|
Vadstena Bracteate
The Vadstena bracteate (Rundata Ög 178, IK 377.1) is a gold C-bracteate found in the ground at Vadstena, Sweden, in 1774.''Nordisk Familjebok'', Owl Edition, pp. 262–6/ref> Along with the bracteate was a gold ring and a piece of gold sheet: all were nearly melted down by a goldsmith who was stopped by a local clergyman. The bracteate was stolen in 1938 from the Swedish Museum of National Antiquities and has not yet been found. Description The bracteate is believed to have been made about AD 500. In the middle of the bracteate is a four-legged animal with a man's head above it, and in front of this a bird separated from the other images by a line. This image is commonly associated with the Norse god Odin in bracteate iconography. Inscription The bracteate is most famous for containing a full listing of the Elder Futhark runic alphabet. The runes in the futhark are divided by dots into three groups of eight runes which are commonly called '' ættir''. The entire inscrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elder Futhark
The Elder Futhark (or Fuþark, ), also known as the Older Futhark, Old Futhark, or Germanic Futhark, is the oldest form of the runic alphabets. It was a writing system used by Germanic peoples for Northwest Germanic dialects in the Migration Period. Inscriptions are found on artifacts including jewelry, amulets, plateware, tools, and weapons, as well as runestones, from the 2nd to the 8th centuries. In Scandinavia, beginning in the late 8th century, the script was simplified to the Younger Futhark, while the Anglo-Saxons and Frisians instead extended it, giving rise to the Anglo-Saxon runes, Anglo-Saxon futhorc. Both the Anglo-Saxon futhorc and the Younger Futhark remained in use during the Early Middle Ages, Early and the High Middle Ages respectively, but knowledge of how to read the Elder Futhark was forgotten until 1865, when it was deciphered by Norwegian scholar Sophus Bugge. Description The Elder Futhark is named after the initial phoneme of the first six rune names: /f/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Norse Language
Proto-Norse (also called Ancient Nordic; Danish and ; ; ; ) was an Indo-European language spoken in Scandinavia that is thought to have evolved as a northern dialect of Proto-Germanic in the first centuries CE. It is the earliest stage of a characteristically North Germanic language, and the language attested in the oldest Scandinavian Elder Futhark inscriptions, spoken from around the 2nd to the 8th centuries CE (corresponding to the late Roman Iron Age and the Germanic Iron Age). It evolved into the dialects of Old Norse at the beginning of the Viking Age around 800 CE, which later themselves evolved into the modern North Germanic languages ( Faroese, Icelandic, the Continental Scandinavian languages, and their dialects). Phonology Proto-Norse phonology probably did not differ substantially from that of Proto-Germanic. Although the phonetic realisation of several phonemes had probably changed over time, the overall system of phonemes and their distribution remained la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Individual Items Of Jewellery
An individual is one that exists as a distinct entity. Individuality (or self-hood) is the state or quality of living as an individual; particularly (in the case of humans) as a person unique from other people and possessing one's own needs or goals, rights and responsibilities. The concept of an individual features in many fields, including biology, law, and philosophy. Every individual contributes significantly to the growth of a civilization. Society is a multifaceted concept that is shaped and influenced by a wide range of different things, including human behaviors, attitudes, and ideas. The culture, morals, and beliefs of others as well as the general direction and trajectory of the society can all be influenced and shaped by an individual's activities. Etymology From the 15th century and earlier (and also today within the fields of statistics and metaphysics) ''individual'' meant " indivisible", typically describing any numerically singular thing, but sometimes meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
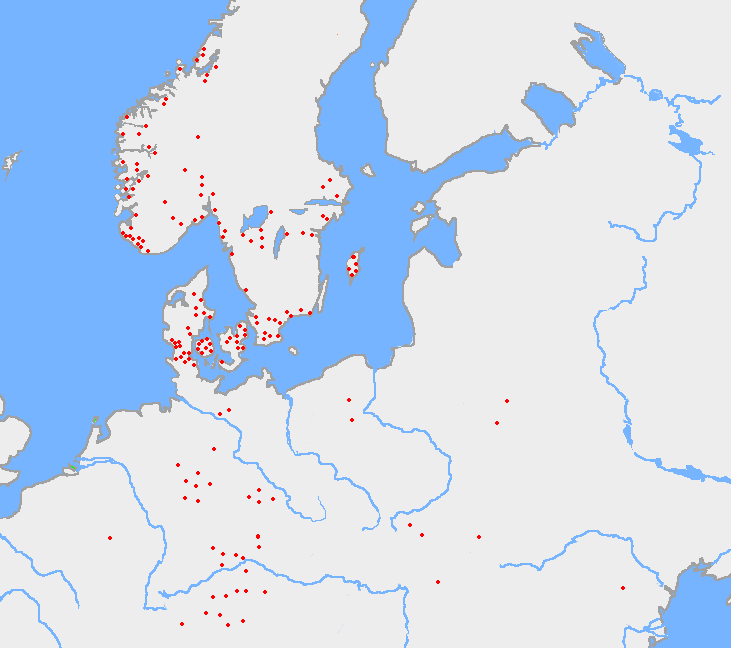
Bracteates
A bracteate (from the Latin ''bractea'', a thin piece of metal) is a flat, thin, single-sided gold medal worn as jewelry that was produced in Northern Europe predominantly during the Migration Period of the Germanic Iron Age (including the Vendel era in Sweden). Bracteate coins are also known from the medieval kingdoms around the Bay of Bengal, such as Harikela and Mon State, Mon city-states. The term is also used for thin discs, especially in gold, to be sewn onto clothing in the ancient world, as found for example in the ancient Persian Oxus treasure, and also later silver coins produced in central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. Gold bracteates from the Migration Period Gold bracteates commonly denote a certain type of jewelry, made mainly in the 5th to 7th century AD, represented by numerous gold specimens. Bead-rimmed and fitted with a loop, most were intended to be worn suspended by a string around the neck, supposedly as an amulet. The gold for the bracteates came ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elder Futhark Inscriptions
An elder is someone with a degree of seniority or authority. Elder or elders may refer to: Positions Administrative * Elder (administrative title), a position of authority Cultural * North American Indigenous elder, a person who has and transmits cultural and philosophical knowledge ** Haudenosaunee Clan Mother * Australian Aboriginal elder, one who has gained recognition as a custodian of knowledge and lore, often a leader in administrative matters Religious * "The Elder", author of the Johannine epistles 2 John and 3 John in the New Testament * Elder (Christianity), a person valued for their wisdom and, in some churches and denominations, holding an administrative or oversight role ** Elder (Methodist), an ordained minister with responsibilities to preach and teach ** Elder (Anglican), a learned minister with responsibilities to teach and/or innovate ** Elder (Latter Day Saints), a priesthood office in the Melchizedek priesthood * Thero or Elder, an honorific ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seeland-II-C
Seeland-II-C (Sjælland bracteate 2) is a Scandinavian bracteate from Zealand, Denmark, that has been dated to the Migration period (around 500 AD). The bracteate bears an Elder Futhark inscription which reads as: The final ttt is a triple- stacked Tiwaz rune. This use of the rune is often interpreted as three invocations of the Norse pagan god Tyr. The central image shows a male's head above a quadruped. This is the defining characteristic of C-bracteates (of which some 400 specimens survive), and is often interpreted as a depiction of the god Odin, healing his horse. Wolfgang Krause translates the inscription as: "Hariuha I am called: the dangerous knowledgeable one: I give chance."Krause, W. (1971). ''Die Sprache der Urnordischen Runeninschriften''. . ''farauisa'' is interpreted as ''fara-uisa'', either "danger-wise" or "travel-wise". Erik Moltke translates this word as "one who is wise about dangers". Moltke, Erik (1976). ''Runerne i Danmark og deres Oprindelse''. . Publis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runic Magic
There is some evidence that, in addition to being a writing system, runes historically served purposes of magic. This is the case from the earliest epigraphic evidence of the Roman to the Germanic Iron Age, with non-linguistic inscriptions and the '' alu'' word. An '' erilaz'' appears to have been a person versed in runes, including their magic applications. In medieval sources, notably the Poetic Edda, the '' Sigrdrífumál'' mentions "victory runes" to be carved on a sword, "some on the grasp and some on the inlay, and name Tyr twice." In the early modern period and modern history, related folklore and superstition is recorded in the form of the Icelandic magical staves. In the early 20th century, Germanic mysticism coined new forms of "runic magic", some of which were continued or developed further by contemporary adherents of Germanic Neopaganism. Modern systems of runic divination are based on Hermeticism, classical occultism, and the ''I Ching''. Historical evidence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norse Clans
The Scandinavian clan or ''ætt/ätt'' (pronounced in Old Norse) was a social group based on common descent, equivalent to a clan. History In the absence of a police force, the clan was the primary force of security in Norse society, as the clansmen were obliged by honour to avenge one another. The Norse clan was not tied to a certain territory in the same way as a Scottish clan, where the chief owned the territory. The land of the Scandinavian clan was owned by the individuals who had close neighbours from other clans. The name of the clan was derived from its ancestor, often with the addition of an -ung or -ing ending. The original meaning of ''ætt/ätt'' seems to have simply been "those who are related". A person could technically belong to several clans, but usually the identification of an individual came with ancestry of most prestige. Therefore, through mostly the exception to the rule, a clan could have matrilineal name if the descent of the ancestral mother was consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runic Alphabet
Runes are the Letter (alphabet), letters in a set of related alphabets, known as runic rows, runic alphabets or futharks (also, see ''#Futharks, futhark'' vs ''#Runic alphabets, runic alphabet''), native to the Germanic peoples. Runes were primarily used to represent a sound value (a phoneme) but they were also used to represent the concepts after which they are named (ideographic runes). Runology is the academic study of the runic alphabets, runic inscriptions, runestones, and their history. Runology forms a specialised branch of Germanic philology. The earliest secure runic inscriptions date from at latest AD 150, with a possible earlier inscription dating to AD 50 and Tacitus's possible description of rune use from around AD 98. The Svingerud Runestone dates from between AD 1 and 250. Runes were generally replaced by the Latin alphabet as the cultures that had used runes underwent Christianisation, by approximately AD 700 in central Europe and 1100 in northern Europe. Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iconography
Iconography, as a branch of art history, studies the identification, description and interpretation of the content of images: the subjects depicted, the particular compositions and details used to do so, and other elements that are distinct from artistic style. The word ''iconography'' comes from the Ancient Greek, Greek ("image") and ("to write" or ''to draw''). A secondary meaning (based on a non-standard translation of the Greek and Russian equivalent terms) is the production or study of the religious images, called "Icon, icons", in the Byzantine art, Byzantine and Eastern Orthodox Churches, Orthodox Christian tradition. This usage is mostly found in works translated from languages such as Greek or Russian, with the correct term being "icon painting". In art history, "an iconography" may also mean a particular depiction of a subject in terms of the content of the image, such as the number of figures used, their placing and gestures. The term is also used in many academic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |