|
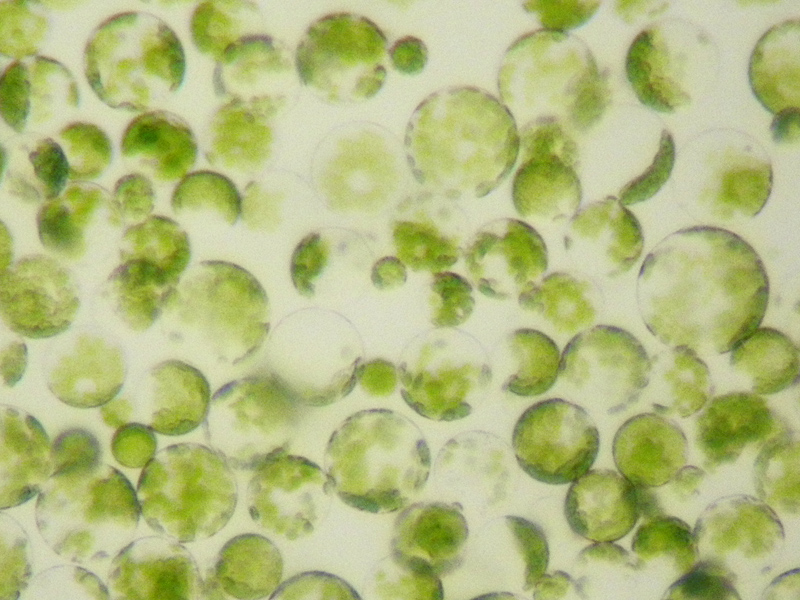
Vampyrella Lateritia
''Vampyrella lateritia'' is a freshwater species of predatory Amoeba, amoebae that feeds on species of algae and is known for its specialized feeding strategy of removing, digesting, and ingesting the cellular contents of its prey. It is the type species of the genus ''Vampyrella'' and has been identified in numerous locations around the world including Brazil, Germany, and the eastern United States. Along with ''Vampyrella pendula'', its genome was sequenced in 2012. Life cycle ''Vampyrella lateritia'' has four life stages that revolve about the feeding cycle: motile Trophozoite, trophozoites (the activated, feeding stage), Plasmodium (life cycle), plasmodia in which the cytoplasm contains many nuclei, digestive cysts, and resting cysts. It has been observed feeding on species from the genera ''Zygnema'', ''Spirogyra'', and ''Mougeotia'' and is considered a specialist predator as its known prey is restricted to a limited number of green algal species. Like other vampyrellid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
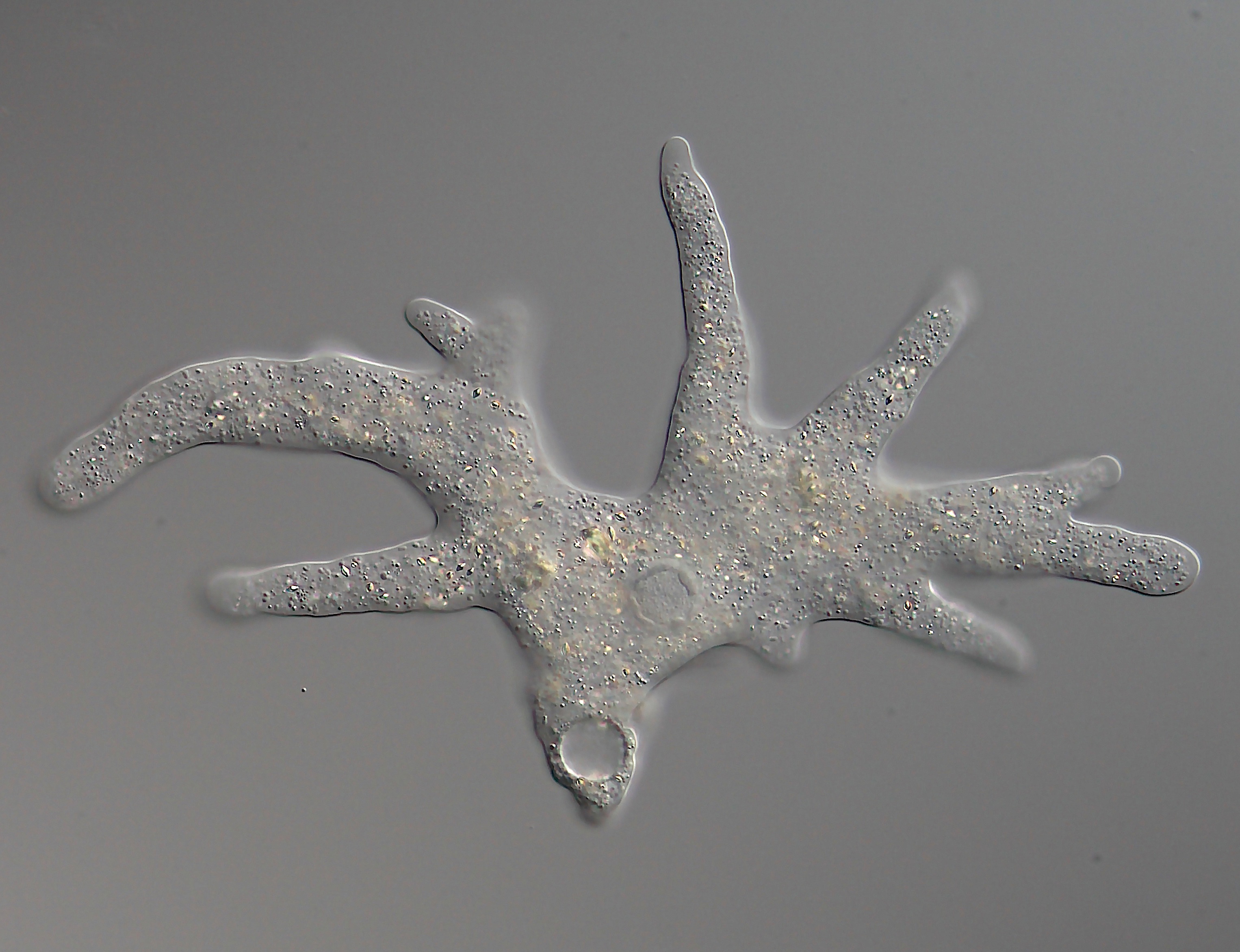
Amoeba
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; : amoebas (less commonly, amebas) or amoebae (amebae) ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of Cell (biology), cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopodia, pseudopods. Amoebae do not form a single Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group; instead, they are found in every major Lineage (evolution), lineage of eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms. Amoeboid cells occur not only among the protozoa, but also in fungi, algae, and animals. Microbiologists often use the terms "amoeboid" and "amoeba" interchangeably for any organism that exhibits amoeboid movement. In older classification systems, most amoebae were placed in the Class (biology), class or subphylum Sarcodina, a grouping of Unicellular organism, single-celled organisms that possess pseudopods or move by protoplasmic flow. However, molecular phylogenetic studies have shown that Sarcodina is not a monophyletic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Column
The (oceanic) water column is a concept used in oceanography to describe the physical (temperature, salinity, light penetration) and chemical ( pH, dissolved oxygen, nutrient salts) characteristics of seawater at different depths for a defined geographical point. Generally, vertical profiles are made of temperature, salinity, chemical parameters at a defined point along the water column. The water column is the largest, yet one of the most under-explored, habitats on the planet; it is explored to better understand the ocean as a whole, including the huge biomass that lives there and its importance to the global carbon and other biogeochemical cycles. Studying the water column also provides understanding on the links between living organisms and environmental parameters, large-scale water circulation and the transfer of matter between water masses. Water columns are used chiefly for environmental studies evaluating the stratification or mixing of thermal or chemically stratif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desiccation
Desiccation is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying. A desiccant is a hygroscopic (attracts and holds water) substance that induces or sustains such a state in its local vicinity in a moderately sealed container. The word desiccation comes . Industry Desiccation is widely employed in the oil and gas industry. These materials are obtained in a hydrated state, but the water content leads to corrosion or is incompatible with downstream processing. Removal of water is achieved by cryogenics, cryogenic condensation, absorption into glycols, and absorption onto desiccants such as silica gel. Laboratory A desiccator is a heavy glass or plastic container, now somewhat antiquated, used in practical chemistry for drying or keeping small amounts of materials very dry. The material is placed on a shelf, and a drying agent or ''desiccant'', such as dry silica gel or anhydrous sodium hydroxide, is placed below the shelf. Often some sort of humidity indicator is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exocytosis
Exocytosis is a term for the active transport process that transports large molecules from cell to the extracellular area. Hormones, proteins and neurotransmitters are examples of large molecules that can be transported out of the cell. Exocytosis is a crucial transport mechanism that enables polar molecules to flow through the cell membranes’ hydrophobic lipid bilayer. The transport process is essential to hormone secretion, immune response and neurotransmission. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes undergo exocytosis. Prokaryotes secrete molecules and cellular waste through translocons that are localized to the cell membrane. In addition, they secrete molecules to other cells through specialized organs. Eukaryotes rely on multiple cellular processes to perform the exocytosis process. Eukaryotes have several organelles and a nucleus in the cytoplasm that are connected through multiple transport routes, that is formally known as the secretory pathway. This is a complex pathway with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in Plant cell, plant and Fungus, fungal Cell (biology), cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in Solutes, solution, though in certain cases they may contain solids which have been engulfed. Vacuoles are formed by the fusion of multiple membrane Vesicle (biology), vesicles and are effectively just larger forms of these. The organelle has no basic shape or size; its structure varies according to the requirements of the cell. Discovery Antonie van Leeuwenhoek described the plant vacuole in 1676. Contractile vacuoles ("stars") were first observed by Spallanzani (1776) in protozoa, although mistaken for respiratory organs. Félix Dujardin, Dujardin (1841) named these "stars" as ''vacuoles''. In 1842, Matthias Jakob Schleiden, Schleiden applied the term for plant cells, to dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protoplast
Protoplast (), is a biology, biological term coined by Johannes von Hanstein, Hanstein in 1880 to refer to the entire cell, excluding the cell wall. Protoplasts can be generated by stripping the cell wall from plant, bacterium, bacterial, or fungus, fungal cells by mechanical, chemical or enzymatic means. Protoplasts differ from spheroplasts in that their cell wall has been completely removed. Spheroplasts retain part of their cell wall. In the case of Gram-negative bacterial spheroplasts, for example, the peptidoglycan component of the cell wall has been removed but the bacterial outer membrane, outer membrane component has not. Enzymes for the preparation of protoplasts Cell walls are made of a variety of polysaccharides. Protoplasts can be made by degrading cell walls with a mixture of the appropriate polysaccharide-degrading enzymes: During and subsequent to digestion of the cell wall, the protoplast becomes very sensitive to osmosis, osmotic stress. This means cell wal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Wall
A cell wall is a structural layer that surrounds some Cell type, cell types, found immediately outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. Primarily, it provides the cell with structural support, shape, protection, and functions as a selective barrier. Another vital role of the cell wall is to help the cell withstand osmotic pressure and mechanical stress. While absent in many eukaryotes, including animals, cell walls are prevalent in other organisms such as fungi, algae and plants, and are commonly found in most Prokaryote, prokaryotes, with the exception of Mollicutes, mollicute bacteria. The composition of cell walls varies across taxonomic groups, species, cell type, and the cell cycle. In Embryophyte, land plants, the primary cell wall comprises Polysaccharide, polysaccharides like cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin. Often, other Polymer, polymers such as lignin, suberin or cutin are anchored to or embedded in plant cell walls. Algae exhibit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are the cytosol (a gel-like substance), the cell's internal sub-structures, and various cytoplasmic inclusions. In eukaryotes the cytoplasm also includes the nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance, or cytoplasmic matrix, that remains after the exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, plant plasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Cortex
The cell cortex, also known as the actin cortex, cortical cytoskeleton or actomyosin cortex, is a specialized layer of cytoplasmic proteins on the inner face of the cell membrane. It functions as a modulator of membrane behavior and cell surface properties. In most eukaryotic cells lacking a cell wall, the cortex is an actin-rich network consisting of F-actin filaments, myosin motors, and actin-binding proteins. The actomyosin cortex is attached to the cell membrane via membrane-anchoring proteins called ERM proteins that plays a central role in cell shape control. The protein constituents of the cortex undergo rapid turnover, making the cortex both mechanically rigid and highly plastic, two properties essential to its function. In most cases, the cortex is in the range of 100 to 1000 nanometers thick. In some animal cells, the protein spectrin may be present in the cortex. Spectrin helps to create a network by cross-linked actin filaments. The proportions of spectrin and actin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudopodia
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a eukaryotic cell membrane that is emerged in the direction of movement. Filled with cytoplasm, pseudopodia primarily consist of actin filaments and may also contain microtubules and intermediate filaments. Pseudopods are used for motility and ingestion. They are often found in amoebas. Different types of pseudopodia can be classified by their distinct appearances. Lamellipodia are broad and thin. Filopodia are slender, thread-like, and are supported largely by microfilaments. Lobopodia are bulbous and amoebic. Reticulopodia are complex structures bearing individual pseudopodia which form irregular nets. Axopodia are the phagocytosis type with long, thin pseudopods supported by complex microtubule arrays enveloped with cytoplasm; they respond rapidly to physical contact. Generally, several pseudopodia arise from the surface of the body, (''polypodial'', for example, '' Amoeba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |