|
Vampire Dugout
The ''Vampire'' dugout (known locally in Belgium as the ''Vampyr'' dugout), is a World War I, First World War Dugout (military), underground shelter located near the Belgium, Belgian village of Zonnebeke. It was created as a British brigade headquarters in early 1918 by the 171st Tunnelling Company of the Royal Engineers after the Third Battle of Ypres/Battle of Passchendaele. Rediscovered in 2007, the ''Vampire'' dugout was the subject of a 2008 British television programme (''Time Team)'' which was also broadcast abroad. The structure is inaccessible to the public, but inspected regularly by battlefield historians. History Background At the end of the Battle of Passchendaele, having expanded the Ypres Salient by retaking Passendale Ridge, the British were left with little natural shelter from the former woods and farms. The artillery of both sides had flattened the landscape. As the static nature of the conflict gave way to a more mobile war, and the opposing sides developed bett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Passchendaele
The Third Battle of Ypres (german: link=no, Dritte Flandernschlacht; french: link=no, Troisième Bataille des Flandres; nl, Derde Slag om Ieper), also known as the Battle of Passchendaele (), was a campaign of the First World War, fought by the Allies against the German Empire. The battle took place on the Western Front, from July to November 1917, for control of the ridges south and east of the Belgian city of Ypres in West Flanders, as part of a strategy decided by the Allies at conferences in November 1916 and May 1917. Passchendaele lies on the last ridge east of Ypres, from Roulers (now Roeselare), a junction of the Bruges-(Brugge)-to-Kortrijk railway. The station at Roulers was on the main supply route of the German 4th Army. Once Passchendaele Ridge had been captured, the Allied advance was to continue to a line from Thourout (now Torhout) to Couckelaere ( Koekelare). Further operations and a British supporting attack along the Belgian coast from Nieuport ( Nieuw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and led to heavy, fairly immobile siege engines. As technology improved, lighter, more mobile field artillery cannons developed for battlefield use. This development continues today; modern self-propelled artillery vehicles are highly mobile weapons of great versatility generally providing the largest share of an army's total firepower. Originally, the word "artillery" referred to any group of soldiers primarily armed with some form of manufactured weapon or armor. Since the introduction of gunpowder and cannon, "artillery" has largely meant cannons, and in contemporary usage, usually refers to shell-firing guns, howitzers, and mortars (collectively called ''barrel artillery'', ''cannon artillery'', ''gun artillery'', or - a lay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4). Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay particles, but become hard, brittle and non–plastic upon drying or firing. Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impurities, such as a reddish or brownish colour from small amounts of iron oxide. Clay is the oldest known ceramic material. Prehistoric humans discovered the useful properties of clay and used it for making pottery. Some of the earliest pottery shards have been dated to around 14,000 BC, and clay tablets were the first known writing medium. Clay is used in many modern industrial processes, such as paper making, cement production, and chemical filtering. Between one-half and two-thirds of the world's population live or work in buildings made with clay, ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
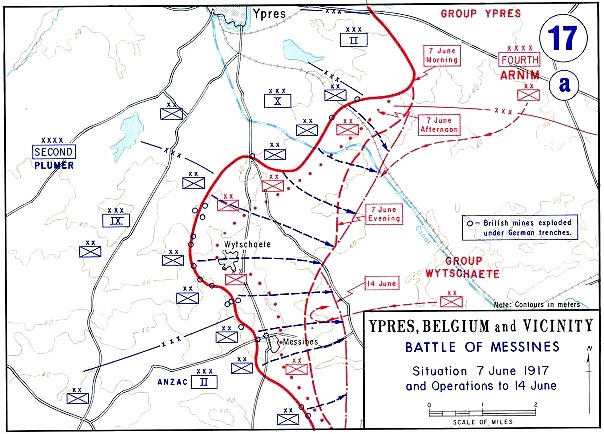
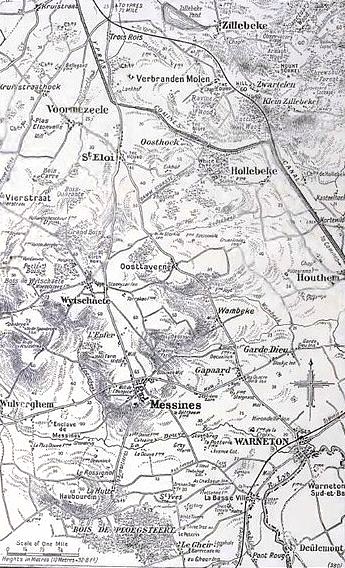
Mines In The Battle Of Messines (1917)
At the start of the Battle of Messines during the First World War, underground explosive charges were detonated by the British Second Army (General Sir Herbert Plumer) beneath the forward position of the German 4th Army near the village of Mesen (''Messines'' in French, historically used in English), in Belgian West Flanders. The mines, secretly planted by British tunnelling units, created craters and killed approximately 10,000 German soldiers. Their joint explosion ranks among the largest non-nuclear explosions of all time. The evening before the attack, General Sir Charles Harington, Chief of Staff of the Second Army, remarked to the press, "Gentlemen, I don’t know whether we are going to make history tomorrow, but at any rate we shall change geography". The Battle of Messines marked the zenith of mine warfare. On 10 August, the Royal Engineers fired the last British deep mine of the war, at Givenchy-en-Gohelle near Arras. Background British mining, 1915–1916 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Messines (1917)
The Battle of Messines (7–14 June 1917) was an attack by the British Second Army (General Sir Herbert Plumer), on the Western Front, near the village of Messines (now Mesen) in West Flanders, Belgium, during the First World War. The Nivelle Offensive in April and May had failed to achieve its more grandiose aims, had led to the demoralisation of French troops and confounded the Anglo-French strategy for 1917. The attack forced the Germans to move reserves to Flanders from the Arras and Aisne fronts, relieving pressure on the French. The British tactical objective was to capture the German defences on the ridge, which ran from Ploegsteert Wood (Plugstreet to the British) in the south, through Messines and Wytschaete to Mt Sorrel, depriving the German 4th Army of the high ground. The ridge gave commanding views of the British defences and back areas of Ypres to the north, from which the British intended to conduct the Northern Operation, an advance to Passchendaele Ridge an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
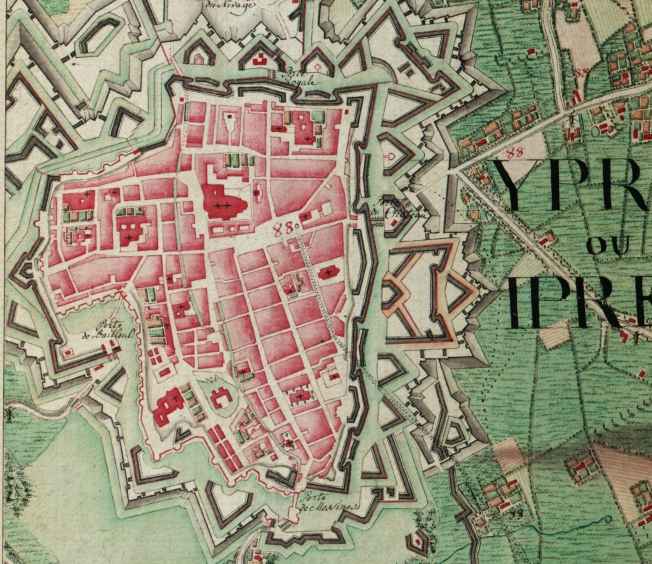
Ypres
Ypres ( , ; nl, Ieper ; vls, Yper; german: Ypern ) is a Belgian city and municipality in the province of West Flanders. Though the Dutch name is the official one, the city's French name is most commonly used in English. The municipality comprises the city of Ypres/Ieper and the villages of Boezinge, Brielen, Dikkebus, Elverdinge, Hollebeke, Sint-Jan, Vlamertinge, Voormezele, Zillebeke, and Zuidschote. Together, they are home to about 34,900 inhabitants. During the First World War, Ypres (or "Wipers" as it was commonly known by the British troops) was the centre of the Battles of Ypres between German and Allied forces. History Origins before First World War Ypres is an ancient town, known to have been raided by the Romans in the first century BC. It is first mentioned by name in 1066 and is probably named after the river Ieperlee on the banks of which it was founded. During the Middle Ages, Ypres was a prosperous Flemish city with a population of 40,000 in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunnelling Companies Of The Royal Engineers
Royal Engineer tunnelling companies were specialist units of the Corps of Royal Engineers within the British Army, formed to dig attacking tunnels under enemy lines during the First World War. The stalemate situation in the early part of the war led to the deployment of tunnel warfare. After the first German Empire attacks on 21 December 1914, through shallow tunnels underneath no man's land and exploding ten mines under the trenches of the Indian Sirhind Brigade, the British began forming suitable units. In February 1915, eight Tunnelling Companies were created and operational in Flanders from March 1915. By mid-1916, the British Army had around 25,000 trained tunnellers, mostly volunteers taken from coal mining communities. Almost twice that number of "attached infantry" worked permanently alongside the trained miners acting as 'beasts of burden'. From the spring of 1917 the whole war became more mobile, with grand offensives at Arras, Messines and Passchendaele. There was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bedroom
A bedroom or bedchamber is a room situated within a residential or accommodation unit characterised by its usage for sleeping and sexual activity. A typical western bedroom contains as bedroom furniture one or two beds (ranging from a crib for an infant, a single or twin bed for a toddler, child, teenager, or single adult to bigger sizes like a full, double, queen, king or California king astern or waterbed size for a couple, a clothes closet, and bedside table and dressing table, both of which usually contain drawers. Except in bungalows, ranch style homes, ground floor apartments, or one-storey motels, bedrooms are usually on one of the floors of a dwelling that is above ground level. History In larger Victorian houses it was common to have accessible from the bedroom a boudoir for the lady of the house and a dressing room for the gentleman. Attic bedrooms exist in some houses; since they are only separated from the outside air by the roof they are typically cold in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blacksmiths
A blacksmith is a metalsmith who creates objects primarily from wrought iron or steel, but sometimes from #Other metals, other metals, by forging the metal, using tools to hammer, bend, and cut (cf. tinsmith). Blacksmiths produce objects such as gates, grilles, railings, light fixtures, furniture, sculpture, tools, agricultural implements, decorative and religious items, cooking utensils, and weapons. There was an historical distinction between the heavy work of the blacksmith and the more delicate operation of a whitesmith, who usually worked in Goldsmith, gold, Silversmith, silver, pewter, or the finishing steps of fine steel. The place where a blacksmith works is called variously a smithy, a forge or a blacksmith's shop. While there are many people who work with metal such as farriers, wheelwrights, and Armourer, armorers, in former times the blacksmith had a general knowledge of how to make and repair many things, from the most complex of weapons and armor to simple things ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workshop
Beginning with the Industrial Revolution era, a workshop may be a room, rooms or building which provides both the area and tools (or machinery) that may be required for the manufacture or repair of manufactured goods. Workshops were the only places of production until the advent of industrialization and the development of larger factories. In the 20th and 21st century, many Western homes contained a workshop in either the garage, basement, or an external shed. Home workshops typically contain a workbench, hand tools, power tools, and other hardware. Along with the practical application of repairing goods, workshops are often used to tinker and make prototypes. Some workshops focus exclusively on automotive repair or restoration although there are a variety of workshops in existence today. Woodworking, metalworking, electronics, and other types of electronic prototyping workshops are among the most common. Backshop In some repair industries, such as locomotives and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitchen
A kitchen is a room or part of a room used for cooking and food preparation in a dwelling or in a commercial establishment. A modern middle-class residential kitchen is typically equipped with a stove, a sink with hot and cold running water, a refrigerator, and worktops and kitchen cabinets arranged according to a modular design. Many households have a microwave oven, a dishwasher, and other electric appliances. The main functions of a kitchen are to store, prepare and cook food (and to complete related tasks such as dishwashing). The room or area may also be used for dining (or small meals such as breakfast), entertaining and laundry. The design and construction of kitchens is a huge market all over the world. Commercial kitchens are found in restaurants, cafeterias, hotels, hospitals, educational and workplace facilities, army barracks, and similar establishments. These kitchens are generally larger and equipped with bigger and more heavy-duty equipment than a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chapel
A chapel is a Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. Firstly, smaller spaces inside a church that have their own altar are often called chapels; the Lady chapel is a common type of these. Secondly, a chapel is a place of worship, sometimes non-denominational, that is part of a building or complex with some other main purpose, such as a school, college, hospital, palace or large aristocratic house, castle, barracks, prison, funeral home, cemetery, airport, or a military or commercial ship. Thirdly, chapels are small places of worship, built as satellite sites by a church or monastery, for example in remote areas; these are often called a chapel of ease. A feature of all these types is that often no clergy were permanently resident or specifically attached to the chapel. Finally, for historical reasons, ''chapel'' is also often the term used by independent or nonconformist denominations for their places of wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_(7563655820).jpg)
