|
Vasum Subpugillare
''Vasum subpugillare'' is an extinct species of medium to large sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Turbinellidae. MolluscaBase eds. (2023). MolluscaBase. Vasum subpugillare (d'Orbigny, 1852) †. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1551528 on 2023-01-26 Description Distribution Fossils of this marine species have been found in Oligocene strata in France France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan .... References * Lozouet, P. (2021). Turbinelloidea, Mitroidea, Olivoidea, Babyloniidae et Harpidae (Gastropoda, Neogastropoda) de l'Oligocène supérieur (Chattien) du bassin de l'Adour (Sud-Ouest de la France). Cossmanniana. 23: 3-69. External links Orbigny A. D. d'. (1850-1852). Prodr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcide D'Orbigny
Alcide Charles Victor Marie Dessalines d'Orbigny (6 September 1802 – 30 June 1857) was a French naturalist who made major contributions in many areas, including zoology (including malacology), palaeontology, geology, archaeology and anthropology. D'Orbigny was born in Couëron (Loire-Atlantique), the son of a ship's physician and amateur naturalist. The family moved to La Rochelle in 1820, where his interest in natural history was developed while studying the marine fauna and especially the microscopic creatures that he named "foraminiferans". In Paris he became a disciple of the geologist Louis Cordier, Pierre Louis Antoine Cordier (1777–1861) and Georges Cuvier. All his life, he would follow the theory of Cuvier and stay opposed to Lamarckism. South American era D'Orbigny travelled on a mission for the Paris Museum, in South America between 1826 and 1833. He visited Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, Argentina, Paraguay, and Brazil, and returned to Franc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Snail
Sea snails are slow-moving marine (ocean), marine gastropod Mollusca, molluscs, usually with visible external shells, such as whelk or abalone. They share the Taxonomic classification, taxonomic class Gastropoda with slugs, which are distinguished from snails primarily by the absence of a visible Gastropod shell, shell. Definition Determining whether some gastropods should be called sea snails is not always easy. Some species that live in brackish water (such as certain Neritidae, neritids) can be listed as either freshwater snails or marine snails, and some species that live at or just above the high tide level (for example, species in the genus ''Truncatella (gastropod), Truncatella'') are sometimes considered to be sea snails and sometimes listed as land snails. Anatomy Sea snails are a very large and diverse group of animals. Most snails that live in salt water respire using a gill or gills; a few species, though, have a lung, are intertidal, and are active only at low tide w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine (ocean)
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Antarctic/Southern, and Arctic Ocean),"Ocean." ''Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary'', Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/ocean . Accessed March 14, 2021. and are themselves mostly divided into seas, gulfs and subsequent bodies of water. The ocean contains 97% of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropod
Gastropods (), commonly known as slugs and snails, belong to a large Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, freshwater, and from the land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and sea slug, slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda is a diverse and highly successful class of mollusks within the phylum Mollusca. It contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Furongian, Late Cambrian. , 721 family (taxonomy), families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently neontology, extant living fossil, with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusk
Mollusca is a phylum of protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum after Arthropoda. The number of additional fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000, and the proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat, as numerous groups are freshwater and even terrestrial species. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known extant i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family (, : ) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". The delineation of what constitutes a family—or whether a described family should be acknowledged—is established and decided upon by active taxonomists. There are not strict regulations for outlining or acknowledging a family, yet in the realm of plants, these classifications often rely on both the vegetative and reproductive characteristics of plant species. Taxonomists frequently hold varying perspectives on these descriptions, leading to a lack of widespread consensus within the scientific community ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbinellidae
Turbinellidae are a family of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the clade Neogastropoda. Members of this family are predators. Distribution Species in this family are found worldwide, mostly in tropical shallow waters but some in deep waters. Subfamilies * sub-family Columbariinae Tomlin, 1928 ** genus ''Columbarium'' Martens, 1881 ** genus '' Coluzea'' Finlay, 1926 ** genus '' Fulgurofusus'' Grabau, 1904 ** genus '' Fustifusus'' Harasewych, 1991 ** genus '' Peristarium'' Bayer, 1971 * sub-family Tudiclinae Cossmann, 1901 ** genus '' Tudicla'' Röding, 1798 * sub-family Turbinellinae Swainson, 1835 ** genus '' Cryptofusus'' Beu, 2011 ** genus ''Syrinx'' Röding, 1798 ** genus '' Turbinella'' Lamarck, 1799 * sub-family Vasinae H. Adams & A. Adams, 1853 (1840) ** genus '' Altivasum'' Hedley, 1914 ** genus '' Enigmavasum'' Poppe & Tagaro, 2005 ** genus '' Pisanella'' Koenen, 1865 ** genus '' Tudivasum'' Rosenberg & Petit, 1987 ** genus '' Vasum'' Röding, 1798 * genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
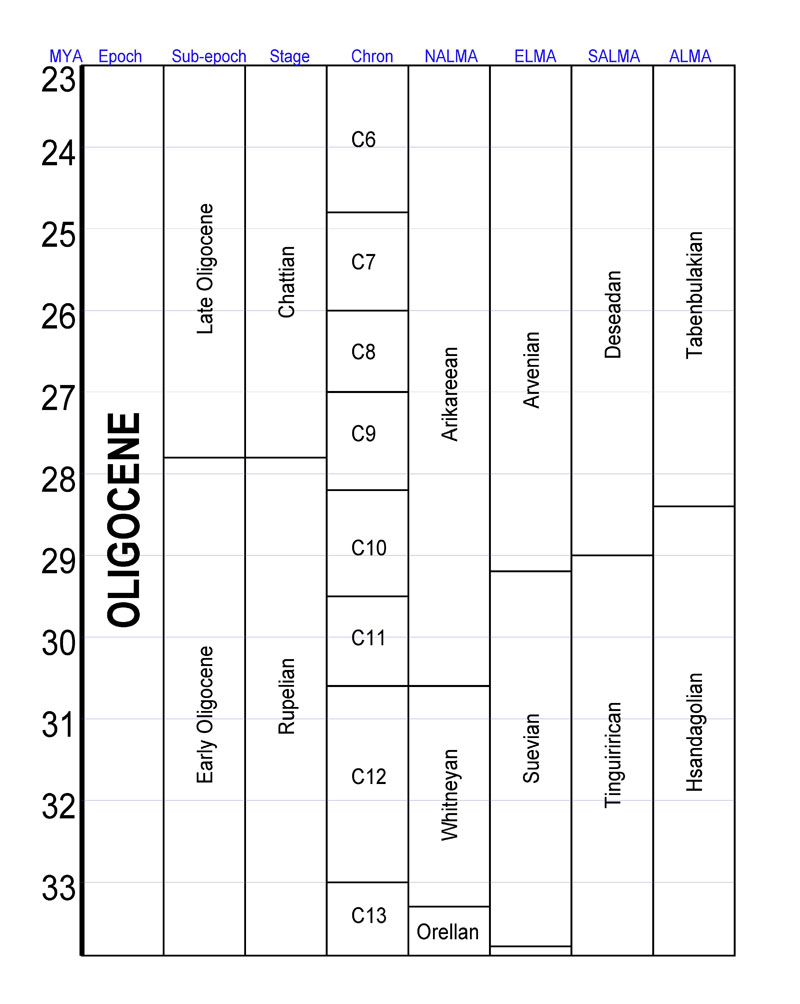
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of Neontology, extant forms of Mollusca, molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasum
''Vasum'', common name the vase snails or vase shells, is a genus of mostly rather large predatory sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the subfamily Vasinae within the family Turbinellidae.Bouchet, P. (2011). Vasum Röding, 1798. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=205505 on 15 April 2012 Shell description Shells of species in this genus are usually somewhat large, and are usually very thick and heavy. They are often vase-shaped, in the sense that the shell of most of the species is more or less widely conical. The shells have a thick periostracum, a low spires, and 2, 3 or 4 plaits on the columella. The shell is oval, oblong, solid, tubercular or spinose, with spinose fascicles below. The spire is short. The apex is not papillary. The aperture is oblong. The siphonal canal is short and somewhat recurved. The columella contains several transverse folds in the middle. The outer lip is thickened and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |