 |
VOL (DOS Command)
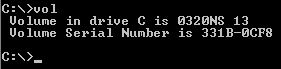
In some operating systems, vol is a command (computing), command within the command-line interpreters (Shell (computing), shells) such as COMMAND.COM and cmd.exe. It is used to display the volume label and volume serial number of a logical drive, such as a Hard disk drive, hard disk partition or a floppy disk, if they exist. Implementations The command is available in various versions of DOS, Digital Research, DR FlexOS, IBM/Toshiba 4690 Operating System, 4690 OS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Microsoft Windows, Windows, and ReactOS. On MS-DOS, the command is available in versions 2 and later. Paragon Software Group, Paragon Technology Systems PTS-DOS 2000 Pro also includes a implementation. The Windows dir (command), dir command also displays the volume label and serial number (if it has one) as part of the directory listing. The command is also available in the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, EFI shell. Syntax vol [Drive:] Arguments: *Drive: This command-line argument speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Windows XP
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct successor to Windows 2000 for high-end and business users and Windows Me for home users. Development of Windows XP began in the late 1990s under the codename "Windows Neptune, Neptune", built on the Architecture of Windows NT#Kernel, Windows NT kernel and explicitly intended for mainstream consumer use. An updated version of Windows 2000 was also initially planned for the business market. However, in January 2000, both projects were scrapped in favor of a single OS codenamed "Whistler", which would serve as a single platform for both consumer and business markets. As a result, Windows XP is the first consumer edition of Windows not based on the Windows 95 kernel or MS-DOS. Upon its release, Windows XP received critical acclaim, noting increased performance and stability (especially compared to Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
FreeDOS
FreeDOS (formerly PD-DOS) is a free software operating system for IBM PC compatible computers. It intends to provide a complete MS-DOS-compatible environment for running Legacy system, legacy software and supporting embedded systems. FreeDOS can be booted from a floppy disk or USB flash drive and is designed to run well under virtualization or x86 Emulator, emulation. The FreeDOS project began under Jim Hall (computer programmer), Jim Hall in 1994, and the first Stable version, stable version was released in 2006. Unlike most versions of MS-DOS, FreeDOS is composed of free software, Software license, licensed under the terms of the GNU General Public License. However, other packages that form part of the FreeDOS project include non-GPL software considered worthy of Digital preservation, preservation, such as 4DOS, which is distributed under a modified MIT License. Distribution FreeDOS 1.1, released on 2 January 2012, is available for download as a CD-ROM image: a limited in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
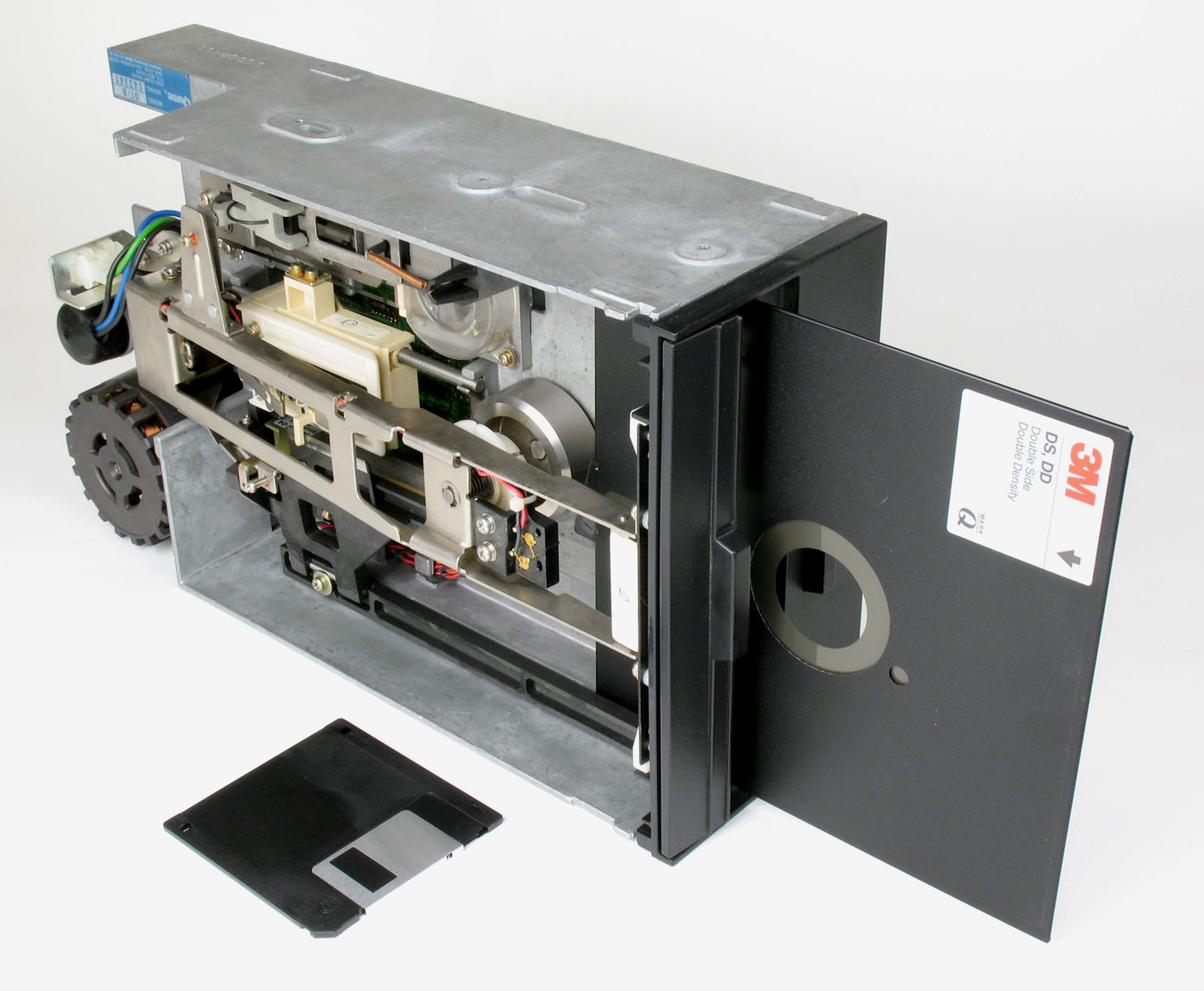 |
Floppy Disk
A floppy disk or floppy diskette (casually referred to as a floppy, a diskette, or a disk) is a type of disk storage composed of a thin and flexible disk of a magnetic storage medium in a square or nearly square plastic enclosure lined with a fabric that removes dust particles from the spinning disk. The three most popular (and commercially available) floppy disks are the 8-inch, 5¼-inch, and 3½-inch floppy disks. Floppy disks store digital data which can be read and written when the disk is inserted into a floppy disk drive (FDD) connected to or inside a computer or other device. The first floppy disks, invented and made by IBM in 1971, had a disk diameter of . Subsequently, the 5¼-inch (133.35 mm) and then the 3½-inch (88.9 mm) became a ubiquitous form of data storage and transfer into the first years of the 21st century. 3½-inch floppy disks can still be used with an external USB floppy disk drive. USB drives for 5¼-inch, 8-inch, and other-size floppy disks are rare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Hard Disk Drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with disk read-and-write head, magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual Block (data storage), blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small disk enclosure, rectangular box. Hard disk drives were introduced by IBM in 1956, and were the dominant secondary storage device for History of general-purpose CPUs, general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Logical Drive
In computer data storage, a volume or logical drive is a single accessible storage area with a single file system, typically (though not necessarily) resident on a single partition of a hard disk. Although a volume might be different from a physical disk drive, it can still be accessed with an operating system's logical interface. However, a volume differs from a partition. Differences from partition A volume is not the same thing as a partition. For example, a floppy disk might be accessible as a volume, even though it does not contain a partition, as floppy disks cannot be partitioned with most modern computer software. Also, an OS can recognize a partition without recognizing any volume associated with it, as when the OS cannot interpret the filesystem stored there. This situation occurs, for example, when Windows NT-based OSes encounter disks with non-Microsoft OS partitions, such as the ext4 filesystem commonly used with Linux. Another example occurs in the Intel world wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
COMMAND
Command may refer to: Computing * Command (computing), a statement in a computer language * command (Unix), a Unix command * COMMAND.COM, the default operating system shell and command-line interpreter for DOS * Command key, a modifier key on Apple Macintosh computer keyboards * Command pattern, a software design pattern in which objects represent actions * Voice command, in speech recognition Military * Military command (instruction) or military order * Command responsibility, the doctrine of hierarchical accountability in cases of war crimes * Command (military formation), an organizational unit * Command and control, the exercise of authority in a military organization * Command hierarchy, a group of people dedicated to carrying out orders "from the top" Music * ''Command'' (album), a 2009 album by Client * Command Records, a record label Sports * Command (baseball), the ability of a pitcher to throw a pitch where he intends to * Kansas City Command, a former profess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Shell (computing)
An operating system shell is a computer program that provides relatively broad and direct access to the system on which it runs. The term ''shell'' refers to how it is a relatively thin Abstraction layer, layer around an operating system. A shell is generally a command-line interface (CLI) program although some graphical user interface (GUI) programs are arguably classified as shells too. Overview Operating systems provide various services to their users, including File manager, file management, Process (computing), process management (running and terminating Application program, applications), batch processing, and operating system monitoring and configuration. Most operating system shells are not ''direct'' interfaces to the underlying Kernel (operating system), kernel, even if a shell communicates with the user via peripheral devices attached to the computer directly. Shells are actually special applications that use the kernel API in just the same way as it is used by ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Command-line Interpreter
A command-line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with software via commands each formatted as a line of text. Command-line interfaces emerged in the mid-1960s, on computer terminals, as an interactive and more user-friendly alternative to the non-interactive mode available with punched cards. For a long time, a CLI was the most common interface for software, but today a graphical user interface (GUI) is more common. Nonetheless, many programs such as operating system and software development utilities still provide CLI. A CLI enables automating programs since commands can be stored in a script file that can be used repeatedly. A script allows its contained commands to be executed as group; as a program; as a command. A CLI is made possible by command-line interpreters or command-line processors, which are programs that execute input commands. Alternatives to a CLI include a GUI (including the desktop metaphor such as Windows), text-based menuing (including DOS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Command (computing)
In computing, a command is an instruction received via an external Interface (computing), interface that directs the behavior of a computer program. Commonly, commands are sent to a program via a command-line interface, a scripting language, script, a network protocol, or as an event triggered in a graphical user interface. Many commands support arguments to specify input and to modify default behavior. Terminology and syntax varies but there are notable common approaches. Typically, an option or a flag is a name (without Whitespace character, whitespace) with a prefix such as dash or Slash (punctuation), slash that modifies default behavior. An option might have a required value that follows it. Typically, flag refers to an option that does not have a following value. A parameter is an argument that specifies input to the command and its meaning is based on its position in the command line relative to other parameters; generally ignoring options. A parameter can specify anything ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of Scheduling (computing), processor time, mass storage, peripherals, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computerfrom cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. , Android (operating system), Android is the most popular operating system with a 46% market share, followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |