|
Utba Ibn Ghazwan Al-Mazini
Utba ibn Ghazwan al-Mazini () (–638) was a well-known companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was the seventh person to convert to Islam and participated in the ''Hijra (Islam), hijra'' to Ethiopia, Abyssinia, but returned to stay with Muhammad in Mecca before making the second ''hijrah'' to Medina. He fought at the battle of Badr (624), the battle of Uhud (625), the Battle of the Trench (627) and many others, including the battles of Yamamah. During the caliphate of Umar (r. 634–644), Utba commanded a force of 2,000 men in a campaign against Ubullah which lasted from June through September 635. Once Uballah was occupied, Utba sent a force across the Tigris River which occupied the district of Furat, Baghdad, Furat, followed by Meisan and Abarqubaz. He was soon appointed governor of Basra (Iraq) by the caliph. In 639 Utba left for the Hijaz to perform hajj and to request Umar to relieve him of his office as governor. Umar refused, but while returning to Basra, Utba fell f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caliph
A caliphate ( ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with Khalifa, the title of caliph (; , ), a person considered a political–religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad and a leader of the entire Muslim world (''ummah''). Historically, the caliphates were polities based on Islam which developed into multi-ethnic trans-national empires. During the medieval period, three major caliphates succeeded each other: the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661), the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750), and the Abbasid Caliphate (750–1517). In the fourth major caliphate, the Ottoman Caliphate, the rulers of the Ottoman Empire claimed caliphal authority from 1517 until the Ottoman caliphate was Abolition of the Caliphate, formally abolished as part of the Atatürk's reforms, 1924 secularisation of Turkey. An attempt to preserve the title was tried, with the Sharifian Caliphate, but this caliphate fell quickly after its conquest by the Sultanate o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Mada'ini
Abu al-Hasan Ali ibn Muhammad ibn Abd Allah ibn Abi Sayf al-Qurashi (; 752/753–843), commonly known by his al-Mada'ini (), was a scholar of Iranian descent who wrote in Arabic and was active under the early Abbasids in Iraq in the first half of the 9th century. A scholar of many interests, he wrote over 200 works, but is best known as a historian. Life Little is known about al-Mada'ini's life. The second edition of the ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'' notes that according to his own account, he was born in 752. However the third edition of the ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'' notes that according to other sources (citing al-Marzubani), he was born in 752/753, which can be treated as "his approximate year of birth". Al-Mada'ini and his family were of Iranian descent, and, according to sources attributed to him, he knew Persian. He was most likely born in Basra, and for most of his life remained in various cities in Iraq. Al-Mada'ini and his family were clients ('' mawlas'') of Abd al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Baladhuri
ʾAḥmad ibn Yaḥyā ibn Jābir al-Balādhurī () was a 9th-century West Asian historian. One of the eminent Middle Eastern historians of his age, he spent most of his life in Baghdad and enjoyed great influence at the court of the caliph al-Mutawakkil. He travelled in Syria and Iraq, compiling information for his major works. His full name was Ahmad Bin Yahya Bin Jabir Al-Baladhuri (), Balazry Ahmad Bin Yahya Bin Jabir Abul Hasan or Abi al-Hassan Baladhuri. Biography Al Baladhuri's ethnicity has been described as Persian by his contemporaries including Ibn Nadim, but some scholars have surmised that he was of Arab descent solely since he spent most of his life in Baghdad. Baladhuri was a Persian speaker who translated Persian works to Arabic. Nonetheless, his sympathies seem to have been strongly with the Arabs, for Masudi refers to one of his works in which he rejects Baladhuri's condemnation of non-Arab nationalism Shu'ubiyya. He is certainly not the first Persian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banu Thaqif
The Banu Thaqif () is an Arab tribe which inhabited, and still inhabits, the city of Ta'if and its environs, in modern Saudi Arabia, and played a prominent role in early Islamic history. During the pre-Islamic period, the Thaqif rivaled and cooperated with the Quraysh tribe of Mecca in trade and land ownership. The tribe initially opposed the Islamic prophet Muhammad, but following the Muslim siege of Ta'if in 630, they came to terms and embraced Islam. The Thaqif's inter-tribal networks and their relatively high education helped them quickly advance in the nascent Muslim state. They took on an especially important role in the conquest and administration of Iraq, providing the Rashidun and Umayyad caliphs capable and powerful governors for that province and the eastern Caliphate. Among their notable governors in Iraq were al-Mughira ibn Shu'ba (638, 642–645), Ziyad ibn Abihi (665–673), and al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf (694–714), while major Thaqafite commanders included Uthman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Harith Ibn Kalada
Al-Hārith ibn Kalada (; d. 13 AH/634–35) was an Arab physician and is said to be one of a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Though scholars differed upon this opinion. He is said to have traveled to Gundeshapur in search of medical knowledge before the advent of Islam. Al-Harith ibn Kalada was Al-Harith ibn Kalada ibn Amr ibn Ilaj ibn Abi Salama ibn Abd al-Aziz ibn Ghurarah ibn Auf ibn Thaqif al-Thaqafi. He was from Thaqif, from the people of Taif in the Hejaz region and he was a freedman of Abu Bakr. He traveled to Persia, and studied medicine in the pre-Islamic era. Ibn Jaljul said: His education Al-Harith ibn Kalada al-Thaqafi, from Thaqif and from the people of Taif, traveled to the Persia and learned medicine from a man from Jundishapur among others. Ibn Jaljul said: "Al-Harith learned medicine in Yemen and Persia, and he practiced there, and he treated patients and earned money there, and he knew the disease and the cure, and he used to play the oud, he learn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expeditions Of Muhammad
__NOTOC__ The list of expeditions of Muhammad includes the expeditions undertaken by the Muslim community during the lifetime of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Some sources use the word ''ghazwa'' and a related plural ''maghazi'' in a narrow technical sense to refer to the expeditions in which Muhammad took part, while using the word ''sariyya'' (pl. ''saraya'') for those early Muslim expeditions where he was not personally present. Other sources use the terms ''ghazwa'' and ''maghazi'' generically to refer to both types of expeditions. Early Islamic sources contain significant divergences in the chronology of expeditions. Unless noted otherwise, the dates given in this list are based on ''Muhammad at Medina'' by Montgomery Watt, who in turn follows the chronology proposed by Leone Caetani. List of expeditions ; Type legend See also * Types of Islamic Jihad * Islam and war * Military career of Muhammad References {{Muhammad2 Expeditions of Muhammad Military expeditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
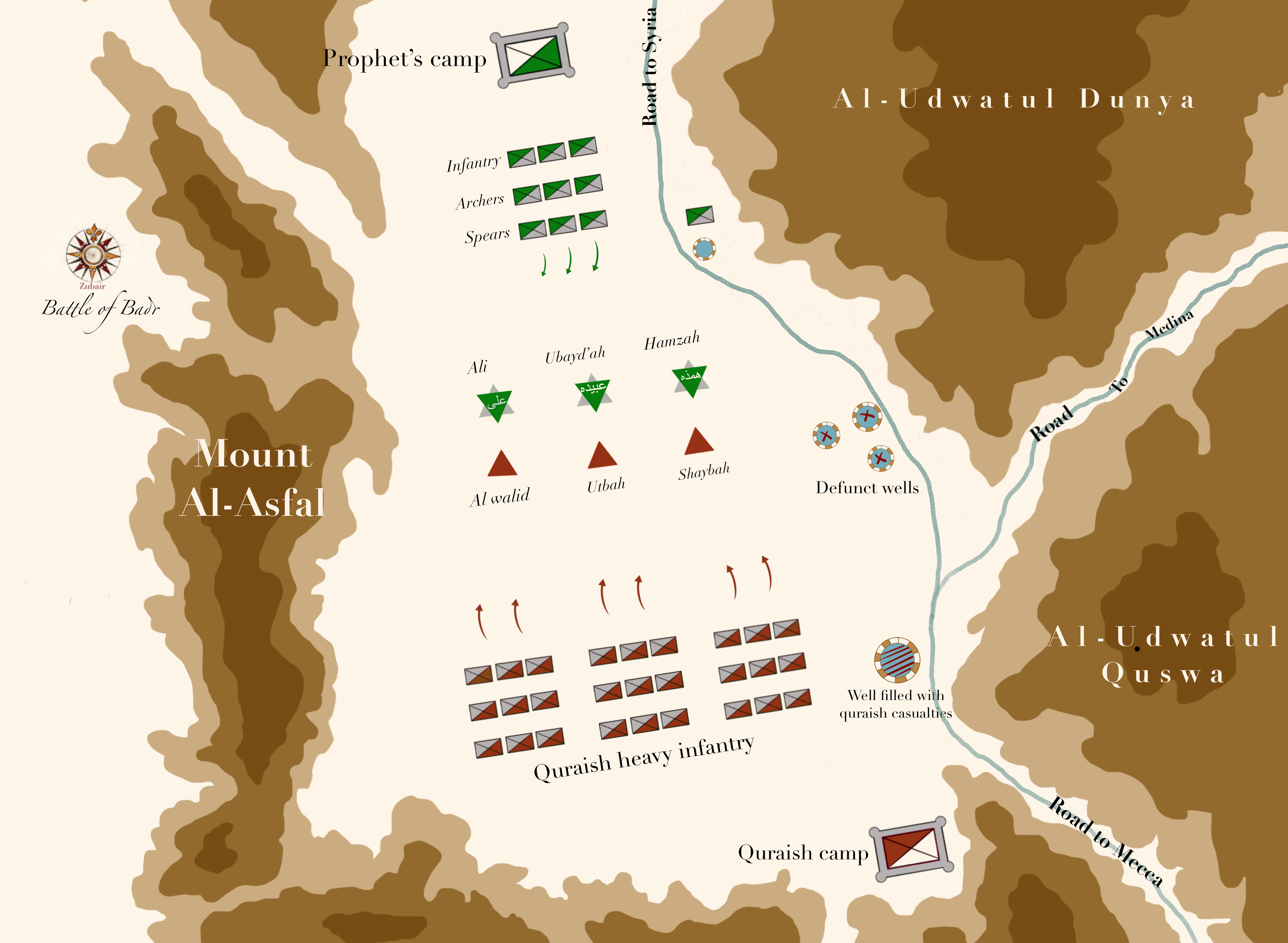
Battle Of Badr
The Battle of Badr or sometimes called The Raid of Badr ( ; ''Ghazwahu Badr''), also referred to as The Day of the Criterion (, ; ''Yawm al-Furqan'') in the Qur'an and by Muslims, was fought on 13 March 624 CE (17 Ramadan, 2 AH), near the present-day city of Badr, Al Madinah Province in Saudi Arabia. Muhammad, commanding an army of his Sahaba, defeated an army of the Quraysh led by Amr ibn Hishām, better known among Muslims as ''Abu Jahl''. The battle marked the beginning of the six-year war between Muhammad and his tribe. The Battle of Badr took place after five or six unsuccessful attempts by the Muslims to intercept and raid Meccan trade caravans between 623 and early 624 CE. Muhammad took keen interest in capturing Meccan caravans and their wealth after his migration to Medina. A few days before the battle, when he learnt of a Makkan caravan returning from the Levant led by Abu Sufyan ibn Harb, Muhammad gathered a small expeditionary force to raid it. Abu Sufyan, le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quraysh
The Quraysh () are an Tribes of Arabia, Arab tribe who controlled Mecca before the rise of Islam. Their members were divided into ten main clans, most notably including the Banu Hashim, into which Islam's founding prophet Muhammad was born. By the seventh century, they had become wealthy merchants, dominating trade between the Indian Ocean, East Africa, and the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean. The tribe ran caravans to Gaza City, Gaza and Damascus in summer and to Yemen (region), Yemen in winter, while also mining and pursuing other enterprises on these routes. When Muhammad Muhammad's first revelation, began preaching Islam in Mecca, the Quraysh initially showed little concern. However, their opposition to his activities quickly grew as he increasingly challenged Religion in pre-Islamic Arabia, Arab polytheism, which was prevalent throughout pre-Islamic Arabia. As relations deteriorated, Muhammad and Early Muslims, his followers migrated to Medina (the journey known as the Hij ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hejaz
Hejaz is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al Bahah, Al-Bahah. It is thus known as the "Western Province",Mackey, p. 101. "The Western Province, or the Hejaz[...]" and it is bordered in the west by the Red Sea, in the north by Jordan, in the east by the Najd, and in the south by Greater Yemen, Yemen. Its largest city is Jeddah, which is the second-largest city in Saudi Arabia, with Mecca and Medina, respectively, being the third- and fourth-largest cities in the country. As the location of the Holy city, holy cities of Mecca and Medina, respectively the first and second holiest sites in Islam, the Hejaz is significant in the Arabo-Islamic historical and political landscape. This region is the most populated in Saudi Arabia, and Arabic is the predominant language, as in the rest of Saudi Arabia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qays
Qays ʿAylān (), often referred to simply as Qays (''Kais'' or ''Ḳays'') were an Arab tribal confederation that branched from the Mudar group. The tribe may not have functioned as a unit in pre-Islamic Arabia (before 630). However, by the early Umayyad Caliphate (661-750), its constituent tribes consolidated into one of the main tribal political factions of the caliphate. The major constituent tribes or tribal groupings of the Qays were the Ghatafan, Hawazin, Amir, Thaqif, Sulaym, Ghani, Bahila and Muharib. Many of these tribes or their clans migrated from the Arabian Peninsula and established themselves in Jund Qinnasrin, the military district of the northern region of Syria and Upper Mesopotamia, which long became their abode. From there they governed on behalf of the caliphs or rebelled against them. The power of the Qays as a unified group diminished with the rise of the Abbasid Caliphate, which did not derive its military strength solely from the Arab tribes. None ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |