|
Variation (game Tree)
A variation can refer to a specific sequence of successive moves in a turn-based game, often used to specify a hypothetical future state of a game that is being played. Although the term is most commonly used in the context of Chess analysis, it has been applied to other games. It also is a useful term used when describing computer tree-search algorithms (for example minimax) for playing games such as Go{{cite web , url=http://www.andromeda.com/people/ddyer/go/search.html, title=Searches, tree pruning and tree ordering in Go, date=21 December 2007 or Chess. A variation can be any number of steps as long as each step would be legal if it were to be played. It is often as far ahead as a human or computer can calculate; or however long is necessary to reach a particular position of interest. It may also lead to a terminal state in the game, in which case the term "winning variation" or "losing variation" is sometimes used. Principal variation The principal variation refers to the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess
Chess is a board game for two players. It is an abstract strategy game that involves Perfect information, no hidden information and no elements of game of chance, chance. It is played on a square chessboard, board consisting of 64 squares arranged in an 8×8 grid. The players, referred to as White and Black in chess, "White" and "Black", each control sixteen Chess piece, pieces: one king (chess), king, one queen (chess), queen, two rook (chess), rooks, two bishop (chess), bishops, two knight (chess), knights, and eight pawn (chess), pawns, with each type of piece having a different pattern of movement. An enemy piece may be captured (removed from the board) by moving one's own piece onto the square it occupies. The object of the game is to "checkmate" (threaten with inescapable capture) the enemy king. There are also several ways a game can end in a draw (chess), draw. The recorded history of chess goes back to at least the emergence of chaturanga—also thought to be an ancesto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Tree
In the context of combinatorial game theory, a game tree is a graph representing all possible game states within a sequential game that has perfect information. Such games include chess, checkers, Go, and tic-tac-toe. A game tree can be used to measure the complexity of a game, as it represents all the possible ways that the game can pan out. Due to the large game trees of complex games such as chess, algorithms that are designed to play this class of games will use partial game trees, which makes computation feasible on modern computers. Various methods exist to solve game trees. If a complete game tree can be generated, a deterministic algorithm, such as backward induction or retrograde analysis can be used. Randomized algorithms and minmax algorithms such as MCTS can be used in cases where a complete game tree is not feasible. Understanding the game tree To better understand the game tree, it can be thought of as a technique for analyzing adversarial games, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimax Algorithm
Minimax (sometimes Minmax, MM or saddle point) is a decision rule used in artificial intelligence, decision theory, combinatorial game theory, statistics, and philosophy for ''minimizing'' the possible loss function, loss for a Worst-case scenario, worst case (''max''imum loss) scenario. When dealing with gains, it is referred to as "maximin" – to maximize the minimum gain. Originally formulated for several-player zero-sum game theory, covering both the cases where players take alternate moves and those where they make simultaneous moves, it has also been extended to more complex games and to general decision-making in the presence of uncertainty. Game theory In general games The maximin value is the highest value that the player can be sure to get without knowing the actions of the other players; equivalently, it is the lowest value the other players can force the player to receive when they know the player's action. Its formal definition is: :\underline = \max_ \min_ W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Go (board Game)
# Go is an abstract strategy game, abstract strategy board game for two players in which the aim is to fence off more territory than the opponent. The game was invented in China more than 2,500 years ago and is believed to be the oldest board game continuously played to the present day. A 2016 survey by the International Go Federation's 75 member nations found that there are over 46 million people worldwide who know how to play Go, and over 20 million current players, the majority of whom live in East Asia. The Game piece (board game), playing pieces are called ''Go equipment#Stones, stones''. One player uses the white stones and the other black stones. The players take turns placing their stones on the vacant intersections (''points'') on the #Boards, board. Once placed, stones may not be moved, but ''captured stones'' are immediately removed from the board. A single stone (or connected group of stones) is ''captured'' when surrounded by the opponent's stones on all Orthogona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principle Variation 16bit
A principle may relate to a fundamental truth or proposition that serves as the foundation for a system of beliefs or behavior or a chain of reasoning. They provide a guide for behavior or evaluation. A principle can make values explicit, so they are expressed in the form of rules and standards. Principles unpack the values underlying them more concretely so that the values can be more easily operationalized in policy statements and actions. In law, higher order, overarching principles establish rules to be followed, modified by sentencing guidelines relating to context and proportionality. In science and nature, a principle may define the essential characteristics of the system, or reflect the system's designed purpose. The effective operation would be impossible if any one of the principles was to be ignored. A system may be explicitly based on and implemented from a document of principles as was done in IBM's 360/370 ''Principles of Operation''. It is important to differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of research in computer science that develops and studies methods and software that enable machines to machine perception, perceive their environment and use machine learning, learning and intelligence to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals. High-profile applications of AI include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google Search); recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon (company), Amazon, and Netflix); virtual assistants (e.g., Google Assistant, Siri, and Amazon Alexa, Alexa); autonomous vehicles (e.g., Waymo); Generative artificial intelligence, generative and Computational creativity, creative tools (e.g., ChatGPT and AI art); and Superintelligence, superhuman play and analysis in strategy games (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Tree
In the context of combinatorial game theory, a game tree is a graph representing all possible game states within a sequential game that has perfect information. Such games include chess, checkers, Go, and tic-tac-toe. A game tree can be used to measure the complexity of a game, as it represents all the possible ways that the game can pan out. Due to the large game trees of complex games such as chess, algorithms that are designed to play this class of games will use partial game trees, which makes computation feasible on modern computers. Various methods exist to solve game trees. If a complete game tree can be generated, a deterministic algorithm, such as backward induction or retrograde analysis can be used. Randomized algorithms and minmax algorithms such as MCTS can be used in cases where a complete game tree is not feasible. Understanding the game tree To better understand the game tree, it can be thought of as a technique for analyzing adversarial games, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backtracking
Backtracking is a class of algorithms for finding solutions to some computational problems, notably constraint satisfaction problems, that incrementally builds candidates to the solutions, and abandons a candidate ("backtracks") as soon as it determines that the candidate cannot possibly be completed to a valid solution. The classic textbook example of the use of backtracking is the eight queens puzzle, that asks for all arrangements of eight chess queens on a standard chessboard so that no queen attacks any other. In the common backtracking approach, the partial candidates are arrangements of ''k'' queens in the first ''k'' rows of the board, all in different rows and columns. Any partial solution that contains two mutually attacking queens can be abandoned. Backtracking can be applied only for problems which admit the concept of a "partial candidate solution" and a relatively quick test of whether it can possibly be completed to a valid solution. It is useless, for exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimax
Minimax (sometimes Minmax, MM or saddle point) is a decision rule used in artificial intelligence, decision theory, combinatorial game theory, statistics, and philosophy for ''minimizing'' the possible loss function, loss for a Worst-case scenario, worst case (''max''imum loss) scenario. When dealing with gains, it is referred to as "maximin" – to maximize the minimum gain. Originally formulated for several-player zero-sum game theory, covering both the cases where players take alternate moves and those where they make simultaneous moves, it has also been extended to more complex games and to general decision-making in the presence of uncertainty. Game theory In general games The maximin value is the highest value that the player can be sure to get without knowing the actions of the other players; equivalently, it is the lowest value the other players can force the player to receive when they know the player's action. Its formal definition is: :\underline = \max_ \min_ W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
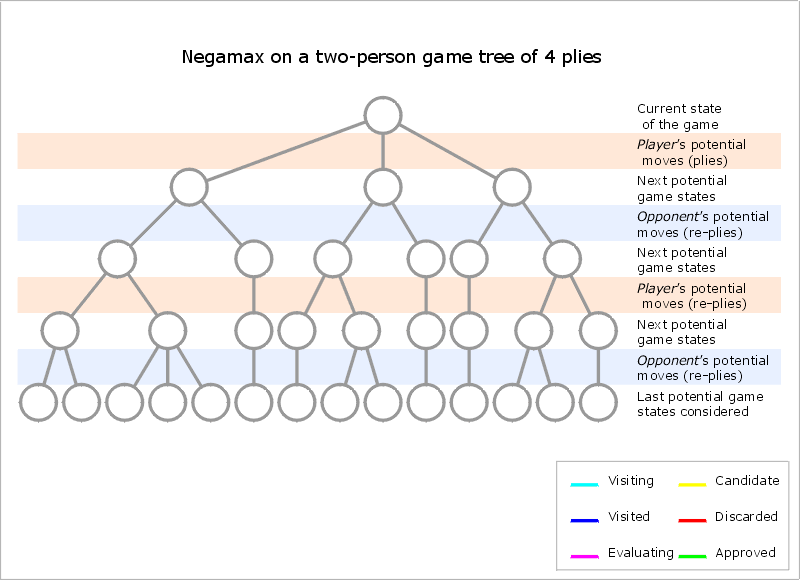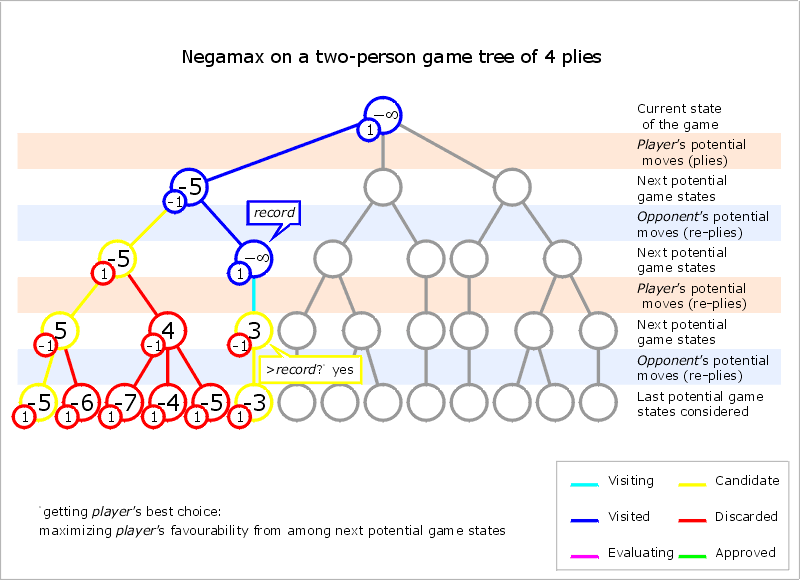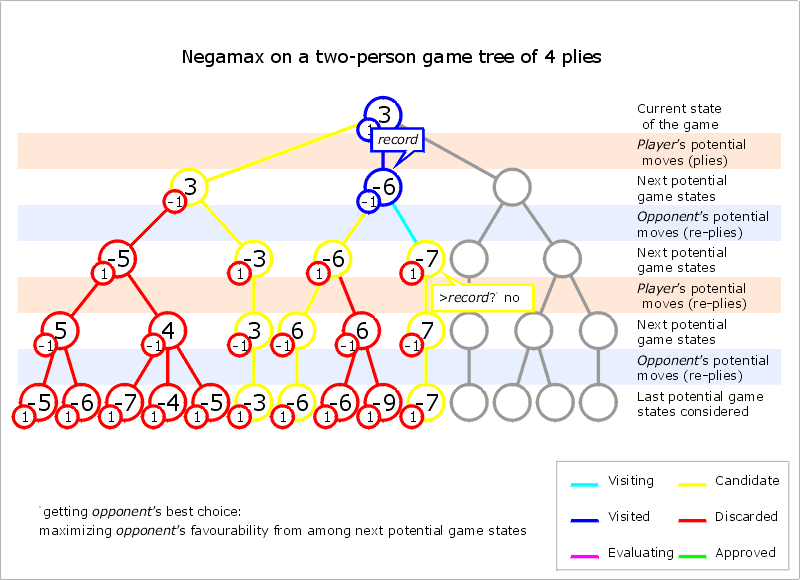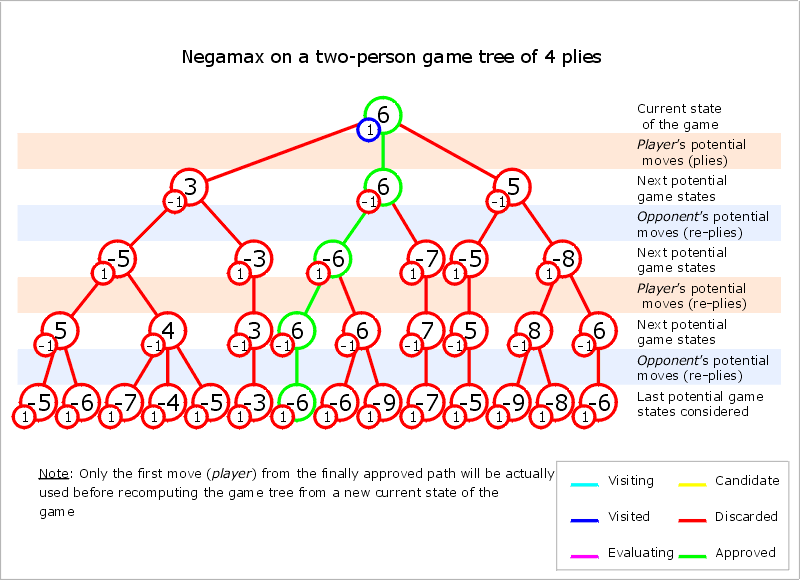
Negamax
Negamax search is a variant form of minimax search that relies on the Zero-sum (Game theory), zero-sum property of a two-player game. This algorithm relies on the fact that to simplify the implementation of the minimax algorithm. More precisely, the value of a position to player A in such a game is the negation of the value to player B. Thus, the player on move looks for a move that maximizes the negation of the value resulting from the move: this successor position must by definition have been valued by the opponent. The reasoning of the previous sentence works regardless of whether A or B is on move. This means that a single procedure can be used to value both positions. This is a coding simplification over minimax, which requires that A selects the move with the maximum-valued successor while B selects the move with the minimum-valued successor. It should not be confused with negascout, an algorithm to compute the minimax or negamax value quickly by clever use of alpha–beta p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-beta Pruning
Alphabeta or Alpha Beta may also refer to: * Alphabeta, an Israeli musical group * Alpha Beta, a former chain of Californian supermarkets * The Greek alphabet, from ''Alpha'' (Αα) and ''Beta'' (Ββ), the first two letters * Alpha and beta anomers (chemistry) * Alpha–beta pruning, a type of search algorithm * Alpha–beta transformation, a mathematical transformation in electrical engineering * α,β-Unsaturated carbonyl compound, a class of organic compounds * Alpha beta filter, a predictive filter * Alpha (finance) and Beta (finance) In finance, the beta ( or market beta or beta coefficient) is a statistic that measures the expected increase or decrease of an individual stock price in proportion to movements of the stock market as a whole. Beta can be used to indicate the c ..., two measures characterizing the return of an investment portfolio * The Alpha Betas, a fraternity in the '' Revenge of the Nerds'' film series * ''Alpha Betas,'' an animated webseries created by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negascout
Principal variation search (sometimes equated with the practically identical NegaScout) is a negamax algorithm that can be faster than alpha–beta pruning. Like alpha–beta pruning, NegaScout is a directional search algorithm for computing the minimax value of a node in a tree. It dominates alpha–beta pruning in the sense that it will never examine a node that can be pruned by alpha–beta; however, it relies on accurate node ordering to capitalize on this advantage. NegaScout works best when there is a good move ordering. In practice, the move ordering is often determined by previous shallower searches. It produces more cutoffs than alpha–beta by assuming that the first explored node is the best. In other words, it supposes the first node is in the principal variation. Then, it can check whether that is true by searching the remaining nodes with a null window (also known as a scout window; when alpha and beta are equal), which is faster than searching with the regular al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |