid was first definitively characterized in 1954 and its absolute configuration determined in 1966. It is a major component in vernonia oil, which is produced in abundance by the genera '' Vernonia'' and ''Euphorbia'' and is a potentially useful biofeedstock. Occurrence Vernonia oil is extracted from the seeds of the '' Vernonia galamensis'' (ironweed), a plant native to eastern Africa. The seeds contain about 40 to 42% oil of which 73 to 80% is vernolic acid. The best varieties of ''V. anthelmintica'' contain about 30% less vernolic acid. Vernolic acid is not commonly found in plants in significant quantities, but some plants which do contain it are '' Vernonia'', '' Stokesia'', '' Crepis'' (from the daisy family), and '' Euphorbia lagascae'' and '' Bernardia pulchella ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Chain Fatty Acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an Branched chain fatty acids, unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important diet (nutrition), dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cell (biology), cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varnish
Varnish is a clear Transparency (optics), transparent hard protective coating or film. It is not to be confused with wood stain. It usually has a yellowish shade due to the manufacturing process and materials used, but it may also be pigmented as desired. It is sold commercially in various shades. Varnish is primarily used as a wood finishing, wood finish where, stained or not, the distinctive tones and grains in the wood are intended to be visible. Varnish finishes are naturally Gloss (material appearance), glossy, but satin/semi-gloss and flat sheens are available. History The word "varnish" comes from Mediaeval Latin ''vernix'', meaning odorous resin, perhaps derived from Middle Greek ''berōnikón'' or ''beroníkē'', meaning amber or amber-colored glass. A false etymology traces the word to the Greek ''Berenice'', the ancient name of modern Benghazi in Libya, where the first varnishes in the Mediterranean area were supposedly used and where resins from the trees of now-v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase
Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) is a bifunctional enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''EPHX2'' gene. sEH is a member of the epoxide hydrolase family. This enzyme, found in both the cytosol and peroxisomes, binds to specific epoxides and converts them to the corresponding diols. A different region of this protein also has lipid-phosphate phosphatase activity. Mutations in the ''EPHX2'' gene have been associated with familial hypercholesterolemia. Tissue distribution While most highly expressed in the liver, sEH is also expressed in other tissues including vascular endothelium, leukocytes, red blood cells, smooth muscle cells, adipocytes and the kidney proximal tubule. In the human brain, the enzyme is distributed widely, mostly in neuronal cell bodies, as well as in astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Catalyzed reactions The form of sEH in the intracellular environment is a homodimer with two distinct activities in two separate structural domains of each monomer: the C-t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
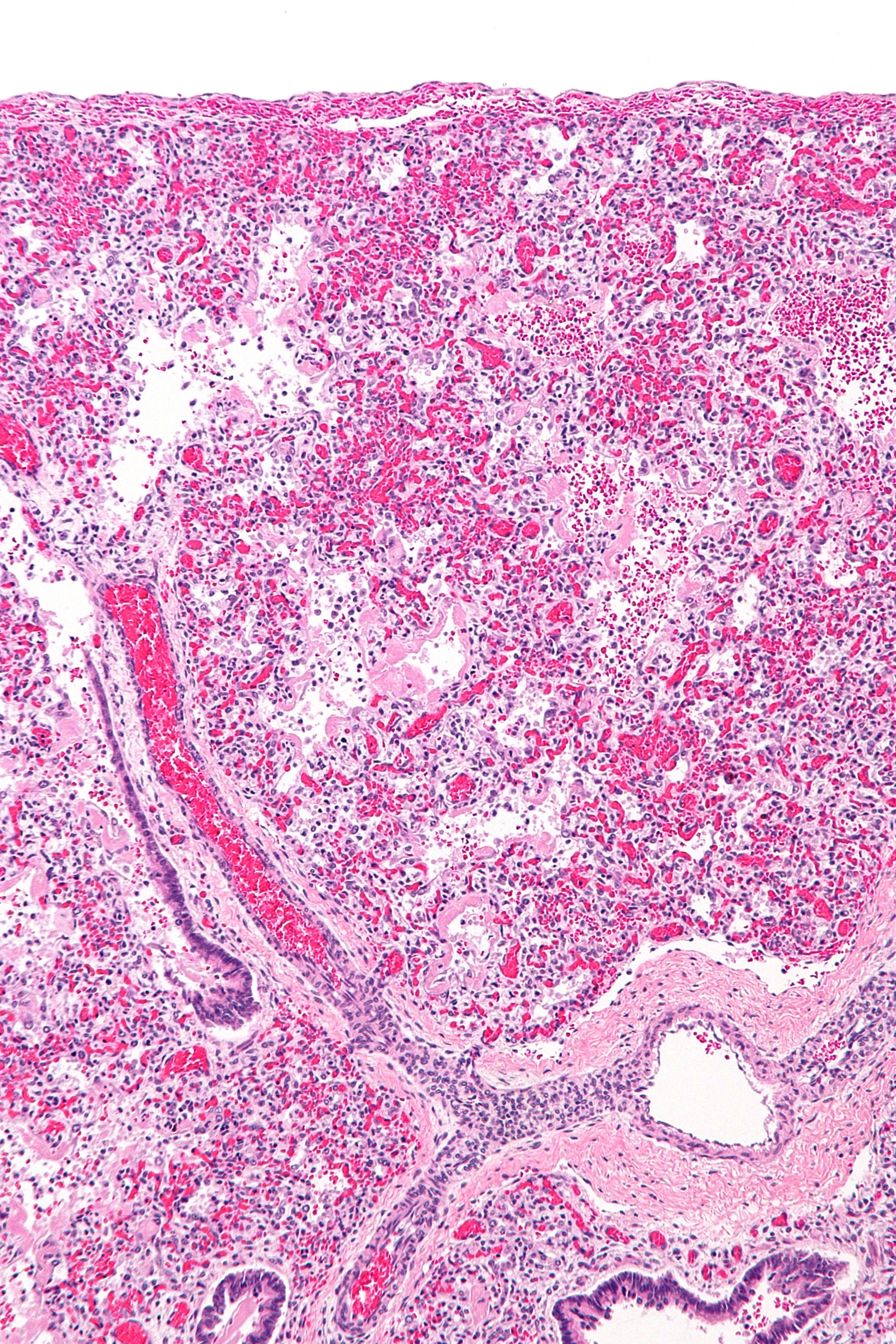
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin coloration (cyanosis). For those who survive, a decreased quality of life is common. Causes may include sepsis, pancreatitis, trauma, pneumonia, and aspiration. The underlying mechanism involves diffuse injury to cells which form the barrier of the microscopic air sacs of the lungs, surfactant dysfunction, activation of the immune system, and dysfunction of the body's regulation of blood clotting. In effect, ARDS impairs the lungs' ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. Adult diagnosis is based on a PaO2/FiO2 ratio (ratio of partial pressure arterial oxygen and fraction of inspired oxygen) of less than 300 mm Hg despite a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of more than 5 cm H2O. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukocytes
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are generally larger than red blood cells. They include three main subtypes: granulocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system. All white blood cells have nuclei, which distinguishes them from the other blood cells, the anucleated red blood cells (RBCs) and platelets. The different white blood cells are usually classified by cell lineage ( myeloid cells or lymphoid cells). White blood cells are part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. Types of white blood cells are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoxygenase
Epoxygenases are a set of membrane-bound, heme-containing cytochrome P450 (CYP450 or just CYP) enzymes that metabolize polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) to epoxide products that have a range of biological activities. The most thoroughly-studied substrate of the CYP epoxygenases is the PUFA arachidonic acid (AA). Eicosanoids are created from AA in three pathways: # Cyclooxygenases metabolize AA to various prostaglandin, thromboxane, and prostacyclin metabolites. # Lipoxygenases metabolize AA to hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (e.g. 5-HETE or 12-HETE) and leukotrienes (e.g. leukotriene B4 or leukotriene C4). # CYP epoxygenases metabolize AA to epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs). Like the first two pathways, the third acts as a signaling pathway wherein the eicosatrienoic acid epoxide products work as secondary signals to activate their parent or nearby cells and thereby orchestrate functional responses. However, these enzymes are not limited to metabolizing AA to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (P450s or CYPs) are a Protein superfamily, superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. However, they are not omnipresent; for example, they have not been found in ''Escherichia coli''. In mammals, these enzymes oxidize steroids, fatty acids, xenobiotics, and participate in many biosyntheses. By hydroxylation, CYP450 enzymes convert xenobiotics into hydrophilic derivatives, which are more readily excreted. P450s are, in general, the terminal oxidase enzymes in electron transfer chains, broadly categorized as P450-containing systems. The term "P450" is derived from the spectrophotometry, spectrophotometric peak at the wavelength of the absorption spectroscopy, absorption maximum of the enzyme (450 nanometre, nm) when it is in the redox, reduced state and complexed with carbon monoxide. Most P450s require a protein partner to deliver one or more electrons to reduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoxidation
In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether, where the ether forms a three-atom ring: two atoms of carbon and one atom of oxygen. This triangular structure has substantial ring strain, making epoxides highly reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale for many applications. In general, low molecular weight epoxides are colourless and nonpolar, and often volatile. Nomenclature A compound containing the epoxide functional group can be called an epoxy, epoxide, oxirane, and ethoxyline. Simple epoxides are often referred to as oxides. Thus, the epoxide of ethylene (C2H4) is ethylene oxide (C2H4O). Many compounds have trivial names; for instance, ethylene oxide is called "oxirane". Some names emphasize the presence of the epoxide functional group, as in the compound ''1,2-epoxyheptane'', which can also be called ''1,2-heptene oxide''. A polymer formed from epoxide precursors is called an ''epoxy''. However, few if any of the epoxy groups in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linseed Oil
Linseed oil, also known as flaxseed oil or flax oil (in its edible form), is a colorless to yellowish oil obtained from the dried, ripened seeds of the flax plant (''Linum usitatissimum''). The oil is obtained by pressing, sometimes followed by solvent extraction. Owing to its polymer-forming properties, linseed oil is often blended with combinations of other oils, resins or solvents as an impregnator, drying oil finish or varnish in wood finishing, as a pigment binder in oil paints, as a plasticizer and hardener in putty, and in the manufacture of linoleum. Linseed oil use has declined over the past several decades with increased availability of synthetic alkyd resins—which function similarly but resist yellowing. Structure and composition : 450px, Representative triglyceride found in a linseed oil, a triester ( , and Linseed oil is a triglyceride, like other fats. Linseed oil is distinctive for its unusually large amount of α-linolenic acid, which oxidises in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soybean Oil
Soybean oil (British English: soyabean oil) is a vegetable oil extracted from soybean (''Glycine max'') legumes. It is one of the most widely consumed cooking oils and the second most consumed vegetable oil. As a drying oil, processed soybean oil is also used as a base for printing inks ( soy ink) and oil paints. Production To produce soybean oil, the soybeans are cracked, adjusted for moisture content, heated to between , rolled into flakes, and solvent-extracted with hexanes. The oil is then refined, blended for different applications, and sometimes hydrogenated. Soybean oils, both liquid and partially hydrogenated are sold as "vegetable oil", or are ingredients in a wide variety of processed foods. Most of the remaining residue ( soybean meal) is used as animal feed. In the 2002–2003 growing season, 30.6 million tons (MT) of soybean oil were produced worldwide, constituting about half of worldwide edible vegetable oil production, and thirty percent of all fats and oils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoxy
Epoxy is the family of basic components or Curing (chemistry), cured end products of epoxy Resin, resins. Epoxy resins, also known as polyepoxides, are a class of reactive prepolymers and polymers which contain epoxide groups. The epoxide functional group is also collectively called ''epoxy''. The IUPAC name for an epoxide group is an oxirane. Epoxy resins may be reacted (cross-linked) either with themselves through catalytic homopolymerisation, or with a wide range of co-reactants including polyfunctional amines, acids (and acid anhydrides), phenols, alcohols and thiols (sometimes called mercaptans). These co-reactants are often referred to as hardeners or curatives, and the cross-linking reaction is commonly referred to as Curing (chemistry), curing. Reaction of polyepoxides with themselves or with polyfunctional hardeners forms a thermosetting polymer, often with favorable mechanical properties and high thermal and chemical resistance. Epoxy has a wide range of application ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil-based Paint
Oil paint is a type of slow-drying paint that consists of particles of pigment suspended in a drying oil, commonly linseed oil. Oil paint also has practical advantages over other paints, mainly because it is waterproof. The earliest surviving examples of oil paint have been found in Asia from as early as the 7th century AD, in examples of Buddhist paintings in Afghanistan. Oil-based paints made their way to Europe by the 12th century and were used for simple decoration, mostly on wood. Common modern applications of oil paint are in finishing and protection of wood in buildings and exposed metal structures such as ships and bridges. Its hard-wearing properties and luminous colors make it desirable for both interior and exterior use on wood and metal. Due to its slow-drying properties, it has recently been used in paint-on-glass animation. The thickness of the coat has considerable bearing on the time required for drying: thin coats of oil paint dry relatively quickly. The visco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |