|
Variations On A Theme By Paganini (Lutosławski)
''Variations on a Theme by Paganini'' ( pl, Wariacje na temat Paganiniego), often referred to as the ''Paganini Variations'', is an arrangement for two pianos of Niccolò Paganini's Caprice No. 24, from Paganini's original set of 24 Caprices for violin, written by Polish composer Witold Lutosławski. The arrangement, originally composed in 1941, was later re-arranged for piano and orchestra. Background Version for two pianos (1941) In the years leading up to Lutosławski's completion of this piece, the composer was a minor officer in the Polish Army when Poland was invaded in the events prior to World War II, by the Soviets from the East and the Nazis from every other direction. After escaping from his initial capture, he fled on foot more than four hundred kilometers towards his home in Warsaw, which rendered him without an official identity until the end of the war. After some time performing in small cafés to make his living, as Germans had banned public concerts, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niccolò Paganini
Niccolò (or Nicolò) Paganini (; 27 October 178227 May 1840) was an Italian violinist and composer. He was the most celebrated violin virtuoso of his time, and left his mark as one of the pillars of modern violin technique. His 24 Caprices for Solo Violin Op. 1 are among the best known of his compositions and have served as an inspiration for many prominent composers. Biography Childhood Niccolò Paganini was born in Genoa (then capital of the Republic of Genoa) on 27 October 1782, the third of the six children of Antonio and Teresa (née Bocciardo) Paganini. Paganini's father was an unsuccessful trader, but he managed to supplement his income by playing music on the mandolin. At the age of five, Paganini started learning the mandolin from his father and moved to the violin by the age of seven. His musical talents were quickly recognized, earning him numerous scholarships for violin lessons. The young Paganini studied under various local violinists, including Giovanni Ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brian Priestman
Brian Priestman (10 February 192718 April 2014) was a British conductor and music educator. Biography Priestman was born in Birmingham, England. He studied at the University of Birmingham (BMus Music; MA Music, 1952) and the Royal Conservatory of Brussels, Belgium. He founded and was principal conductor of the Opera da Camera and the Orchestra da Camera in Birmingham, and Music Director of the Royal Shakespeare Theatre at Stratford-upon-Avon (1960–1963). He was Music Director of the Edmonton Symphony Orchestra (1964–1968), Music Director of the Handel Society of New York (1966–1970), Resident Conductor of the Baltimore Symphony Orchestra (1968–1970), Music Director of the Denver Symphony Orchestra (1970–1978), Principal Conductor of the New Zealand National Orchestra (1973–1976), Music Director of the Florida Philharmonic (1977–1980), Principal Conductor of the Cape Town Symphony (1980–1986), and Principal Guest Conductor of the Malmö Symphony Orchestra (1988� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
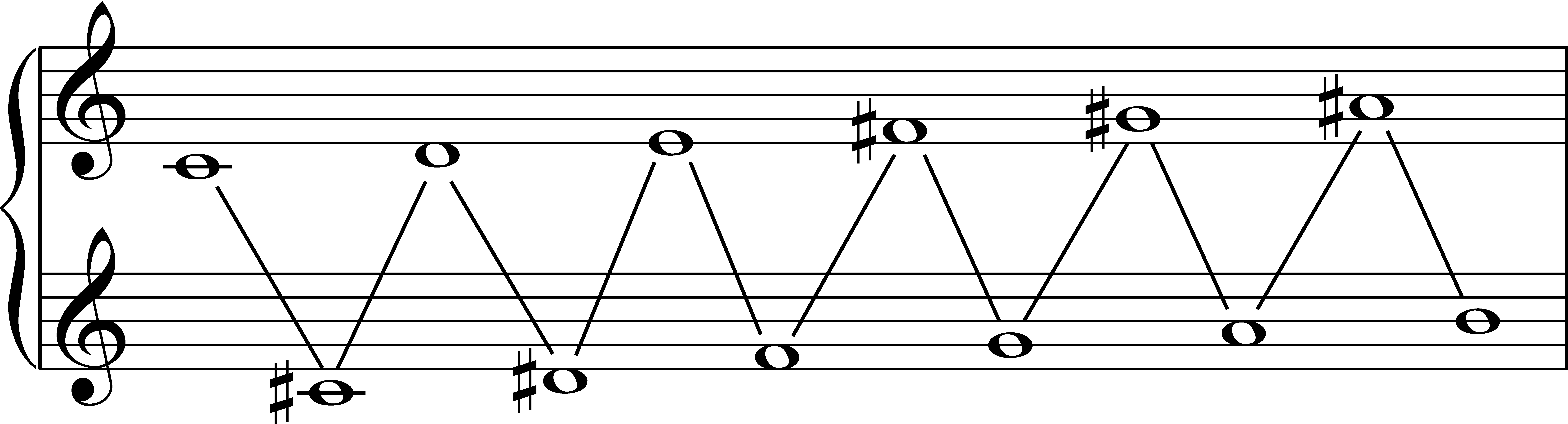
Marta Ptaszyńska
Marta Ptaszyńska (born 29 July 1943) is a Polish composer, percussionist and professor of music at the University of Chicago. She has been described by the Polish Music Center of the University of Southern California as "one of the best known Polish woman composers" as well as "a virtuoso percussionist specializing in performances of contemporary music". (archive from 5 June 2016), accessed 27 September 2018. Career Ptaszyńska was born in , Poland. In 1998, she was appointed a Professor of Music and the Humanities at the University of Chicago. Since 2005 she holds ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whole-tone Scale
In music, a whole-tone scale is a scale in which each note is separated from its neighbors by the interval of a whole tone. In twelve-tone equal temperament, there are only two complementary whole-tone scales, both six-note or '' hexatonic'' scales. A single whole-tone scale can also be thought of as a "six-tone equal temperament". : : The whole-tone scale has no leading tone and because all tones are the same distance apart, "no single tone stands out, ndthe scale creates a blurred, indistinct effect". This effect is especially emphasised by the fact that triads built on such scale tones are all augmented triads. Indeed, all six tones of a whole-tone scale can be played simply with two augmented triads whose roots are a major second apart. Since they are symmetrical, whole-tone scales do not give a strong impression of the tonic or tonality. The composer Olivier Messiaen called the whole-tone scale his first mode of limited transposition. The composer and music t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triplet (music)
In music, a tuplet (also irrational rhythm or groupings, artificial division or groupings, abnormal divisions, irregular rhythm, gruppetto, extra-metric groupings, or, rarely, contrametric rhythm) is "any rhythm that involves dividing the beat into a different number of equal subdivisions from that usually permitted by the time-signature (e.g., triplets, duplets, etc.)" This is indicated by a number, or sometimes two indicating the fraction involved. The notes involved are also often grouped with a bracket or (in older notation) a slur. The most common type of tuplet is the triplet. Terminology The modern term 'tuplet' comes from a rebracketing of compound words like quintu(s)-(u)plet and sextu(s)-(u)plet, and from related mathematical terms such as " tuple", "-uplet" and "-plet", which are used to form terms denoting multiplets (''Oxford English Dictionary'', entries "multiplet", "-plet, ''comb. form''", "-let, ''suffix''", and "-et, ''suffix''1"). An alternative modern t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon (music)
In music, a canon is a contrapuntal ( counterpoint-based) compositional technique that employs a melody with one or more imitations of the melody played after a given duration (e.g., quarter rest, one measure, etc.). The initial melody is called the leader (or ''dux''), while the imitative melody, which is played in a different voice, is called the follower (or ''comes''). The follower must imitate the leader, either as an exact replication of its rhythms and intervals or some transformation thereof. Repeating canons in which all voices are musically identical are called rounds—" Row, Row, Row Your Boat" and " Frère Jacques" are popular examples. An accompanied canon is a canon accompanied by one or more additional independent parts that do not imitate the melody. History Medieval and Renaissance During the Middle Ages, Renaissance, and Baroque—that is, through the early 18th century—any kind of imitative musical counterpoints were called fugues, with the strict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadence (music)
In Western musical theory, a cadence (Latin ''cadentia'', "a falling") is the end of a phrase in which the melody or harmony creates a sense of full or partial resolution, especially in music of the 16th century onwards. Don Michael Randel (1999). ''The Harvard Concise Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', pp. 105-106. . A harmonic cadence is a progression of two or more chords that concludes a phrase, section, or piece of music. A rhythmic cadence is a characteristic rhythmic pattern that indicates the end of a phrase. A cadence can be labeled "weak" or "strong" depending on the impression of finality it gives. While cadences are usually classified by specific chord or melodic progressions, the use of such progressions does not necessarily constitute a cadence—there must be a sense of closure, as at the end of a phrase. Harmonic rhythm plays an important part in determining where a cadence occurs. Cadences are strong indicators of the tonic or central pitch of a pas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F♯ (musical Note)
F (F-sharp; also known as fa dièse or fi) is the seventh semitone of the solfège. It lies a chromatic semitone above F and a diatonic semitone below G, thus being enharmonic to ''sol bémol'' or G (G-flat). However, in some temperaments, it is not the same as G. G is a major third below B, whereas F is a major third above D (a minor third below A). Another enharmonic note is E (E-double sharp). When calculated in equal temperament with a reference of A above middle C as 440 Hz, the frequency of the F above middle C (or F4) is approximately 369.994 Hz. See pitch (music) for a discussion of historical variations in frequency. Designation by octave Scales Common scales beginning on F * F major: F G A B C D E F * F natural minor: F G A B C D E F * F harmonic minor: F G A B C D E F * F melodic minor ascending: F G A B C D E F * F melodic minor descending: F E D C B A G F Diatonic scales * F Ionian: F G A B C D E F * F Dorian: F G A B C D E F * F Phrygian: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterpoint
In music, counterpoint is the relationship between two or more musical lines (or voices) which are harmonically interdependent yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. It has been most commonly identified in the European classical tradition, strongly developing during the Renaissance and in much of the common practice period, especially in the Baroque period. The term originates from the Latin ''punctus contra punctum'' meaning "point against point", i.e. "note against note". In Western pedagogy, counterpoint is taught through a system of species (see below). There are several different forms of counterpoint, including imitative counterpoint and free counterpoint. Imitative counterpoint involves the repetition of a main melodic idea across different vocal parts, with or without variation. Compositions written in free counterpoint often incorporate non-traditional harmonies and chords, chromaticism and dissonance. General principles The term "counterpoint" has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tritone
In music theory, the tritone is defined as a musical interval composed of three adjacent whole tones (six semitones). For instance, the interval from F up to the B above it (in short, F–B) is a tritone as it can be decomposed into the three adjacent whole tones F–G, G–A, and A–B. Narrowly defined, each of these whole tones must be a step in the scale, so by this definition, within a diatonic scale there is only one tritone for each octave. For instance, the above-mentioned interval F–B is the only tritone formed from the notes of the C major scale. More broadly, a tritone is also commonly defined as any interval with a width of three whole tones (spanning six semitones in the chromatic scale), regardless of scale degrees. According to this definition, a diatonic scale contains two tritones for each octave. For instance, the above-mentioned C major scale contains the tritones F–B (from F to the B above it, also called augmented fourth) and B–F (from B to the F above ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Fifths
In music, consecutive fifths or parallel fifths are progressions in which the interval of a perfect fifth is followed by a ''different'' perfect fifth between the same two musical parts (or voices): for example, from C to D in one part along with G to A in a higher part. Octave displacement is irrelevant to this aspect of musical grammar; for example, a parallel twelfth (i.e., an octave plus a fifth) is equivalent to a parallel fifth.Thus, the word "parallel" is not truly synonymous with "consecutive", as a fifth followed by another fifth approached with contrary motion would still count as consecutive fifths. The term ''parallel fifths'' may therefore be misleading because some consecutive fifths occur with contrary motion: from a true uncompounded fifth to a twelfth, for example. If parts move by oblique motion (for example, one part moving from a C to a higher C, and another part repeating a G higher than both of those Cs), the intervals are not considered to differ in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polytonality
Polytonality (also polyharmony) is the musical use of more than one key (music), key simultaneity (music), simultaneously. Bitonality is the use of only two different keys at the same time. Polyvalence or polyvalency is the use of more than one diatonic function, harmonic function, from the same key, at the same time. Some examples of bitonality superimpose fully harmony, harmonized sections of music in different keys. History In traditional music Lithuanian traditional singing style sutartines is based on polytonality. A typical sutartines song is based on a six-bar melody, where the first three bars contains melody based on the notes of the triad of a major key (for example, in G major), and the next three bars is based on another key, always a major second higher or lower (for example, in A major). This six-bar melody is performed as a canon (music), canon, and repetition starts from the fourth bar. As a result, parts are constantly singing in different tonality (key) simultan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |