|
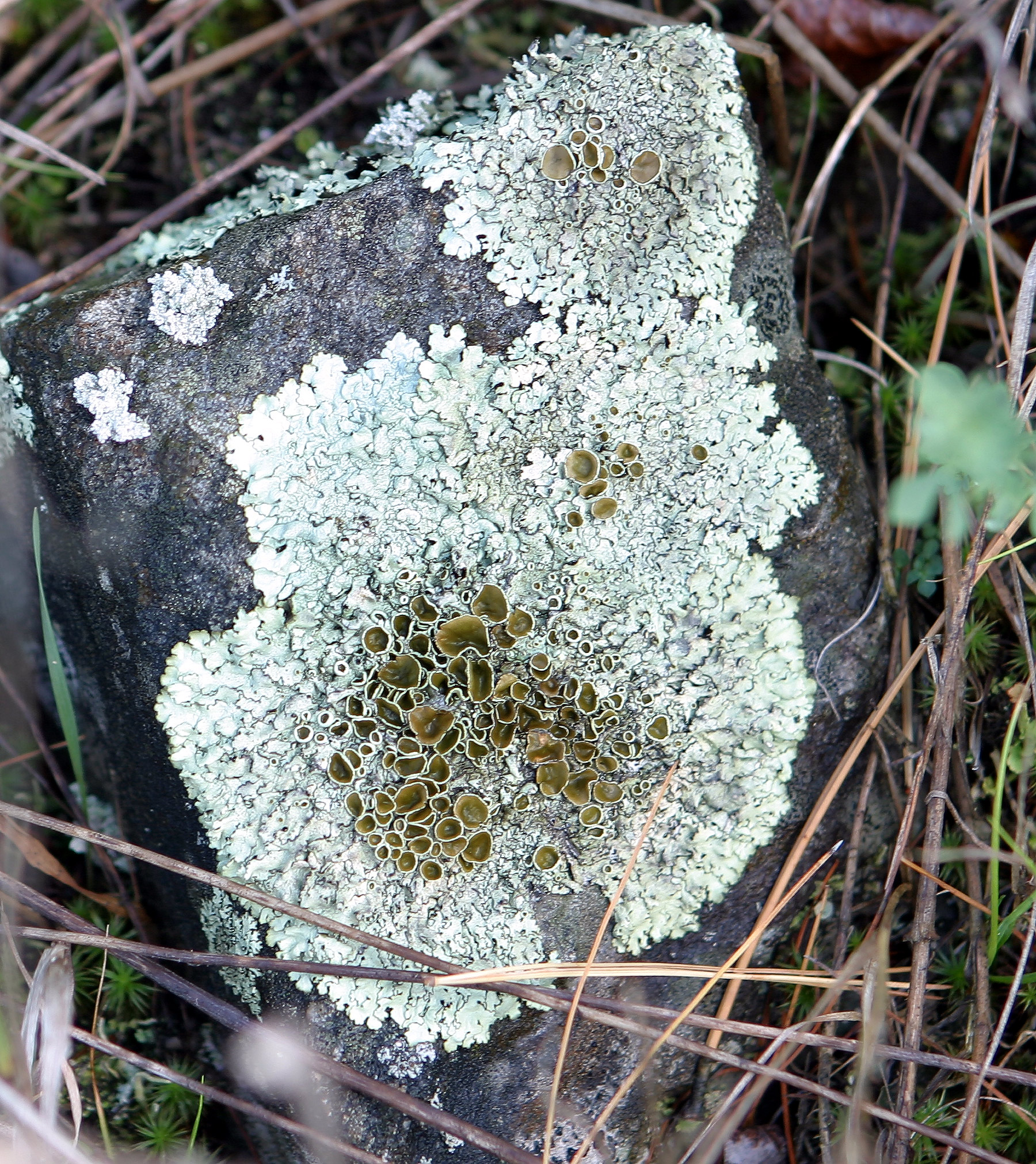
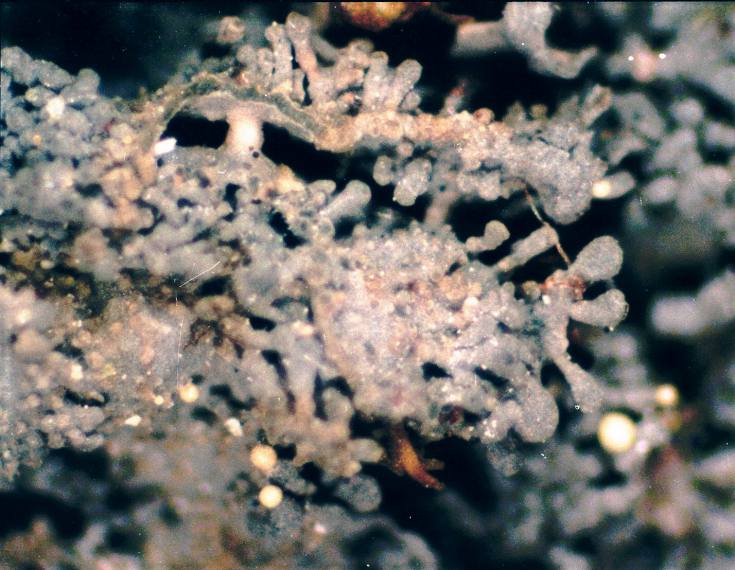
Usnea Mutabilis
''Usnea mutabilis'' is a grayish-yellowish pale green, unequally branching, shrubby (fruticose) 3–7 cm long lichen commonly anchored on holdfasts on trees, mostly in eastern North America, sometimes in chaparral shrubs or pines in California.Field Guide to California Lichens, Stephen Sharnoff, Yale University Press, 2014, It is darker green than other members of the genus ''Usnea''. The surface is covered with isolated, or clusters of, isidia. It lacks apothecia An ascocarp, or ascoma (: ascomata), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. As .... The common name is bloody beard lichen. The thick axis and medulla are dull red. See also * List of ''Usnea'' species References mutabilis Lichen species Lichens of North America Lichens described in 1881 Taxa named by James Stirton {{Parmeliacea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delmarva
The Delmarva Peninsula, or simply Delmarva, is a peninsula on the East Coast of the United States, occupied by the majority of the state of Delaware and parts of the Eastern Shore of Maryland and Eastern Shore of Virginia. The peninsula is long. In width, it ranges from near its center, to at the isthmus on its northern edge, to less near its southern tip of Cape Charles (headland), Cape Charles. It is bordered by the Chesapeake Bay on the west, Pocomoke Sound on the southwest, and the Delaware River, Delaware Bay, and the Atlantic Ocean on the east. The population of the twelve counties entirely on the peninsula totals 818,014 people as of the 2020 census. Etymology In older sources, the peninsula between Delaware Bay and Chesapeake Bay was variously known as the Delaware and Chesapeake Peninsula or simply the Chesapeake Peninsula. The toponym ''Delmarva'' is a clipped compound of Delaware, Maryland, and Virginia (ISO 3166-2:US#Current codes, official abbreviation ''VA'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fruticose Lichen
A fruticose lichen is a form of lichen fungi that is characterized by a coral-like shrubby or bushy growth structure. It is formed from a symbiotic relationship of a photobiont such as green algae or less commonly cyanobacteria and one, two or more mycobionts. Fruticose lichens are not a monophyletic and holophyletic lineage, but are a form encountered in many classes. Fruticose lichens have a complex vegetation structure, and are characterized by an ascending, bushy or pendulous appearance. As with other lichens, many fruticose lichens can endure high degrees of desiccation. They grow slowly and often occur in habitats such as on tree barks, on rock surfaces and on soils in the Arctic and mountain regions. Characteristics Characteristic of fruticose lichen is the shape of the thallus. Like crustose lichen, fruticose lichen is composed of a holdfast which will act as an anchor for the lichen to grow in rock fissures, over loose sand or soil. Growth and structure Fruticose or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), mutualistic relationship.Introduction to Lichens – An Alliance between Kingdoms . University of California Museum of Paleontology. . Lichens are the lifeform that first brought the term symbiosis (as ''Symbiotismus'') into biological context. Lichens have since been recognized as important actors in nutrient cycling and producers which many higher trophic feeders feed on, such as reindeer, gastropods, nematodes, mites, and springtails. Lichens have properties different from those of their component organisms. They come in man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holdfast (biology)
A holdfast is a root-like structure that anchors aquatic sessile organisms, such as seaweed, other sessile algae, stalked crinoids, benthic cnidarians, and sponges, to the substrate. Holdfasts vary in shape and form depending on both the species and the substrate type. The holdfasts of organisms that live in muddy substrates often have complex tangles of root-like growths. These projections are called haptera and similar structures of the same name are found on lichen A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony (biology), colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among hypha, filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualism (biology), m ...s. The holdfasts of organisms that live in sandy substrates are bulb-like and very flexible, such as those of sea pens, thus permitting the organism to pull the entire body into the substrate when the holdfast is contracted. The holdfasts of organisms that liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes Middle America (Americas), Middle America (comprising the Caribbean, Central America, and Mexico) and Northern America. North America covers an area of about , representing approximately 16.5% of Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. , North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in list of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaparral
Chaparral ( ) is a shrubland plant plant community, community found primarily in California, southern Oregon, and northern Baja California. It is shaped by a Mediterranean climate (mild wet winters and hot dry summers) and infrequent, high-intensity crown fires. Many chaparral shrubs have hard sclerophyllous evergreen leaves, as contrasted with the associated soft-leaved, drought-deciduous, scrub community of coastal sage scrub, found often on drier, southern-facing slopes. Three other closely related chaparral shrubland systems occur in southern Arizona, western Texas, and along the eastern side of central Mexico's mountain chains, all having summer rains in contrast to the Mediterranean climate of other chaparral formations. Etymology The name comes from the Spanish language, Spanish word , which translates to "place of the scrub oak". ''Scrub oak'' in turn comes from the Basque language, Basque word , which has the same meaning. Overview In its natural state, chaparral is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an international border with the Mexico, Mexican state of Baja California to the south. With almost 40million residents across an area of , it is the List of states and territories of the United States by population, largest state by population and List of U.S. states and territories by area, third-largest by area. Prior to European colonization of the Americas, European colonization, California was one of the most culturally and linguistically diverse areas in pre-Columbian North America. European exploration in the 16th and 17th centuries led to the colonization by the Spanish Empire. The area became a part of Mexico in 1821, following Mexican War of Independence, its successful war for independence, but Mexican Cession, was ceded to the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usnea
''Usnea'' is a genus of fruticose lichens in the large family Parmeliaceae. The genus, which currently contains roughly 130 species, was established by Michel Adanson in 1763. Species in the genus grow like leafless mini-shrubs or tassels anchored on bark or twigs. Members of the genus are commonly called old man's beard, beard lichen, or beard moss. Usnea lichens are characterized by their shrubby growth form, elastic branches with a central cord, and distinctive soralia that produce vegetative propagules. They vary in colour from pale green to yellow-green, grey-green, reddish, or variegated, and range in size from a few millimetres in polluted areas to over three metres long in species like '' Usnea longissima''. Members of the genus are similar to those of the genus '' Alectoria''.Field Guide to California Lichens, Stephen Sharnoff, Yale University Press, 2014, A distinguishing test is that the branches of ''Usnea'' are somewhat elastic, but the branches of ''Alectoria'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isidia
An isidium (plural: isidia) is a tiny, wart- or finger-like outgrowth on the thallus surface of certain lichen species. It is one of two principal types of vegetative reproduction, vegetative reproductive structures in lichens, the other being soredium, soredia. Each isidium contains both fungus, fungal and algae, algal partners and is wrapped in a thin protective layer (the ), distinguishing it from soredia, which lack this covering. While both function in vegetative reproduction, the heavier, corticate structure of isidia means they tend to establish in microhabitats close to the parent thallus, often favouring stable, humid niches where mechanical protection improves survival. Unlike spores, which are microscopic and easily carried over long distances by wind, isidia are larger, multicellular fragments that rely on external forces such as wind, rain, or animal contact, but typically disperse over much shorter ranges. Isidia are morphology (biology), morphologically diverse, ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apothecia
An ascocarp, or ascoma (: ascomata), is the fruiting body ( sporocarp) of an ascomycete phylum fungus. It consists of very tightly interwoven hyphae and millions of embedded asci, each of which typically contains four to eight ascospores. Ascocarps are most commonly bowl-shaped (apothecia) but may take on a spherical or flask-like form that has a pore opening to release spores (perithecia) or no opening (cleistothecia). Classification The ascocarp is classified according to its placement (in ways not fundamental to the basic taxonomy). It is called ''epigeous'' if it grows above ground, as with the morels, while underground ascocarps, such as truffles, are termed ''hypogeous''. The structure enclosing the hymenium is divided into the types described below (apothecium, cleistothecium, etc.) and this character ''is'' important for the taxonomic classification of the fungus. Apothecia can be relatively large and fleshy, whereas the others are microscopic—about the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulla (lichenology) zone, but above the lower cortex.Galloway, D.J. (1992). Flora of Australia - ''Lichen Glossary'' The medulla generally has a cottony appearance. It is the widest layer of a heteromerous lichen thallus.
The medulla is a horizontal layer within a lichen thallus. It is a loosely arranged layer of interlaced hyphae below the upper cortex and photobiont A lichen ( , ) is a hybrid colony of algae or cyanobacteria living symbiotically among filaments of multiple fungus species, along with yeasts and bacteria embedded in the cortex or "skin", in a mutualistic relationship. References Fungal morphology and anatomy Lichenology {{lichen-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |