|
VCalendar
The Internet Calendaring and Scheduling Core Object Specification (iCalendar) is a media type which allows users to store and exchange calendaring and scheduling information such as events, to-dos, journal entries, and free/busy information, and together with its associated standards has been a cornerstone of the standardization and interoperability of digital calendars across different vendors. Files formatted according to the specification usually have an extension of . With supporting software, such as an email reader or calendar application, recipients of an iCalendar data file can respond to the sender easily or counter-propose another meeting date/time. The file format is specified in a proposed Internet standard (RFC 5545) for calendar data exchange. The standard and file type are sometimes referred to as "iCal", which was the name of the Apple Inc. calendar program until 2012 (see iCal), which provides one of the implementations of the standard. iCalendar is used and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calendar
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A calendar date, date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is also a physical record (often paper) of such a system. A calendar can also mean a list of planned events, such as a court calendar, or a partly or fully chronological list of documents, such as a calendar of wills. Periods in a calendar (such as years and months) are usually, though not necessarily, synchronized with the cycle of the solar calendar, sun or the lunar calendar, moon. The most common type of pre-modern calendar was the lunisolar calendar, a lunar calendar that occasionally adds one intercalary month to remain synchronized with the solar year over the long term. Etymology The term ''calendar'' is taken from , the term for the first day of the month in the Roman calendar, related to the verb 'to call out', referring to the " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU Emacs
GNU Emacs is a text editor and suite of free software tools. Its development began in 1984 by GNU Project founder Richard Stallman, based on the Emacs editor developed for Unix operating systems. GNU Emacs has been a central component of the GNU project and a flagship project of the free software movement. The program's tagline is "the extensible self-documenting text editor." Most functionality in GNU Emacs is implemented in user-accessible Emacs Lisp, allowing deep extensibility directly by users and through community-contributed packages. Its built-in features include a file browser and editor (Dired), an advanced calculator (Calc), an email client and news reader (Gnus), a Language Server Protocol integration, and the productivity system Org-mode. A large community of users have contributed extensions such as the Git interface Magit, the Vim (text editor), Vim emulation layer Evil, several search frameworks, the window manager EXWM, and tools for working with a wide range of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lotus Development Corporation
Lotus Software (called Lotus Development Corporation before its acquisition by IBM) was an American software company based in Massachusetts; it was sold to India's HCL Technologies in 2018. Lotus is most commonly known for the Lotus 1-2-3 spreadsheet application, the first feature-heavy, user-friendly, reliable, and WYSIWYG-enabled product to become widely available in the early days of the IBM PC, when there was no graphical user interface. Much later, in conjunction with Ray Ozzie's Iris Associates, Lotus also released a groupware and email system, Lotus Notes. IBM purchased the company in 1995 for US$3.5 billion, primarily to acquire Lotus Notes and to establish a presence in the increasingly important client–server computing segment, which was rapidly making host-based products such as IBM's OfficeVision obsolete. On December 6, 2018, IBM announced the sale of Lotus Software/Domino to HCL for $1.8 billion. History Lotus was founded in 1982 by partners Mitch Kapo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Text Corporation
OpenText Corporation (styled as opentext) is a global software company that develops and sells information management software. OpenText, headquartered in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, is Canada's fourth-largest software company as of 2022, and recognized as one of Canada's top 100 employers 2025 by Mediacorp Canada Inc. OpenText software applications manage content and unstructured data for large companies, government agencies, and professional service firms. OpenText's main business offerings include data analytics, enterprise information management, AI, cloud solutions, security, and products that address information management requirements, including management of large volumes of content, compliance with regulatory requirements, and mobile and online experience management. OpenText employs 22,900 people worldwide, and is a publicly traded company, listed on the Toronto Stock Exchange and the NASDAQ (OTEX). History Timothy Bray, with the University of Waterloo professors F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTML
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It defines the content and structure of web content. It is often assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript, a programming language. Web browsers receive HTML documents from a web server or from local storage and browser engine, render the documents into multimedia web pages. HTML describes the structure of a web page Semantic Web, semantically and originally included cues for its appearance. HTML elements are the building blocks of HTML pages. With HTML constructs, HTML element#Images and objects, images and other objects such as Fieldset, interactive forms may be embedded into the rendered page. HTML provides a means to create structured documents by denoting structural semantics for text such as headings, paragraphs, lists, Hyperlink, links, quotes, and other items. HTML elements are delineated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XHTML
Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) is part of the family of XML markup languages which mirrors or extends versions of the widely used HyperText Markup Language (HTML), the language in which Web pages are formulated. While HTML, prior to HTML5, was defined as an application of Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML), a flexible markup language framework, XHTML is an application of XML, a more restrictive subset of SGML. XHTML documents are well-formed and may therefore be parsed using standard XML parsers, unlike HTML, which requires a lenient HTML-specific parser. XHTML 1.0 became a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) recommendation on 26 January 2000. XHTML 1.1 became a W3C recommendation on 31 May 2001. XHTML is now referred to as "the XML syntax for HTML" and being developed as an XML adaptation of the HTML living standard. Overview XHTML 1.0 was "a reformulation of the three HTML 4 document types as applications of XML 1.0". The World Wide Web Consortiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microformats
Microformats (μF) are predefined HTML markup (like HTML classes) created to serve as descriptive and consistent metadata about HTML element, elements, designating them as representing a certain type of data (such as address book, contact information, geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinates, events, products, recipes, etc.). They allow software agent, software to process the information reliably by having set classes refer to a specific type of data rather than being arbitrary. Microformats emerged around 2005 and were predominantly designed for use by search engines, web syndication and news aggregator, aggregators such as RSS. Google confirmed in 2020 that it still parses microformats for use in content indexing. Microformats are referenced in several W3C social web specifications, including IndieAuth and Webmention. Although the content of web pages has been capable of some "automated processing" since the inception of the web, such processing is difficult bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HCalendar
hCalendar (short for ''HTML iCalendar'') is a microformat standard for displaying a semantic (X)HTML representation of iCalendar-format calendar information about an event, on web pages, using HTML classes and ''rel'' attributes. It allows parsing tools (for example other websites, or browser add-ons like Firefox's Operator extension) to extract the details of the event, and display them using some other website, index or search them, or to load them into a calendar or diary program, for instance. Multiple instances can be displayed as timelines. Example Consider this semi-fictional example: The English Wikipedia was launched on 15 January 2001 with a party from 2-4pm at Jimmy Wales' house (more information). The HTML mark-up might be: The English Wikipedia was launched on 15 January 2001 with a party from 2-4pm at Jimmy Wales' house (more information) hCalendar mark-up may be added using span HTML elements and the classes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SyncML
SyncML, or Synchronization Markup Language, was originally developed as a platform-independent standard for information synchronization. Established by the SyncML Initiative, this project has evolved to become a key component in data synchronization and device management. The project is currently referred to as ''Open Mobile Alliance Data Synchronization and Device Management''. The purpose of SyncML is to offer an open standard as a replacement for existing data synchronization solutions; which have mostly been somewhat vendor, application, or operating system specific. SyncML 1.0 specification was released on December 17, 2000, and 1.1 on February 26, 2002. A SyncML message is a well-formed XML document that adheres to the document type definition (DTD), but which does not require validation. Internals SyncML works by exchanging commands, which can be requests and responses. As an example: * the mobile phone sends an Alert command for signaling the wish to begin a refres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
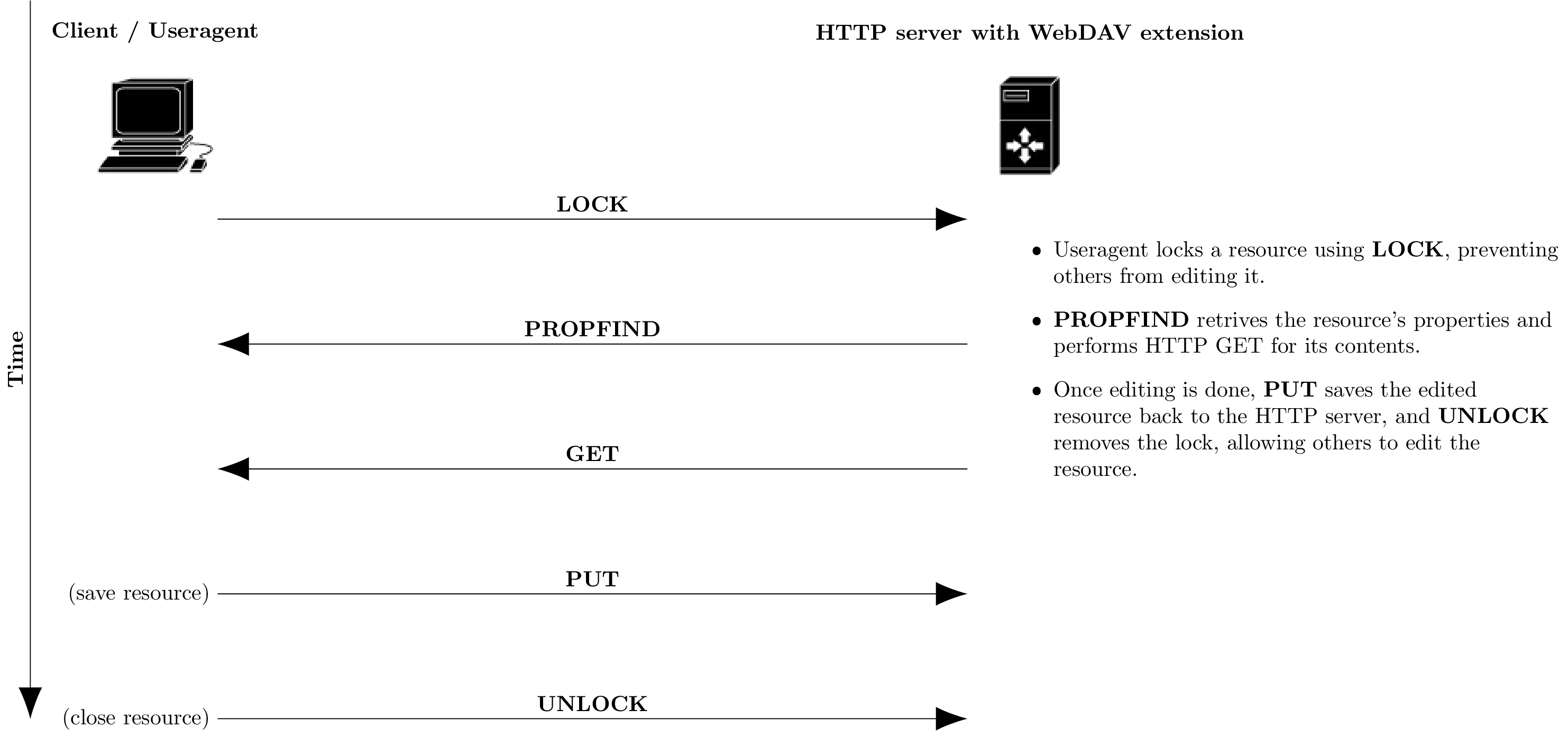
WebDav
WebDAV (Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning) is a set of extensions to the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), which allows user agents to collaboratively author contents ''directly'' in an HTTP web server by providing facilities for concurrency control and namespace operations, thus allowing the Web to be viewed as a ''writeable, collaborative medium'' and not just a read-only medium. WebDAV is defined in by a working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). The WebDAV protocol provides a framework for users to create, change and move documents on a server. The most important features include the maintenance of properties about an author or modification date, namespace management, collections, and overwrite protection. Maintenance of properties includes such things as the creation, removal, and querying of file information. Namespace management deals with the ability to copy and move web pages within a server's namespace. Collections deal with the creation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novell GroupWise
GroupWise is a messaging and collaboration platform from OpenText that supports email, calendaring, personal information management, instant messaging, and document management. The GroupWise platform consists of desktop client software, which is available for Windows, (formerly Mac OS X, and Linux), and the server software, which is supported on Windows Server and Linux. The platform also supports WebAccess, its browser-based webmail client. Mobile access to messaging, calendaring, contacts and other data from smartphones and tablet computers is supported (through the GroupWise Mobility Service software) via the Exchange ActiveSync protocol. Enterprise instant messaging and presence is handled by GroupWise Messenger, which integrates with GroupWise. The product's ownership history includes WordPerfect, Novell and Attachmate; Micro Focus's 2014 acquisition of ''Attachmate'' resulted in the product's Micro Focus GroupWise name. Micro Focus was acquired by OpenText and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |